Genetics: Punnett Squares & Probability Worksheet
advertisement

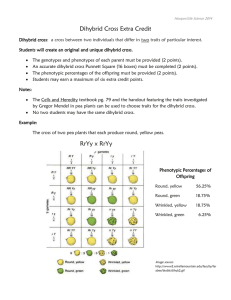
Section 6.5: Traits and Probability Vocabulary Punnett square Monohybrid cross Dihybrid cross Testcross Law of independent assortment Probability Review Questions 1. In the Punnett square below, you can think of dominant A as being a yellow pea seed and recessive a as a green pea seed. Please answer the questions below the Punnett square. A a AA Aa Aa aa A a a. Why does each parent contribute only one allele to the offspring? Because the alleles segregated during gamete formation (meiosis) when the homologous chromosomes separated. b. What is a genotypic ratio? What is the genotypic ratio of the offspring? A comparison that indicates the proportion of offspring that have a particular genotype. c. What is a phenotypic ratio? What is the phenotypic ratio of the offspring? A comparison that indicates the proportion of offspring that have a particular phenotype. 2. Probability predicts the average number of occurrences, not the exact number of occurrences. 3. To calculate the probability that two independent events will happen together, multiply the probability of each individual event. 4. What is a testcross? Why is it useful? A cross between an organism with the recessive phenotype and an organism with an unknown genotype. 5. What is independent in the law of independent assortment? Allele pairs are independent. They separate independently of each other during gamete formation in meiosis. 6. What is the difference between a monohybrid and a dihybrid cross? A monohybrid cross examines the inheritance of one specific trait. A dihybrid cross examines the inheritance of two traits. Is this a monohybrid or a dihybrid cross? How do you know – explain differences between the two? It is a dyhybrid cross. Dihybrid crosses examine, as stated above, the inheritance of two traits, which is what we see in this case. The Law of Independent Assortment was developed by Mendel as a result of examining dihybrid crosses. He determined that the inheritance of one trait does not influence the inheritance of a second trait.