CP Biology Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Section 1: The Nature of Matter (pg
advertisement

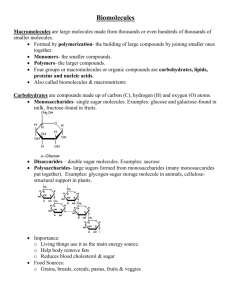
CP Biology Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Section 1: The Nature of Matter (pg. 35-39) Vocab: Atoms: Basic unit of matter Nucleus: Located at the center of an atom, made up of protons and neutrons. Electron: Negatively charged particle Element: Pure substance that consists entirely of one typed of atom. Isotope: Atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons they contain Compound: A substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in definite proportions. Ionic Bond: Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another. Ion: Positively and negatively charged atoms Covalent Bond: Forms when electrons are shared between atoms Molecule: The smallest unit of most compounds Van der Waals forces: Intermolecular forces of attraction Chapter 2 Section 2: Properties of Water (pg. 40 – 43) Vocab: Cohesion: Is an attraction between molecules of the same substance. Adhesion: is an attraction between molecules of different substances. Mixture: A material composed of two or more elements or compounds that are physically mixed together but not chemically combined. Solution: ions gradually disperse forming a type of mixture Solute: the substance tat is dissolved. Solvent: the substance in which the solute dissolves. Suspension: Mixtures of water and nondissolved material pH Scale: Measurement system to indicate the concentration of H+ ions in solutions Acid: any compound that forms H+ ions in solution. Higher concentrations of H+ than pure water and have pH values below 7 Base: a compound that produces hydroxide ions in solution. Lower concentrations of H+ than pure water and have pH values above 7 Buffer: weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids and bases to prevent sharp sudden changes in pH. Chapter 2 Section 3: Carbon Compounds (Pg. 44-48) Monomer: Smaller units that join together (polymerization) to form polymers Polymer: monomers join together to form polymers. Carbohydrate: Compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Usually in a ratio of 1:2:1. Living things use carbohydrates as their main source of energy. Plants and some animals also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. Monosaccharide: Single sugar molecules. Polysaccharide: The large macromolecules formed from monosaccharides Lipid: Large and varied group of biological molecules that are generally not soluble in water. Made mostly from carbon and hydrogen atoms. Fates, oils, and waxes. Lipids can be used to store energy. Nucleic Acid: Macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus. Nucleic acids are polymers assembled from individual monomers known as nucleotide. Nucleic acids store and transmit heredity or genetic information. Nucleotide: Made up of three parts: 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. Individual nucleotides can be joined by covalent bonds to form polynucleotides or nucleic acid. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA): Nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose. Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA): Nucleic acid that contains the sugar deoxyribose. Protein: are macromolecules that contain nitrogen as well as carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Proteins are polymers of molecules called amino acids. Amino Acid: Protein polymers of molecules. Amino acids are compounds with an amino group on one end and a carboxyl group on the other end. Chapter 2 Section 4: Chemical Reactions and Enzymes (pg. 49-53) Chemical Reaction: a process that changes, or transforms, on set of chemicals into another. Reactants: Elements or compounds that enter into a chemical reaction. Products: The elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction. Activation Energy: Energy that is needed to get a reaction started. Catalyst: a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction. Enzymes: proteins that act as biological catalysts. Substrates: The reactants of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.