Maltese Road Primary Year 3 Curriculum Overview
advertisement
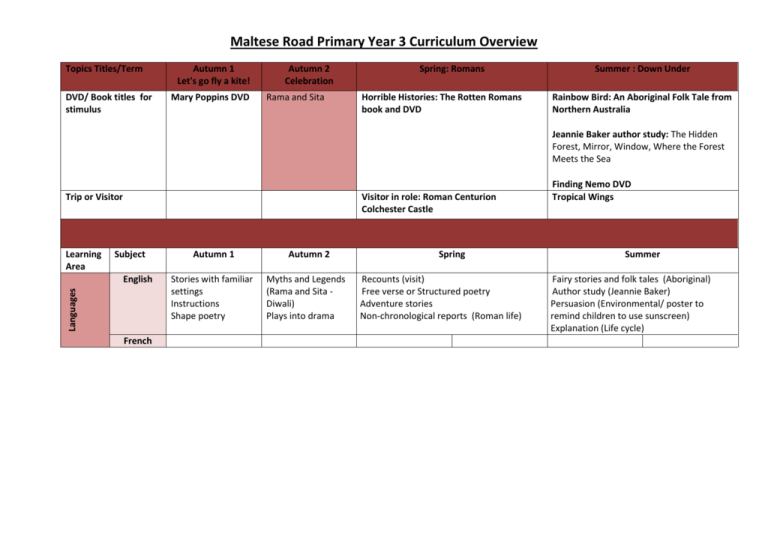
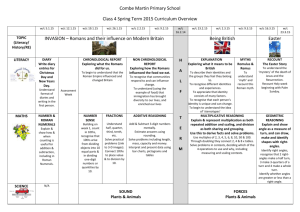
Maltese Road Primary Year 3 Curriculum Overview Topics Titles/Term DVD/ Book titles for stimulus Autumn 1 Let's go fly a kite! Mary Poppins DVD Autumn 2 Celebration Rama and Sita Spring: Romans Horrible Histories: The Rotten Romans book and DVD Summer : Down Under Rainbow Bird: An Aboriginal Folk Tale from Northern Australia Jeannie Baker author study: The Hidden Forest, Mirror, Window, Where the Forest Meets the Sea Trip or Visitor Learning Area Visitor in role: Roman Centurion Colchester Castle Subject Languages English French Autumn 1 Stories with familiar settings Instructions Shape poetry Autumn 2 Myths and Legends (Rama and Sita Diwali) Plays into drama Spring Recounts (visit) Free verse or Structured poetry Adventure stories Non-chronological reports (Roman life) Finding Nemo DVD Tropical Wings Summer Fairy stories and folk tales (Aboriginal) Author study (Jeannie Baker) Persuasion (Environmental/ poster to remind children to use sunscreen) Explanation (Life cycle) Maths Maths Number – use mulitples of 5 and 10 to solve addition and subtractions, compare and order 3 digit numbers, know multiplication for 5,10,2,4,and 3 Measures – days, weeks months, years, tell time to 5 minutes on analogue Geometry – know properties of 3D shapes Number – double and halve numbers to 100, add and subtract 2 digit numbers by partitioning, place 3 digit numbers on number line, times tables and related division Measures – use money to add and subtract, choose instrument to measure to cm, know 1 litre, estimate and measure capacity in mm Number- Place value of 3 digit numbers, multiply and divide by 10, add pairs of 2 digit numbers, recognise and sort multiples of 2,3,4,5 and 10. Fractions – identify ½, 1/3, ¼ and 1/8, place fractions on number line Geometry – Recognise right angles, know degree symbol, perimeter, name properties of 2D shapes Number – place value of 3 digit numbers, vertical written addition, add 2 digit numbers mentally, investigate patterns in numbers, double and halve numbers to 100, know relationship between multiply and divide Measurement – tell time to nearest minute on analogue and digital, calculate time intervals Number – Add 3 digit and 1 digit numbers mentally, multiply by 2,3,4,5,8, use scaling to multiply heights and weights, divide without remainders, use grid method to multiply Fractions – compare and order fractions with the same denominator Statistics – draw and interpret bar graphs and pictograms, draw tally charts Measure – know grams and Kilgrams Number – column addition, word problems, grid method, divide using chunking, column written addition Geometry – identify, name and draw angles in 2D shapes and horizontal, vertical, parallel and perpendicular lines, measure perimeter Measures – Tell time to nearest munite Science and Technology Science Computing Kaye Forces and magnets: Compare how things move on different surfaces. Notice that some forces need contact between two objects, but magnetic forces can act at a distance. Observe how magnets attract or repel each other and attract some materials and not others. Compare and group together a variety of everyday materials on the basis of whether they are attracted to a magnet, and identify some magnetic materials. Describe magnets as having two poles. Predict whether two magnets will attract or repel each other, depending on which poles are facing. My Learning VLE: To use an email address book. To be able to open an email and send an attachment. Coding Light: Recognise that they need light in order to see things and that dark is the absence of Light. Notice that light is reflected from surfaces. Recognise that light from the sun can be dangerous and that there are ways to protect eyes. Recognise that shadows are formed when the light from a light source is blocked by a solid object. Sound: Plants: Identify how sounds are made, associating some of them with something vibrating. Identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants: roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers. Recognise that vibrations from sounds travel through a medium to the ear. Find patterns between the pitch of a sound and features of the object that produced it. Find patterns between the volume of a sound and the strength of the vibrations that produced it. Recognise that sounds get fainter as the distance from the sound source increases. Explore the requirements of plants for life and growth (air, light, water, nutrients from soil, and room to grow) and how they vary from plant to plant. Investigate the way in which water is transported within plants. Explore the part that flowers play in the life cycle of flowering plants, including pollination, seed formation and seed dispersal. Find patterns in the way that the size of shadows change. To review images on a camera and delete unwanted images. To experience downloading images from a camera into files on the computer. Word-processing skills (graphics, font) To find relevant information by browsing a menu. To create a presentation that moves from To be able search for an image, copy and paste slide to slide and is aimed at a specific it into a document. audience. To be able to input data into a prepared To combine text, images and sounds and show database. awareness of audience. To sort and search a database to answer simple questions. Coding Coding D&T Amy Disassembly: kites and toys. Investigate and analyse a range of existing products. Design and make kites/ toys. Investigate Diwali lamp pots - thumb pots, coil pots etc. investigate and analyse a range of existing products. Apply their understanding of how to strengthen, stiffen and reinforce Structures such as kites. Design and make a pot for a tealight. Select from and use a wider range of tools and equipment to perform practical tasks accurately: cutting, shaping, joining and finishing. Select from and use a wider range of materials and components, including construction Materials and textiles according to their functional properties and aesthetic qualities. Make a simple fridge magnet (Science link) http://www.bbc.co.uk/e ducation/clips/zt8b4wx Select from and use a wider range of tools and equipment to perform practical tasks accurately: shaping, joining and finishing. design, create and evaluate their own Roman drawstring purses, Hanging mobiles Musical Instruments Study some examples of Roman shields (called scutum), looking at size, patterns and colours, before encouraging your class to think about how they could design, make and evaluate their own Romabn shields. Humanities History A study of an aspect or theme in British history that extends pupils’ chronological knowledge beyond 1066: changes in an aspect of social history, such as toys and childhood, from Victorian times to the present. The Roman Empire and its impact on Britain: Examples (non-statutory) Julius Caesar’s attempted invasion in 5554 BC. The Roman Empire by AD 42 and the power of its army. Successful invasion by Claudius and conquest, including Hadrian’s Wall. British resistance, for example, Boudica. ‘Romanisation’ of Britain: sites such as Caerwent and the impact of technology, culture and beliefs, including early Christianity. Roman withdrawal from Britain in c. AD 410 and the fall of the western Roman Empire. The legacy of Roman culture (art, architecture or literature) on later periods in British history, including the present day. A non-European society that provides contrasts with British history: The Aboriginal People Famous Explorer: James Cook. A study of his life, voyages and achievements. Geography Geographical skills and fieldwork Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate India and the village of Chembokoli Locational knowledge Identify the position and significance of Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the prime/ Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night). Human and physical geography Describe and understand key aspects of human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water. Compare Great Baddow with Chembokoli. Geographical skills and fieldwork Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries in Europe and to locate modern Italy and Rome. Geographical skills and fieldwork Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate continents and countries and describe features studied. Locational knowledge Locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including the location of Russia), concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities. Locational knowledge Identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the Prime/Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night) Name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), and land-use patterns; and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time. Locate important Roman settlements and sites. Place knowledge To understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the United Kingdom and a region within Italy. Human and physical geography Describe key aspects of physical geography of Australia such as rainforests, Ayers Rock or Uluru and the Great Barrier Reef. http://www.parksaustralia.gov.au/index.html To understand the weather of Australia and the different temperatures at different times of the year compared to Britain R.E (Use Essex S.O.W) CPSHE (SEAL) Michelle The Local Anglican Church New Beginnings To identify ways of making people feel safe and welcome. Hindu gods and goddesses Worshiping and celebrating in the home with Hindus. Getting On & Falling Out To identify peaceful strategies to resolve issues. Living as a Christian, the bible and prayer Guru Nanak, Guru Gobind Singh and the Khalsa – Sikhism The Buddha’s life Story Say No to Bullying Going for Goals Good to be Me To identify ways of solving a bullying situation with others. To predict the consequences of actions, solutions or goals for myself, other individuals or groups. To know why it is sometimes important to stop and think when we feel angry or stressed. Relationships & Changes To be able to explain how it feels to belong to a group and how important it is for everyone. Talents Art Amy P.E Faye Music Lin Use 'Umbrellas' by Renoir. Predict with accuracy the colours that they mix. Know where each of the primary and secondary colours sits on the colour wheel. Create a background using a wash. Create tones and shades. To explore different brushstrokes To throw and catch with control when under limited pressure. Use 'Stomp' as a stimulus for percussive music playing. Sing songs from Mary Poppins Add to their work to create texture and shape. To create pop-ups To use their sketch books to express feelings about a subject and to describe likes and dislikes. To be able to cut very accurately. To be able to overlap materials. To experiment using different colours. Aboriginal art Use the Internet to explore a range of symbolic art from different cultures. Designing own aboriginal art pebbles To be able to make a printing block. To create a 2 colour print. Mosaics To use a greater number of their own ideas for movement in response to a task. To adapt sequences to suit different types of apparatus and their partner’s ability. To improvise freely, translating ideas from a stimulus into movement. To share and create phrases with a partner and in small groups. To follow a map in a familiar context. To move from one location to another following a map. http://www.singup.org/nc/singupsongbank/songs-and-warm-ups/songdetail/type/song/view/416-just-like-aroman/ Sing Up: Just like a Roman To run at fast, medium and slow speeds, changing speed and direction. To link running and jumping activities with some fluency, control and consistency? To explain why it is important to warm-up and cool-down. To identify some muscle groups used in gymnastic activities. Looking at the didgeridoo—listening to some didgeridoo music and designing own ‘didgeridoos’ Australian traditional folk music - waltzing Matilda