Biology
advertisement
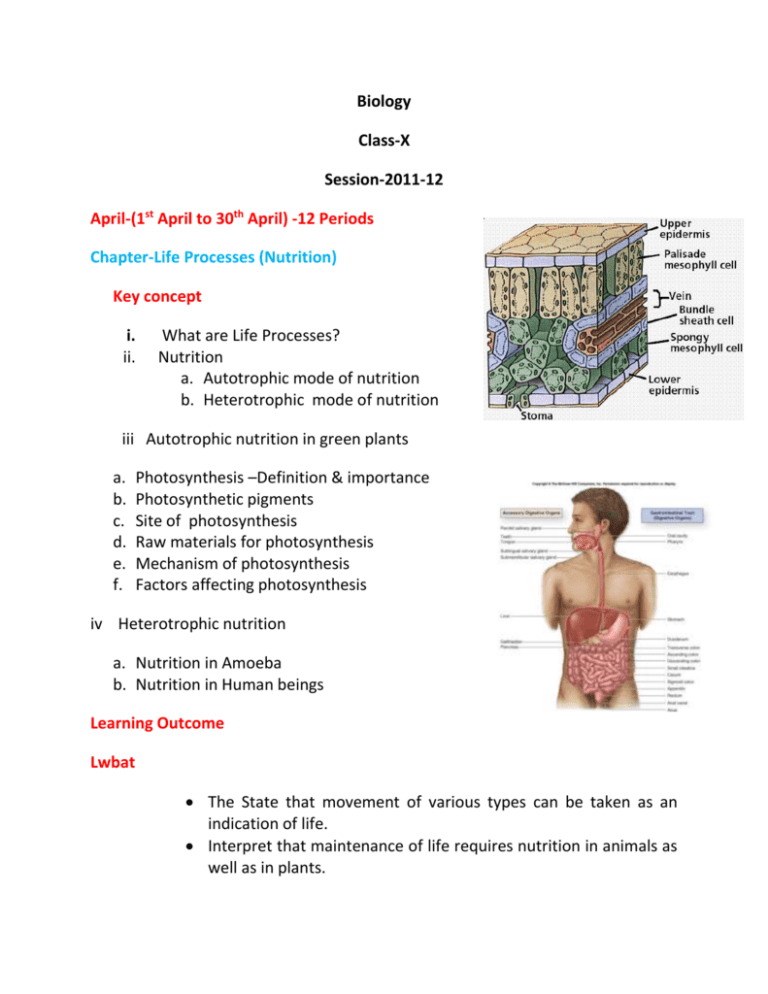
Biology Class-X Session-2011-12 April-(1st April to 30th April) -12 Periods Chapter-Life Processes (Nutrition) Key concept i. ii. What are Life Processes? Nutrition a. Autotrophic mode of nutrition b. Heterotrophic mode of nutrition iii Autotrophic nutrition in green plants a. b. c. d. e. f. Photosynthesis –Definition & importance Photosynthetic pigments Site of photosynthesis Raw materials for photosynthesis Mechanism of photosynthesis Factors affecting photosynthesis iv Heterotrophic nutrition a. Nutrition in Amoeba b. Nutrition in Human beings Learning Outcome Lwbat The State that movement of various types can be taken as an indication of life. Interpret that maintenance of life requires nutrition in animals as well as in plants. Discuss that autotrophic nutrition involves the intake of simple inorganic materials from the environment and using sun to synthesize complex high energy organic material. Distinguish between autotrophic &heterotrophic nutrition Interpret that heterotrophic nutrition involves the intake of complex material prepared by other organisms. Explain that in human beings, the food eaten is broken down by various steps along the alimentary canal and sent to all cells in the body. Develop diagrammatic skills. Activity-i. To demonstrate that chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis. ii.To demonstrate that light is essential for Photosynthesis. iii.To demonstrate the action of saliva on starch. iv.To peel a leaf to show stomata under microscope. Formative Assessment (10 Marks) Class work note book Practical manual Paper &Pen objective type test FA-1 (24th April onwards) Sample Questions 1. What kind of nutrition occurs in Fungi? 2. Which raw material is responsible for reduction of CO2 into carbohydrates? 3. Name the cell that regulates the opening & closing of stomata. 4. What kind of nutrition takes place in Pitcher plants? 5. What is the exact function of chlorophyll? 6. In multicellular organisms -------- meet the requirements of all the cells. 7. Why is the leaf boiled in water and alcohol before testing for the presence of starch? 8. Label the parts shown below by the arrows(figure given). 9. Write the well balanced chemical equation of photosynthesis. 10.Rewrite the terms in correct order---water molecule, oxygen, grana, Hydrogen, Hydroxyl ions, Photons. 11.Write the full form of NADP & ADP. 12.Give the exact location & function of Thylakoids. Chapter- Respiration May- 3 Periods (2nd to 7th May) June- 3 Periods (15th June to 25th June) extra class June-2 Periods (27th June to 30th June) school reopens Key concept i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. Concept of breathing & cellular respiration Types of cellular respiration Exchange of gases in plants Exchange of gases in aquatic & terrestrial organisms Respiratory system in human beings Mechanism of breathing Exchange of gases in tissues Learning outcome i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. viii. ix. x. xi. Recall the definition of respiration taught in previous class. Define cellular respiration. Name the different organs of human respiratory system. Explain the breathing mechanism. Distinguish between breathing & respiration. Translate the respiration exist in plants. Understand exchange of gases in aquatic organisms. Analyze that during exchange of gases CO2 &O2 Exhaled &inhaled respectively. Draw human respiratory system with proper labeling. Justify that it is smoking which badly affects the lungs. Recommend that one should inhale & exhale deeply early morning to get fresh air to keep healthy lungs. Activity- i.To demonstrate that we breathe out carbon dioxide. ii. To study the process of breathing in fishes. iii. To demonstrate that germinating seeds give out carbon dioxide. Evaluation Test1. The process of breakdown of glucose takes place in --------part of the cell. 2. In aerobic respiration Pyruvate breaks into------ and ---------. 3. Energy released during respiration is used to synthesize -----4. ATP is equal to --------Kj/mol. 5. In plants exchange of organisms gases takes place through the process called-----------6. Aquatic organisms use oxygen from ……….. 7. Rate of breathing is faster in ………… organisms. 8. …………Structures present in wind pipe protects it from being collapsed. 9. After expiration volume of air left in lungs for gaseous exchange is called……….. 10.In human body CO2 is mainly transported by……. 11.Schematic diagram of breakdown of 1 mol. Of glucose by various pathways. Chapter-Transportation July-(1st to 30th) -12 Periods Key concepts Introduction Transportation Transportation in Human beings Blood vascular system Blood clotting (in brief) Blood vessels The human heart Double circulation Lymphatic system (in brief) Transportation of water & materials in plants Ascent of sap Transpiration Transportation of food and other substances Learning outcome LWBAT Tell that mammalian heart is four chambered State that in human beings & other mammals and other vertebrates transport of materials are carried out by circulatory system. Name the types of blood vessels present in the human body Explain the structure of heart Distinguish between artery, vein & capillary Interpret the requirement of ‘Double circulation’ of blood in human body Draw a well labeled diagram of internal structure of heart Examine the functions of pulmonary vein and pulmonary artery Analyse that it is due to platelets the blood in our body clots during any injury Justify the fact that, ventricles can pump blood due to its thick walls Learn the importance of Lymph and its functions Evaluation Diagram test-10 Mark Cross word puzzle-10 Mark Note book checking- 10 Mark Chapter-Excretory system 18th July to 30thJuly (6 periods) and 3 extra periods Key concepts Introduction Excretion in human beings Structure and functions of nephron Artificial kidney (Haemodialysis) Excretion in plants Learning outcome LWBAT name the organs of excretory system learnt in previous class locate the excretory organs in the body explain the structure of nephron and urine formation interpret that deposition of salts in the kidney form kidney stones draw well labelled diagram of excretory system and nephron analyse that one must have healthy food and proper life style understand that if both kidneys become diseased or damaged one undergoes kidney transplantation justify the fact that one must take plenty of water to get rid of toxic substances from the body learn the excretory products of plants and the strategy of excretion Chapter-Nervous System 1ST August to 12th August (14periods) FA-2 (16th August onwards) 16th August to 14th Sept (12 periods) Key concepts Introduction Animals-Nervous system Neuron, synapses, Human brain, reflex action Co-ordination in plants Phototropism &Geotropism Hormones in animals Learning outcome LWBAT Tell the parts of a neuron learnt in previous class Describe the structure and function of a neuron Outline the flow of impulses in reflex action Distinguish between receptors and effectors Draw a well labeled structure of neuron ,Brain & Reflex action Analyse that it is due to Nervous & muscular tissues human beings have well controlled body Justify the cause of movements of muscles due to change in shapes & their arrangements in cellular proteins Define tropism Name types of growth movements and also define them Examine from the experiment(ppt) shown, the photropism &Geotropism Classify growth regulators depending upon their functions Analyse that due to the plant hormones only different types of changes occur in the plants Explain the sudden release of Adrenaline hormone in our body Imagine that it is due to Nervous and Hormonal control together the function of control & co-ordination in human body can be performed Discuss the effects of all hormones in our body with their teacher Marvel on the mechanism of human body EVALUATION TEST Project work (Integrated )-10 mark Diagram -10 Mark notebook -10 Mark Classtest-10 Mark SA-1 (15 th September onwards -80 Marks) Question paper procured from the BOARD







