Final Exam fill in the blanks bulk transport worksheet - APBio09-10
advertisement

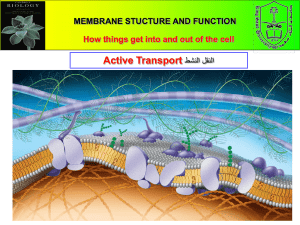
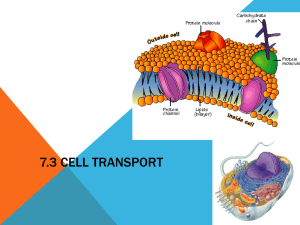
Cell-to-cell recognition area Bulk Transport fill-in-the-blank glycolipids large quantities Large distances glycoproteins Bulk transport is actually a type of active transport. Bulk transport allows substances to be transported in large quantities using energy*. *Water moving up vessel elements is not considered bulk transport. However, sugar moving into the sieve-tube elements is. , the cell’s way of releasing molecules out of the cell, is an example of bulk transport. Using energy, the Golgi body releases vesicles containing substances that need to be “shipped out.” The vesicles touch the cell membrane, turn “inside out,” and release the substances. Exocytosis also allows the cell to much add area to its lipid bilayer. The vesicle that turns inside out increases the cell’s surface area. These vesicles could also allow the membrane to obtain membrane and for . Steps 3 and 4 describes how vesicles fuse with the cellular membrane and its effect. Step 3: The vesicle with transmembrane proteins and other substances are shipped out of the Golgi body. Step 4: The vesicle touches the plasma membrane, turning inside out and exposing the transmembrane proteins and other cell-to-cell recognition molecules. receptor mediated endocytosis Ligand phagocytosis Unspecific Specific Pseudopodium pinocytosis Lysosomes reduced molecules into endocytosis Contrasting exocytosis, transports large quantities of substances endocytosis, the cell’s surface area is The bulk transport mechanism called the cell. In all cases of as the cell engulfs substances it needs. , “cellular eating,” allows a molecule to engulf large molecules and “eat” them. Using (“false feet”), the cell would wrap around food and consume it. The food is then digested using . Amoebas are highly reliant on phagocytosis, as they are heterotropic organisms. Another bulk transport mechanism called pinocytosis, “cellular drinking,” allows the cell to consume fluids using energy. However, the cell doesn’t need the fluids themselves, but rather the molecules in the droplets. When a cell does pinocytosis, the cell is unspecific about what molecules it drinks. Of all the endocytosis mechanisms discussed, acquire (RME) enables the cell to substances that it needs using energy. Any substance that a cell specifically needs is called a . They attach to receptors on the cell’s plasma membrane, causing RME to occur, allowing the cell to acquire the in large quantities. An example of ligands in the human body are LDLs (“healthy fats,” as described in a health class). Since body cells need LDLs, LDLs will attach to receptors, allowing cells to consume LDLs in large quantities.