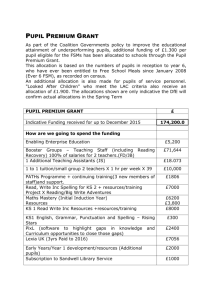
Requirements for state master exam from pedagogy
advertisement

Requirements for state master exam from pedagogy:
a study of teaching primary school, secondary school, special education, SPZP, FACULTY
of MEDICINE (medical science) and all forms of teaching master’s study
During the exam the student has to prove that he acquires the curriculum of pedagogical
disciplines and can link to the experience acquired in the context of teaching practice 1 to 3.
Topics:
1. Pedagogy as a discipline (the subject of its research, sources of knowledge, educational
disciplines and their focus, the current problems of pedagogy).
2. Educational research and methodology (research problem, the quantitative and qualitative
oriented research, validity and reliability of the research tools, research methods, methods
of processing and interpretation of the data).
3. The educational activities of the school (humanization of education, changes in the
relations between teacher and pupil, the curricular reform, The Framework educational
programme, school educational program, the relationship between the teacher
competencies and pupil competencies).
4. Social and historical conditions and its reflection in educational and training models
(System concept of education, situational concept of education, transmissive and
constructivist education, alternative educational conceptions).
5. A pedagogical legacy of John Amos Comenius (overview of pedagogical ideas, assessing
their timelessness, the characteristics of one of his basic writings).
6. Selected educational problems in the works of figures of 17-19th century (e. g. the
education of a gentleman in J. Lock´s writings, free and natural education in J. J.
Rousseau´s writing, educational views and crucial tendencies in the work of J. H.
Pestalozzi, J. F. Herbart, K. D. Ushinsky, L. N. Tolstoy).
7. The development of modern Czech School education and “theresien” reforms. The Czech
school and education of 20th century-its tradition and the international context.
8. Pedagogical reformism at the beginning of 20th century, its characteristics, resources, and
representatives of the main streams. The current educational reform efforts.
9. Organization and management of the educational system in the Czech Republic. The basic
legal standard of management education and training in the Czech Republic. (The national
programme for the development of education in the Czech Republic. The Education Act
number 561/2004 Sb., act number 563/2004 Sb. about pedagogical staff). The Framework
Educational programme for Basic Education (key competences of pupils, educational
areas, cross-curricular subjects).
10. School and class management. Methods for the evaluation of educational and training
facilities (outer, inner options). The image of the school. State administration in the
management of education of the Czech Republic. Autonomy in the management of
education of the Czech Republic. The Czech school inspection. Schools facilities and
school services.
11. Axiological dimension and value orientation of humans as part of his education (axiology,
concept of value – the value, the relationship between the need and the value, the kinds of
values, the dimension of the biological, cultural and civilizational, global threats,
consumerist orientation, humanism, tolerance).
12. Moral education of pupils (target, content, the process of moral education, moral
education methods, sociability, education for sociability, project Ethics education, ethical
aspects of The Framework Educational programme for Basic Education in the
competences of the pupil, in educational areas, in cross-curricular subjects).
13. The problem of discipline and freedom in education (socio-philosophical context of
discipline and freedom, anomie, liberalism, postmodernism, the discipline, the kinds of
discipline, individual and social functions of discipline, the causes of undisciplined
behaviour of pupils; the basic conditions, means and methods of education to school
discipline).
14. Authority in educational contexts (the authority, the authority and social roles, authority,
formal and informal, the authority of the school, authority of the teacher, the teacher and
the pupil's partner relationships, freedom and order, responsibility).
15. Educational Diagnostics of pupil and school classes. The teacher's self-reflection of
educational action (the notion of Educational Diagnostics, diagnostic procedure, stages,
the methods of pedagogical Diagnostics, the specific example of the application of some
of the diagnostic methods; the importance of self-reflection for teachers, phase of selfreflection, methods of self-reflection).
16. Behavioural disorders of pupils and their possible remedies (the behaviour problem,
behavioural disorders, evaluating behaviour, disposition for behavioural disorders, risk
approaches to the education of pupils with behavioural disorders, perspective approaches
to the education of pupils with behavioural disorders).
17. Physical culture, physical education, health education (physical culture, physical
education, sport, motion recreation, tasks of physical education, exercise regime of
people, health-oriented fitness pupils; holistic and interactive concept of health, health
promotion, project school that support health, education to support healthy lifestyle).
18. The family as an educational environment. Cooperation in the educational relationship
between the teacher and the parents of the pupils (family, family functions, characters of
functional family, the position of the family between the educational actors, family
education of children of school age, the components of the family environment of the
pupils, cooperation, cooperation as a reciprocity, cooperation as a partnership, the basic
models of cooperation with the family, the types of family background of the pupil, the
cooperative skills of the teacher).
19. The concept of a global, ecological/environmental education. Education for the 21st
century (ecological/environmental education, education for sustainable development,
ecological thinking, value approach, ecological and environmental education as a crosscurricular theme of the Framework Educational programme for Basic Education).
20. Teacher at primary and secondary school (the role of teacher, competencies of the teacher,
tasks of class teacher, the criteria of professional ethics of teachers).
21. The content of teaching, the criteria for the determination of the content, curriculum,
documents defining the content (the national education development programme, the
Framework Educational programme for Basic Education or the Framework Educational
programme for Secondary Education {according to the focus of the study of student},
school educational programme), teaching plan, curriculum, textbooks.
22. The aims of basic education in the Framework Educational programme for Basic
Education or the Framework Educational programme for Secondary Education; key
competencies, educational areas, field of study, cross-curricular themes.
23. Didactic principles (the principles). The principles of classic; principles of modern
didactics.
24. Teaching strategies (deductive, inductive, and socially-mediated teaching); the
methodological practices in teaching. Types of teaching: teaching informative, heuristic,
productive and regulatory. Teaching style as an individual characteristic of the teacher.
25. Teaching methods and their classification. A systematic overview of all teaching methods.
The selection criteria for the methods in teaching process.
26. Verbal teaching methods. Total overview, the specifics of the individual methods. The
advantages and disadvantages of verbal teaching methods. Verbal and nonverbal speech
of teacher. Use of verbal teaching methods in teaching.
27. Illustrative and practical teaching methods. Total overview, the specifics of the individual
methods. The conditions for their creative application in the school.
28. Problem method and problem teaching. Project teaching. Cooperative learning.
Development activities, independence and creativity of students. Reading and writing for
critical thinking.
29. The organisation of teaching. Organizational forms of teaching; teaching lesson (hour), its
construction and appearance. Collective, group and individualized teaching. The home
preparation of pupils for teaching and homework.
30. The survey of results of teaching, examination and didactic tests. Evaluation and
classification of pupils. Formative and summative evaluation, grading and assessment.
The school "success" and "failure" of the pupils.
31. Educational diagnostics, its area and methods, relation to psychological diagnosis. The
diagnostic work of teachers, his collaboration with parents and pedagogical-psychological
counselling centre. Teacher self-diagnostics and its resources.
32. Differentiation and individualization of teaching and learning. Work with talented and
lagging pupils learning in the current differentiated school. The conditions of the
individual approach to pupils.


![afl_mat[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005387843_1-8371eaaba182de7da429cb4369cd28fc-300x300.png)