View
advertisement
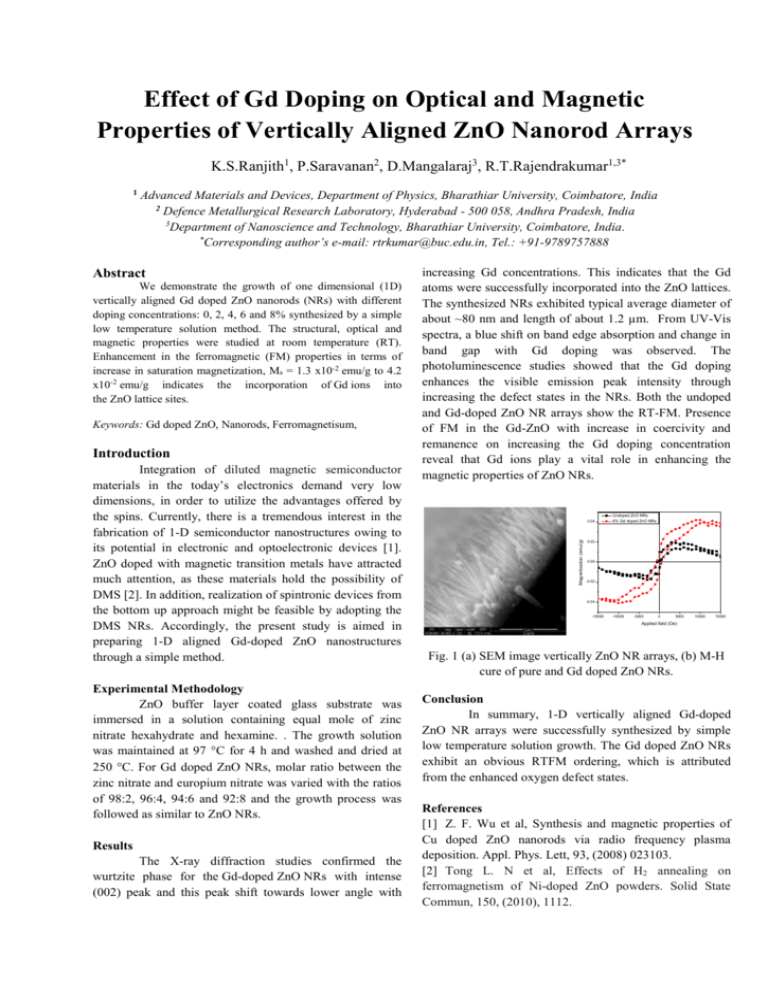
Effect of Gd Doping on Optical and Magnetic Properties of Vertically Aligned ZnO Nanorod Arrays K.S.Ranjith1, P.Saravanan2, D.Mangalaraj3, R.T.Rajendrakumar1,3* Advanced Materials and Devices, Department of Physics, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore, India 2 Defence Metallurgical Research Laboratory, Hyderabad - 500 058, Andhra Pradesh, India 3 Department of Nanoscience and Technology, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore, India. * Corresponding author’s e-mail: rtrkumar@buc.edu.in, Tel.: +91-9789757888 Abstract We demonstrate the growth of one dimensional (1D) vertically aligned Gd doped ZnO nanorods (NRs) with different doping concentrations: 0, 2, 4, 6 and 8% synthesized by a simple low temperature solution method. The structural, optical and magnetic properties were studied at room temperature (RT). Enhancement in the ferromagnetic (FM) properties in terms of increase in saturation magnetization, Ms = 1.3 x10-2 emu/g to 4.2 x10-2 emu/g indicates the incorporation of Gd ions into the ZnO lattice sites. Keywords: Gd doped ZnO, Nanorods, Ferromagnetisum, Introduction Integration of diluted magnetic semiconductor materials in the today’s electronics demand very low dimensions, in order to utilize the advantages offered by the spins. Currently, there is a tremendous interest in the fabrication of 1-D semiconductor nanostructures owing to its potential in electronic and optoelectronic devices [1]. ZnO doped with magnetic transition metals have attracted much attention, as these materials hold the possibility of DMS [2]. In addition, realization of spintronic devices from the bottom up approach might be feasible by adopting the DMS NRs. Accordingly, the present study is aimed in preparing 1-D aligned Gd-doped ZnO nanostructures through a simple method. Experimental Methodology ZnO buffer layer coated glass substrate was immersed in a solution containing equal mole of zinc nitrate hexahydrate and hexamine. . The growth solution was maintained at 97 °C for 4 h and washed and dried at 250 C. For Gd doped ZnO NRs, molar ratio between the zinc nitrate and europium nitrate was varied with the ratios of 98:2, 96:4, 94:6 and 92:8 and the growth process was followed as similar to ZnO NRs. Results The X-ray diffraction studies confirmed the wurtzite phase for the Gd-doped ZnO NRs with intense (002) peak and this peak shift towards lower angle with increasing Gd concentrations. This indicates that the Gd atoms were successfully incorporated into the ZnO lattices. The synthesized NRs exhibited typical average diameter of about ~80 nm and length of about 1.2 µm. From UV-Vis spectra, a blue shift on band edge absorption and change in band gap with Gd doping was observed. The photoluminescence studies showed that the Gd doping enhances the visible emission peak intensity through increasing the defect states in the NRs. Both the undoped and Gd-doped ZnO NR arrays show the RT-FM. Presence of FM in the Gd-ZnO with increase in coercivity and remanence on increasing the Gd doping concentration reveal that Gd ions play a vital role in enhancing the magnetic properties of ZnO NRs. 0.04 Magnetisation (emu/g) 1 Undoped ZnO NRs 6% Gd doped ZnO NRs 0.02 0.00 -0.02 -0.04 -15000 -10000 -5000 0 5000 10000 15000 Applied field (Oe) Fig. 1 (a) SEM image vertically ZnO NR arrays, (b) M-H cure of pure and Gd doped ZnO NRs. Conclusion In summary, 1-D vertically aligned Gd-doped ZnO NR arrays were successfully synthesized by simple low temperature solution growth. The Gd doped ZnO NRs exhibit an obvious RTFM ordering, which is attributed from the enhanced oxygen defect states. References [1] Z. F. Wu et al, Synthesis and magnetic properties of Cu doped ZnO nanorods via radio frequency plasma deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett, 93, (2008) 023103. [2] Tong L. N et al, Effects of H2 annealing on ferromagnetism of Ni-doped ZnO powders. Solid State Commun, 150, (2010), 1112.