Unit 6: Genetics and Heredity Explain and apply laws of heredity
advertisement
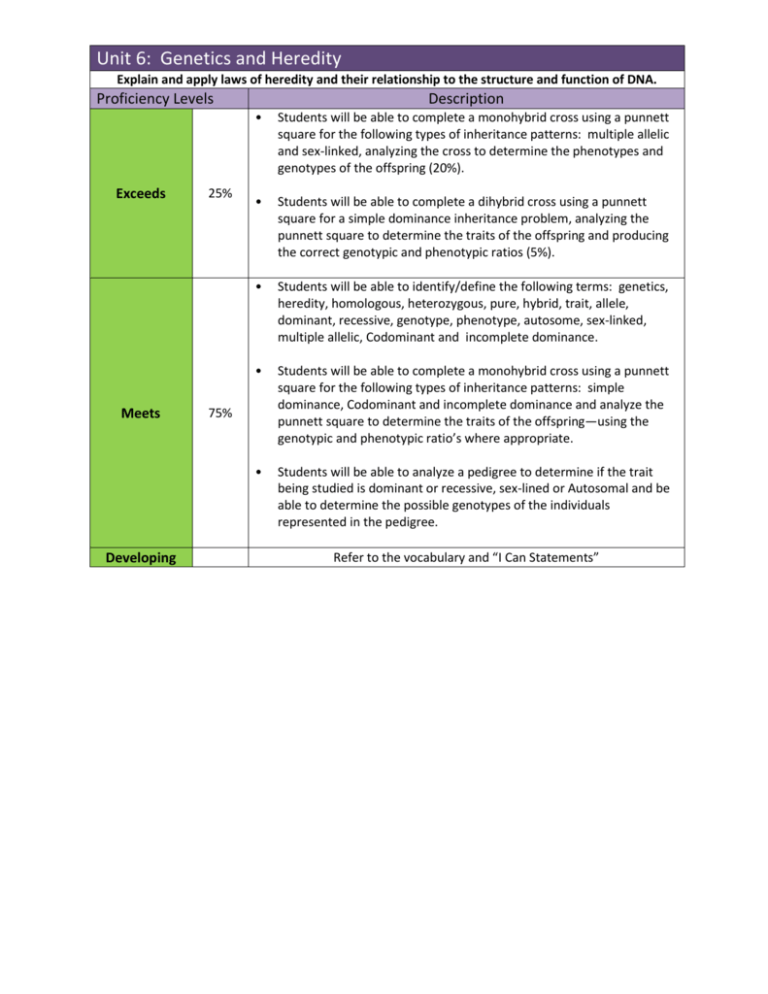
Unit 6: Genetics and Heredity Explain and apply laws of heredity and their relationship to the structure and function of DNA. Proficiency Levels Exceeds Meets Developing 25% Description • Students will be able to complete a monohybrid cross using a punnett square for the following types of inheritance patterns: multiple allelic and sex-linked, analyzing the cross to determine the phenotypes and genotypes of the offspring (20%). • Students will be able to complete a dihybrid cross using a punnett square for a simple dominance inheritance problem, analyzing the punnett square to determine the traits of the offspring and producing the correct genotypic and phenotypic ratios (5%). • Students will be able to identify/define the following terms: genetics, heredity, homologous, heterozygous, pure, hybrid, trait, allele, dominant, recessive, genotype, phenotype, autosome, sex-linked, multiple allelic, Codominant and incomplete dominance. • Students will be able to complete a monohybrid cross using a punnett square for the following types of inheritance patterns: simple dominance, Codominant and incomplete dominance and analyze the punnett square to determine the traits of the offspring—using the genotypic and phenotypic ratio’s where appropriate. • Students will be able to analyze a pedigree to determine if the trait being studied is dominant or recessive, sex-lined or Autosomal and be able to determine the possible genotypes of the individuals represented in the pedigree. 75% Refer to the vocabulary and “I Can Statements” Unit 6: Genetics and Heredity VOCABULARY allele genotypic ratio monohybrid recessive autosome heredity multiple alleles sex-linked codominance heterozygous pedigree simple dominance dihybrid homologous phenotype trait dominant hybrid phenotypic ratio dihybrid genetics incomplete dominance Polygenic trait genotype inheritance pattern punnett square 1. I can explain the difference between a sex chromosome and autosomal chromosome and I can tell you how many pairs of each naturally occur within a human cell. (11.1) 2. I can explain the difference between genetics and heredity.(12.1) 3. I can tell the difference between a genotype and a phenotype.(12.2) 4. I can explain the differences and similarities for the following terms: hybrid, pure, heterozygous and homozygous. (12.2) 5. I can define trait and allele and explain how they are similar and different.(12.1-12.2) 6. I can identify the difference between a homozygous dominant, heterozygous and homozygous recessive genotype.(12.2) 7. I can look at any genotype if I know the inheritance pattern and I can tell you the correct phenotype. (12.3) 8. I can read a genetic problem and determine the genotypes of the parents to set up a cross.(12.3) 9. I can complete a monohybrid punnett square for simple dominance and determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios. (12.3) 10. I can complete a monohybrid punnett square for incomplete dominance and analyze the offspring’s phenotypes using percents.(12.3) 11. I can complete a dihybrid punnett square for simple dominance. 12. I can look at a pedigree and determine which individuals are male or female and be able to determine which generation they belong to.(12.3) 13. After I have analyzed a pedigree and have determined the inheritance pattern and type of chromosome being affected, I can determine the possible genotypes of the individuals within the pedigree. (12.3) 14. I can analyze a pedigree to determine if the trait being studied is dominant or recessive, and autosomal or sex-linked. (12.3) 15. I can complete a monohybrid punnett square for Sex-Linked inheritance pattern and analyze the offspring’s phenotypes using percents. (12.4) 16. I can complete a monohybrid punnett square for Codominance and analyze the offspring’s phenotypes using percents. (12.4) 17. I can complete a monohybrid punnett square for Multiple Allele inheritance pattern (blood type) and analyze the offspring’s phenotypes using percents. (12.4) 18. I can identify and explain the difference in the following inheritance patterns: simple dominance, codominance, incomplete dominance, multi-allele and sex-linked.(12.4) 19. I can complete a dihybrid punnett square for Simple Dominance and calculate the genotypic ratio.(12.2) Quiz #1 /4 Quiz #2 /4







![[11.1,11.2,11.3] COMPLEX INHERITANCE and HUMAN HEREDITY](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006715925_1-acaa49140d3a16b1dba9cf6c1a80e789-300x300.png)