Chapter 2 Combined Notes
advertisement

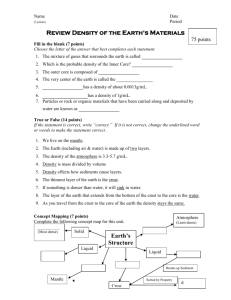
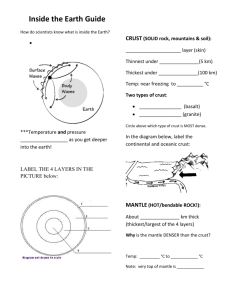
CHAPTER 2 Section 1 – Earth: A Unique Planet Earth Basics Third planet from the sun in our solar system 4.6 billions years old 71% of the surface is covered by water Global ocean – relatively thin layer of water that covers earth’s surface shape of earth is an oblate spheroid – slightly flattened sphere polar regions flatten and the equator is bulged (why?) surface is relatively smooth Earth’s Interior Discoveries made by seismic waves – vibrations that travel through earth Compositional Zones 1. crust – thin, solid outermost zone of Earth a. oceanic crust – crust beneath oceans b. continental crust – crust that makes up the continents 2. mantle – the layer that underlies the crust a. denser than the crust b. nearly 2900 km thick c. 2/3 of earth’s mass 3. core – central part of the Earth below the mantle a. iron b. nickel Structural Zones 1. lithosphere – the solid, outer layer of Earth that consist of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle 2. asthenosphere – the solid, plastic layer of the mantle beneath the lithosphere; made of mantle rock that flows very slowly, which allows tectonic plates to move on top of it 3. mesosphere – the “middle sphere”; the strong lower part of the mantle between the asthenosphere and the outer core 4. outer core – a dense liquid at a depth of 2900 km 5. inner core – a dense, rigid solid at a depth of 5900 km Earth as a Magnet Two magnetic poles Extends beyond the atmosphere and affects a region of space called the magnetosphere - source may be the liquid iron core - may be produced by motions within the core that produces electric currents that in turn create Earth’s magnetic field - Sun and Moon also have magnetic fields Earth’s Gravity Gravity – the force of attraction that exists between all matter in the universe Law of Gravitation – the force of attraction between any two objects depends on the masses of the objects and distance between the two objects Weight and Mass Weight – a measure of the strength of the pull of gravity on an object. The Newton (N) is the SI unit used to measure weight. The mass of an object does not change regardless of location, but the weight of the object will change. Why? Weight and Location Weight varies according to the location on Earth’s surface. Weight at the equator would be about 0.3% less than the weight at the poles. Why? Section 2 Energy in the Earth System System an organized group of related objects or components that interact to create a whole vary in size (subatomic to universe) all have boundaries Earth system is an interaction between matter and energy o Matter – anything that has mass and volume o Energy – the ability to do work Heat Light Vibrations Electromagnetic waves Closed system – energy is exchanged, not matter Open system – both energy and matter are exchanged Earth system is almost closed because matter exchange is very limited Earth’s Four Spheres Atmosphere blanket of gases that surrounds Earth’s surface provides the air that you breath shields Earth from sun’s harmful radiation 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and 1% a mixture of gases Hydrosphere all of Earth’s water except the water that is in gaseous form in the atmosphere 71% of Earth’s surface is covered 97% of water is in salty oceans Geosphere mostly solid part of the Earth all of the rock and soil on the surface and on the ocean floor includes the solid and molten interior of the Earth Biosphere composed of all of the forms of life in the geosphere, in the hydrosphere, and in the atmosphere any organic matter that has not decomposed extends from the deepest parts of the ocean to the atmosphere a few kilometers above Earth’s surface Earth’s Energy Budget First law of Thermodynamics Energy Budget Second law of Thermodynamics Internal Energy Sources decay of radioactive atoms convection – movement of hot materials toward the surface o cooler, denser materials sink o this process drives plate tectonics External Energy Sources sun o movement of air masses o generates wind and ocean currents o allows plants to produce food the pull of the sun and the moon on the oceans, combined with Earth’s rotation, generates tides that cause currents and drive the mixing of ocean water Cycles in the Earth System Reservoir – a place where matter and energy is stored Cycle – a group of processes in which matter and energy repeatedly move through a series of reservoirs Nitrogen Cycle – nitrogen moves from air to soil, soil to plants and animals and back to air again Carbon Cycle Phosphorous Cycle – moves through every sphere except the atmosphere Water Cycle – water to gas to precipitation to water Section 3 – Ecology Ecology – the study of the complex relationships between living things and their non-living, or abiotic, environment Ecosystems A community of organisms and their abiotic environment Producers – organisms that can make their own food Consumers – organisms that get their energy by eating other organisms Decomposers – organisms that get their energy by breaking down dead organisms Balancing Forces in Ecosystems Carrying capacity – the largest population that an environment can support at any given time Ecological Responses to Change ecosystems react to changes in ways to maintain or restore balance in the ecosystem predictable patterns of return to a damaged ecosystem o grasses and fast growing plants start to grow o shrubs and small animal species will return o larger tree species and larger animals return Energy Transfer ultimate source or energy is the sun photosynthesis – plants using sunlight to produce food energy pyramid o producers form the base o consumers form the next level o decomposers form the top of the pyramid as you move up the pyramid, more energy is lost at each level Food Chains and Food Webs food chain – the sequence in which organisms consume other organisms food web – a diagram that shows the feeding relationships among organisms in an ecosystem Human Stewardship of the Environment Ecological balances can be disrupted by human activity o Overconsumption of resources o Conversion of natural areas to agriculture or urban areas o Pollution – the contamination of the environment with harmful waste products or impurities