Effect of Fe doped on structural, morphological and optical
advertisement
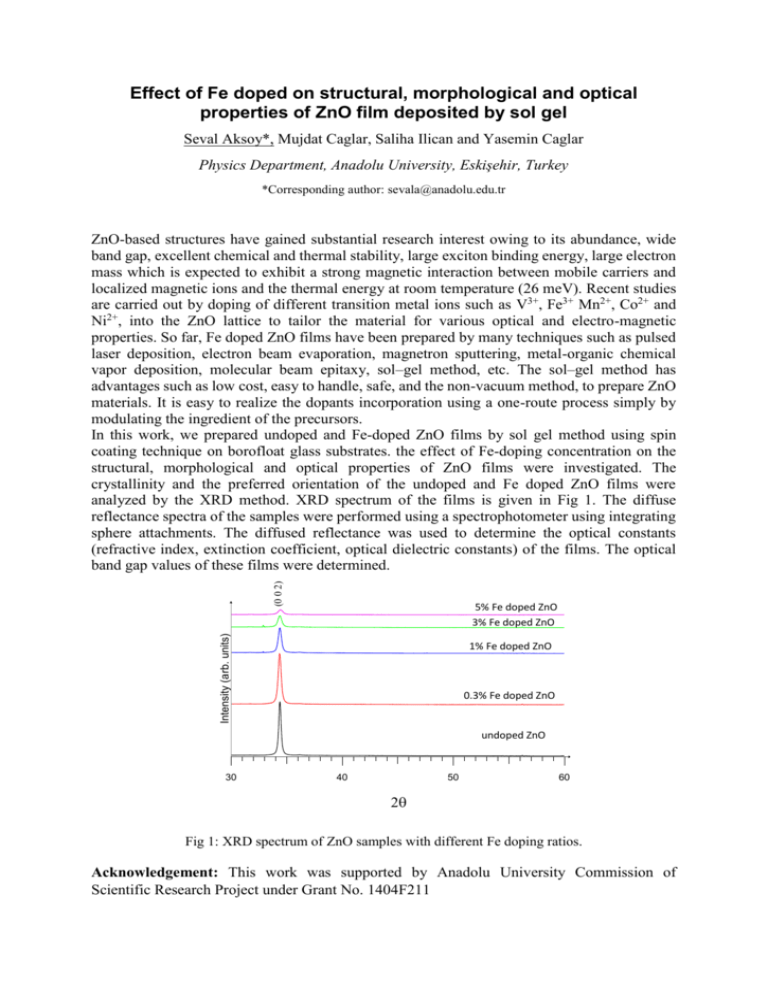
Effect of Fe doped on structural, morphological and optical properties of ZnO film deposited by sol gel Seval Aksoy*, Mujdat Caglar, Saliha Ilican and Yasemin Caglar Physics Department, Anadolu University, Eskişehir, Turkey *Corresponding author: sevala@anadolu.edu.tr (0 0 2) ZnO-based structures have gained substantial research interest owing to its abundance, wide band gap, excellent chemical and thermal stability, large exciton binding energy, large electron mass which is expected to exhibit a strong magnetic interaction between mobile carriers and localized magnetic ions and the thermal energy at room temperature (26 meV). Recent studies are carried out by doping of different transition metal ions such as V3+, Fe3+ Mn2+, Co2+ and Ni2+, into the ZnO lattice to tailor the material for various optical and electro-magnetic properties. So far, Fe doped ZnO films have been prepared by many techniques such as pulsed laser deposition, electron beam evaporation, magnetron sputtering, metal-organic chemical vapor deposition, molecular beam epitaxy, sol–gel method, etc. The sol–gel method has advantages such as low cost, easy to handle, safe, and the non-vacuum method, to prepare ZnO materials. It is easy to realize the dopants incorporation using a one-route process simply by modulating the ingredient of the precursors. In this work, we prepared undoped and Fe-doped ZnO films by sol gel method using spin coating technique on borofloat glass substrates. the effect of Fe-doping concentration on the structural, morphological and optical properties of ZnO films were investigated. The crystallinity and the preferred orientation of the undoped and Fe doped ZnO films were analyzed by the XRD method. XRD spectrum of the films is given in Fig 1. The diffuse reflectance spectra of the samples were performed using a spectrophotometer using integrating sphere attachments. The diffused reflectance was used to determine the optical constants (refractive index, extinction coefficient, optical dielectric constants) of the films. The optical band gap values of these films were determined. Intensity (arb. units) 5% Fe doped ZnO 3% Fe doped ZnO 1% Fe doped ZnO 0.3% Fe doped ZnO undoped ZnO 30 40 50 60 Fig 1: XRD spectrum of ZnO samples with different Fe doping ratios. Acknowledgement: This work was supported by Anadolu University Commission of Scientific Research Project under Grant No. 1404F211