sex linked worksheet answers
advertisement
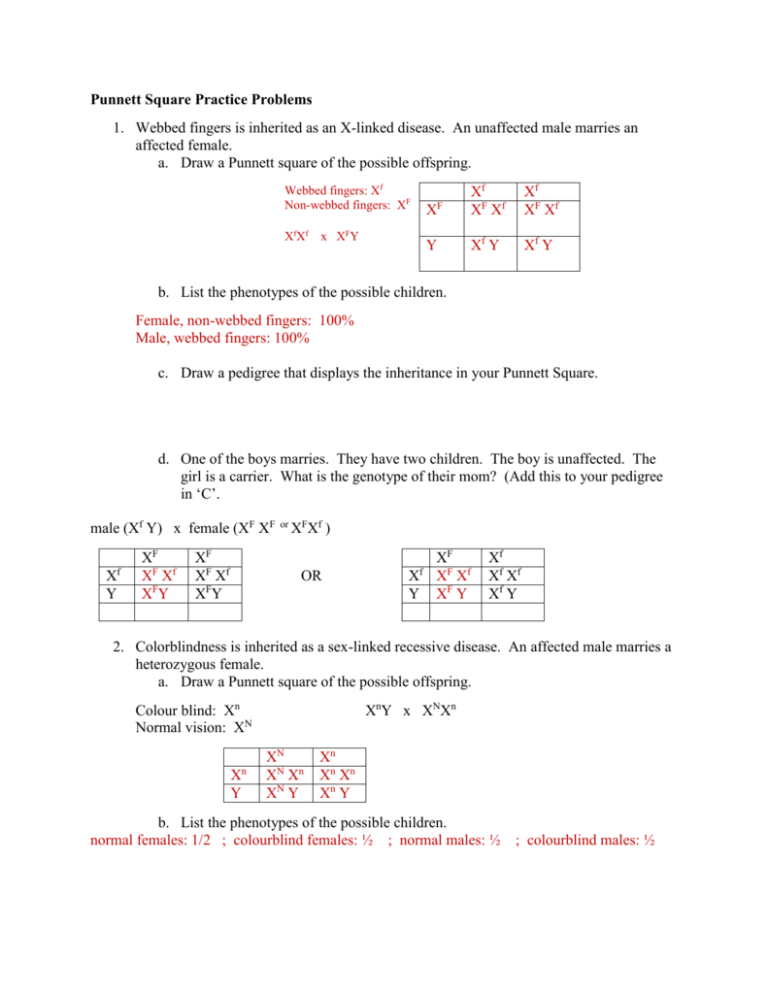
Punnett Square Practice Problems 1. Webbed fingers is inherited as an X-linked disease. An unaffected male marries an affected female. a. Draw a Punnett square of the possible offspring. Webbed fingers: Xf Non-webbed fingers: XF X fX f X Xf XF Xf Xf XF Xf Y Xf Y Xf Y F x XFY b. List the phenotypes of the possible children. Female, non-webbed fingers: 100% Male, webbed fingers: 100% c. Draw a pedigree that displays the inheritance in your Punnett Square. d. One of the boys marries. They have two children. The boy is unaffected. The girl is a carrier. What is the genotype of their mom? (Add this to your pedigree in ‘C’. male (Xf Y) x female (XF XF f X Y XF XF Xf XFY XF XF Xf XFY or XFXf ) OR f X Y XF XF Xf XF Y Xf Xf Xf Xf Y 2. Colorblindness is inherited as a sex-linked recessive disease. An affected male marries a heterozygous female. a. Draw a Punnett square of the possible offspring. Colour blind: Xn Normal vision: XN Xn Y XnY x XNXn XN XN Xn XN Y Xn Xn Xn Xn Y b. List the phenotypes of the possible children. normal females: 1/2 ; colourblind females: ½ ; normal males: ½ ; colourblind males: ½ c. Draw a pedigree that displays the inheritance in your Punnett Square. d. If the heterozygous daughter marries an unaffected male, can you predict the offspring? If so, add the information to your pedigree. If not, explain why. XN Xn XN Y All females normal vision ½ males colourblind ½ males normal vision x XN XN XN XN Y XN Y Xn XN Xn Xn Y