Reproduction & Chem (1)
advertisement

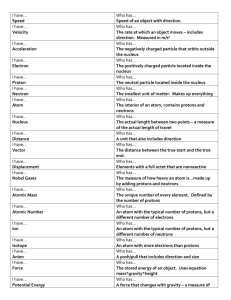
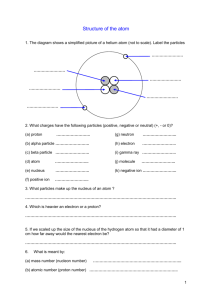
Science 9: Exam Review- Part 1 *The following is an outline only. Students are responsible for studying all material covered in class and all question types from tests, even if it is not represented in this outline. Reproduction Unit Review 1. List the 5 types of asexual reproduction discussed in class. 2. Explain each of the 5 types of asexual reproduction listed above. 3. Give an example of an organism that performs each type of asexual reproduction listed in #7. 4. What part of a computer would have the same function as the DNA in a cell? 5. List the 3 main parts to a DNA molecule? 6. How do the nitrogen bases in a DNA molecule pair up? 7. Where is a DNA molecule located in the cell? 8. Explain how a normal cell turns into a cancerous cell. 9. List 5 groups of substances that are considered carcinogens. 10. List 2 main differences between sexual and asexual reproduction. 11. Explain how an animal is cloned? 12. Draw and explain each stage of mitosis. 13. Explain the following and use a diagram to show your understanding or Mitosis and Meiosis: a) Haploid – b) Diploid – 14. List the three parts of the Cell Theory: 15. Label the following cell and give the function of each organelle that we discussed in class. What kind of cell is it? Key Points – Reproduction Unit Test 1. The structure responsible for providing energy to the cell is ____________? 2. Animal cells are different from plant cells in that (a) animal cells have a cell wall and plant cells do not. (b) plant cells have a nucleus and animal cells do not. (c) animal cells have mitochondria, plant cells do not. (d) plant cells have a cell wall, animal cells do not. 3. The structure responsible for giving instructions to the cell is ____________? 4. The structure responsible for making proteins in the cell is the ____________? 5. This question refers to Figure 1 below. The correct sequence of events is (a) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 (b) 2, 3, 1, 4, 5 (c) 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 (d) 4, 3, 2, 5, 1 6. As a result of asexual reproduction, the daughter cells are (a) identical to each other and the mother cell. (b) different from the mother cell. (c) different from each other and the mother cell. (d) none of the above. 7. DNA is to the cell as software is to a ___________________? 8. Which of the following is not part of a DNA molecule? (a) A sugar molecule (b) A phosphate molecule. (c) A fat molecule. (d) A nitrogen base. 9. Choose the one that is not a nitrogen base. (a) Adenine (b) Thymine (c) Cytosine (d) Uracil 10. Which of the following shows the most logical organization of the terms? (a) DNA -> Genes -> Chromosomes (b) Chromosomes -> DNA -> Genes (c) DNA -> Chromosomes -> Genes (d) Genes -> DNA -> Chromosomes 11. A mutation (a) is a change in the DNA that may be harmful. (b) is a change in the DNA that may be harmless. (c) can be caused by chemicals, radiation, or viruses. (d) is all of the above. 12. A carcinogen may be (a) a chemical compound. (b) a virus. (c) radiation. (d) all of the above. 13. A cancer cell differs from a normal cell in that _________________________? 14. Which of the following describes the main advantages of sexual reproduction? (a) Two parents share the duties of caring for offspring. (b) Contributions from the parents allow for genetic variation. (c) Each offspring is able to survive better than the parent. (d) The parents are better able to survive than the offspring. 15. Cloning is considered to be sexual/asexual (circle response) reproduction. 16. Frogs can be cloned by injecting a nucleus into a(n) ________________ cell. 17. When bacteria exchange small pieces of genetic information this is called _______________ and is a type of sexual/asexual (circle response) reproduction. 18. When sperm from a male fertilizes the egg from a female this is sexual/asexual (circle response) reproduction. 19. When an organism creates both male and female sex cells (a) asexual reproduction (b) separate sexes (c) hermaphrodites (d) conjugation 20. Humans have ________________(# of pairs of chromosomes) in normal cells. 21. Reproductive or sex cells have _________________(# of chromosomes) in humans. 22. Draw four sets of duplicated chromosomes in each of the mitosis stages. Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase 23. Discuss two ways that cancer cells are different from "normal" cells. Write your answer in full sentences. 24. Match the columns. ___ Haploid ___Diploid ___External fertilization ___Internal fertilization A. The product when a sperm cell joins an egg cell B. Sperm meets egg outside the body C. Number of chromosomes in a normal body cell D. The event of sperm joining egg ___Asexual reproduction E. The number of chromosomes in a gamete ___Sexual reproduction F. Sperm meets egg inside the body ___Zygote ___Fertilization G. Reproduction involving two parents H. Reproduction involving only one parent 25. Give two differences between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 26. Fill in the missing numbers of chromosomes in the diagrams. Mitosis 4 6 Meiosis 4 6 27. Draw a plant cell and label at least 6 parts. 28. List the 3 parts of Cell Theory. 29. Describe the steps involved in cloning a frog. You can use diagrams. 30. Explain fully how sexual reproduction benefits organisms. Matter Unit Review 1. 2. 3. What is matter? What does WHMIS stand for and what is it used for? Name & explain each of the following WHMIS symbols: a) b) c) Properties of Matter 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. What do we mean by the properties of an object? Differentiate between the two categories that we use to classify the properties of matter. List the 9 physical properties that we studied. Define each of the 9 physical properties that we studied. List 2 chemical properties. Define both of the chemical properties above. Physical and Chemical Changes 10. Write a definition for each of the following terms: a. Physical Change b. Chemical Change List the 4 statements that make up the particle theory of matter: 11. Write the name or symbol of the following elements: a) F __________________________________ b) Cl __________________________________ c) Ag __________________________________ d) Br __________________________________ e) N __________________________________ f) Mg __________________________________ g) Li __________________________________ h) Be __________________________________ i) Potassium __________________________________ j) Mercury __________________________________ k) Sodium __________________________________ l) Carbon __________________________________ m) Boron __________________________________ n) Phosphorus __________________________________ o) Hydrogen __________________________________ p) Helium __________________________________ 12. Write the chemical formula & name the compounds that would be created by the following metals & nonmetals: a) Magnesium & sulfur b) Sodium & phosphorus c) Calcium & nitrogen 13. Draw a Matter Diagram that shows how each of the following terms are related to one another: Compound Mixtures Element Heterogeneous Pure Substances 14. Explain the difference between a molecule and a compound. Label each of the following areas of the periodic table: q) r) s) t) Halogens Metals Alkali Metals Transition Metals Key Points – Matter Unit Test 1. Which of the following properties of sugar is not a physical property? (a) Sugar turns black when it is heated. (b) Sugar dissolves readily in water. (c) Sugar has a sweet taste. (d) Sugar is a white solid at room temperature. 2. Which of the following is a chemical property of sulphur? (a) It is bright yellow in colour. (b) It is a solid at room temperature. (c) It is brittle. (d) It is combustible. 3. Which of the following describes a chemical property? (a) Hydrogen reacts explosively with oxygen. (b) Mercury is a liquid at room temperature. (c) Aluminum is malleable. (d) The density of gold is 19.3 g/cm3. Homogeneous Matter 4. All of the following are properties of magnesium. Identify the physical property. (a) Magnesium burns in air with a brilliant white flame. (b) Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce a gas. (c) Magnesium is a good conductor of electricity. (d) Magnesium combines with nitrogen to form a black powder. 5. Identify the chemical change in the following list: (a) the crushing of stones (b) the formation of clouds (c) the separation of cream from milk (d) the burning of a candle 6. Matter can exist in one of three states. These are (a) physical, chemical, metal (b) alloy, crystal, hydrocarbon (c) reactant, product, precipitate (d) solid, liquid, gas 7. When some solid mothballs are placed in a clothes closet, they gradually disappear over a period of time. The change of state that occurs is (a) evaporation (b) sublimation (c) condensation (d) melting 8. All of the following statements are part of the particle theory of matter except one. Identify the exception. (a) Different substances are made of different particles. (b) The particles in solids are harder than the particles in liquids. (c) The particles are always moving. (d) There are forces of attraction between the particles. 9. Only one of the following statements is correct. Identify that statement. (a) All compounds are pure substances. (b) All mixtures are heterogeneous. (c) All pure substances are elements. (d) All solutions consist of a solid dissolved in a liquid. 10. Air is classified as a mixture because (a) it is clear and colourless. (b) it contains at least two different pure substances. (c) its composition never changes. (d) its major components are elements. 11. A pure substance consisting of two or more kinds of atom is considered to be (a) an element. (b) a solution. (c) a compound. (d) a heterogeneous mixture. 12. Substances composed of identical atoms are (a) mixtures. (b) elements. (c) compounds. (d) solutions. 13. Which one of the following substances is an element? (a) Water (b) Salt (c) Helium (d) Milk 14. Which substance in the following list is a compound? (a) Salt (b) Carbon (c) Sulphur (d) Neon 15. A heterogeneous mixture differs from a solution because (a) a heterogeneous mixture is always solid. (b) a heterogeneous mixture consists of elements. (c) the different components can be seen in a heterogeneous mixture. (d) a heterogeneous mixture consists of more substances than a solution. 16. Which one of the following is a heterogeneous mixture? (a) Cooking oil (b) Vinegar and water (c) Salt water (d) Oil and water 17. Only one of the following lists does not consist entirely of symbols for elements. Which one? (a) C, He, Mg, Cu (b) H, ASA, P, Fe (c) He, N, Cl, O (d) Ca, Ne, Fe, He 18. The total number of atoms represented by the formula K 2Cr2O7 is (a) 1 (b) 3 (c) 11 (d) 28 19. The atomic model has been modified many times over the years. This happened because (a) scientists have become smarter with time. (b) new evidence became available to scientists. (c) the actual nature of the atom has changed with time. (d) more elements were discovered. 20. Protons are (a) positively charged particles found outside the nucleus in an atom. (b) negatively charged particles found outside the nucleus in an atom. (c) neutral particles found in the nucleus in an atom. (d) positively charged particles found in the nucleus in an atom. 21. Electrons are (a) positively charged particles found outside the nucleus in an atom. (b) negatively charged particles found outside the nucleus in an atom. (c) neutral particles found in the nucleus in an atom. (d) negatively charged particles found in the nucleus in an atom. 22. Neutrons are (a) negatively charged particles found outside the nucleus in an atom. (b) neutral particles found outside the nucleus in an atom. (c) neutral particles found in the nucleus in an atom. (d) positively charged particles found in the nucleus in an atom. 23. The number of electrons in an atom is the same as (a) the number of neutrons in the atom. (b) the mass number of the atom. (c) the number of protons in the atom. (d) the difference between the mass number and atomic number. 24. The particles that make up most of the mass of an atom are (a) the protons and electrons. (b) the neutrons and electrons. (c) the protons and neutrons. (d) only the neutrons. 25. An atom with an atomic number of 38 and a mass number of 88 contains (a) 50 neutrons (b) 50 electrons (c) 38 neutrons (d) 88 protons 26. The particles formed when atoms lose or gain electrons are called (a) isotopes (b) neutrons (c) ions (d) beta particles 27. An atom can form a positive ion by (a) losing electrons (b) gaining electrons (c) losing protons (d) gaining protons 28. An atom can form a negative ion by (a) losing electrons (b) gaining electrons (c) losing protons (d) gaining protons 29. Chemists believe that the chemical properties of an element are directly related to the (a) number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. (b) atomic mass of the atom. (c) electrons in the outermost orbit of the atom. (d) the mass number of the atom. 30. Moving down a column in the periodic table, the number of electrons in the highest orbit (a) increases gradually. (b) decreases gradually. (c) shows no pattern. (d) remains constant 31. The group 1 elements are similar in that they (a) are all very unreactive. (b) all form ions with a charge of 2+. (c) all have one electron in the outer level. (d) all have one less electron than the noble gases. 32. The noble gases are very unreactive because (a) they are very rare. (b) their outer orbits are filled. (c) they have very low densities. (d) they have low boiling points. 33. The most reactive elements in the periodic table are found in (a) groups 1 and 18. (b) groups 2 and 15. (c) groups 3 and 4. (d) groups 1 and 17. 34. Elements that possess some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals are called (a) alkali metals. (b) metalloids. (c) noble gases. (d) heavy metals. 35. Rows in the periodic table are also referred to as (a) periods. (b) families. (c) groups. (d) columns. 36. The least reactive element in the following list is (a) argon. (b) gold. (c) potassium. (d) copper Short Answer 1. Write standard atomic notation for the following atoms. (a) a magnesium atom with 13 neutrons and 12 protons (b) a potassium atom with 20 neutrons and 19 protons 2. Complete the blanks in the following table. Atomic Number 9 Mass Number 19 __________ ____________ _________ 56 Number of Number of Number of Protons Electrons Neutrons ______________ _____________ ______________ 20 _____________ _______________ 26 21 ______________ 3. Draw the Bohr – Rutherford diagram for the first 20 elements. 4. What are ions and how are they formed? Give an example of a positive and a negative ion (include symbols and charges). 5. List the all of the physical properties discussed in class and your notes. Write the definition for each.