Membrane Transport
advertisement

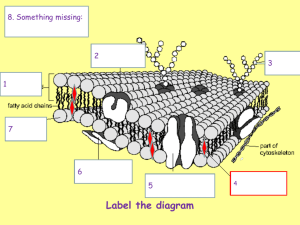
Name ______________ Date _______ Block __ Use your book, the notes on my web site and the links provided to complete these in class notes. My School Site Membrane Transport Membrane transport—movement of substances into and out of the cell Two basic methods of transport ___________ transport No energy is required ___________ transport Cell must provide metabolic energy (ATP) Solutions and Transport Solution—homogeneous mixture of two or more components ___________ —dissolving medium; typically water in the body ___________ —components in smaller quantities within a solution ___________ fluid—nucleoplasm and cytosol A solution containing small amounts of gases, nutrients, and salts, dissolved in water ___________ fluid—fluid on the exterior of the cell Thought of as a rich, nutritious “soup” Selective Permeability The plasma membrane allows some materials to pass while ___________ others This permeability influences movement both into and out of the cell http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q7hP7QUpkWU Passive Transport Processes ___________ Particles tend to distribute themselves evenly within a solution Movement is from ________ concentration to low concentration, or down a concentration _______ Continually moving water, glucose and oxygen in the low concentration cell from the blood Continually moving carbon dioxide and waste out of the high concentration cell into the blood Types of diffusion ___________ diffusion An unassisted process Solutes are lipid-soluble materials or small enough to pass through membrane pores Osmosis—simple diffusion of ___________ Highly polar water molecules easily cross the plasma membrane through aquaporins Short - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SSS3EtKAzYc&feature=c4-overviewvl&list=PL668F75DB391A1AB5 Long - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MLrDRfr0OQM Facilitated diffusion Substances require a ___________ carrier for passive transport Transports lipid-insoluble and large substances Filtration Water and solutes are forced through a membrane by ___________, or ___________ pressure A pressure gradient must exist Solute-containing fluid is pushed from a high-pressure area to a lower pressure area Occurs in the ___________ (What organ?) Active Transport Processes Substances are transported that are unable to pass by diffusion Substances may be too ___________ Substances may not be able to dissolve in the fat core of the membrane Substances may have to move against a ___________ gradient ___________ is used for transport http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zF3JR97vmew Two common forms of active transport Active transport (solute pumping) Vesicular(Bulk) transport Exocytosis Endocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Active transport (solute pumping) Amino acids, some sugars, and ions are transported by protein carriers called solute pumps ___________ energizes protein carriers In most cases, substances are moved against concentration gradients Quick Overview http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=awz6lIss3hQ In Depth http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z9tPTDRjCYU Vesicular(Bulk) transport Exocytosis Moves materials _______ of the cell Material is carried in a membranous vesicle Vesicle migrates to plasma membrane Vesicle combines with ___________ ___________ Material is emptied to the outside Endocytosis Extracellular substances are engulfed by being enclosed in a membranous vescicle Types of endocytosis ___________ —“cell eating” ___________ —“cell drinking”