RTL Study Guide CLASSIFICATION rev 2105
advertisement

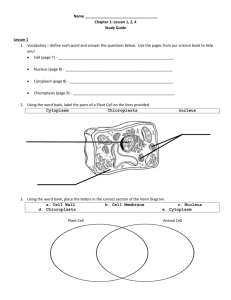
Read-to-Learn Study Guide - Classification of Organisms Learning Objectives: Analyze the historical development of classification Analyze the similarities and differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes Analyze the similarities between and differences among kingdoms: Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protists, Fungi, Plants, and Animals. Classify organisms using dichotomous keys. Read to Learn In biology, an organism is any complete living system (such as an animal, fungus, micro-organism, or plant). In at least some form, all organisms are capable of metabolizing nutrients for energy, responding to stimuli, and maintaining homeostasis. Living things also grow and develop over time and reproduce by passing on genes to their offspring which is referred to as heredity. All living things are made of a basic building block called a cell but an organism may either be unicellular (made of a single cell) or, as in the case of humans, comprised of trillions of cells grouped into specialized tissues and organs. The term multicellular (many cells) describes any organism made up of more than one cell. There are over 10 million different forms or species of life on Planet Earth! This tremendous degree of diversity makes necessary the development of a system for classifying and grouping organisms. Based on cell type, organisms may be divided into prokaryotic and eukaryotic groups. The prokaryotes are now represented in two kingdoms Eubacteria and Archaebacteria. The organisms in both kingdoms are prokaryotic (having no nucleus), and are unicellular. Under Whittaker’s initial schema all prokaryotes were in one group called Moneran. Eukaryotic organisms are constructed of complex cells with a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts (in plants). Protista, fungi, animals and plants are examples of species that are eukaryotes. Most members of the kingdom Protista are unicellular, some are autotrophs (can photosynthesize their own food) and some are heterotrophs. Most members of the kingdom Fungi are multicellular, all are heterotrophs and have cell walls made of chitin. All members of the kingdom Plantae are multicellular autotrophs. Most plants cannot move about, and the cells have cell walls made of cellulose. All members of the kingdom Animalia are multicellular heterotrophs. Most animals can move about and their cells lack cell walls. Classification: Taxonomy is a branch of biology dealing with the identification and naming of organisms. The ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle apparently began the discussion on taxonomy. British naturalist John Ray is credited with revising the concept of naming and describing organisms. During the 1700s, Swedish botanist Carolus Linneus classified all thenknown organisms into two large groups: the kingdoms Plantae and Animalia. Robert Whittaker in 1969 proposed five kingdoms: Plantae, Animalia, Fungi, Protista, and Monera. Other schemes involving an even greater number of kingdoms have lately been proposed, however many biologists still employ Whittaker's five kingdoms. Linnaeus was the first to use a two name system called binomial nomenclature (which literally means two names) to help classify and name organisms. In this system all organisms are classified into levels called taxons or taxa. Linneaus’ system has seven levels, which run from the largest, most diverse and inclusive taxon called kingdoms to the smallest, most specific and exclusive taxon called species. This system of classification is shown in the figure at left. For example, Homo sapiens is the Latin scientific name for modern humans. All members of the species sapiens are, at least in theory, genetically able to interbreed. Several species may belong to a genus, but the members of different species within a genus are unable to interbreed to produce fertile offspring. Homo, however, only has one surviving species, sapiens, which are modern humans. Prehistoric humans species like Homo erectus, Homo neanderthalensis, etc. became extinct thousands of years ago. Several genera belong to the same family and so on up the hierarchy, eventually reaching the kingdom (Animalia, in the case of humans). All living organisms known to science are given classification by this system which can be used to confirm which groups of organisms are most closely related. The rule of thumb to follow is: The more taxa organism share, the more closely related they must be. Key Vocabulary – match the vocabulary word with its definition _____ 1. Multicellular _____ 2. Binomial _____3. Taxonomy _____4. Linnaeus _____5. Genus _____6. Eukaryotic _____7. Eubacteria _____8. Prokaryotic _____9. Species _____10. Heterotrophic _____11. Autotrophic _____12. Kingdom a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. Naming system that gives each organism a two-word name Developed the first system of classification Branch of biology that groups and names organisms Consists of a group of similar species Kingdom that bacteria belong to Describes organisms that must eat other organisms for nutrients The most exclusive taxon; identifies the second part of an organism’s scientific name. Largest, most inclusive taxon; all living things fall into 1 of these 5 categories Describes organisms that can produce nutrients using energy from light Describes one of two groups of organisms that lack a cell nucleus Describes organisms constructed of many cells that work in groups to form tissues. Describes organisms whose cells contain complex membrane-bound organelles and nucleus Putting Vocabulary to Use! Linnaeus, binomial, taxonomy ________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ eukaryotic, protists, bacteria, unicellular _______________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Show What You Know! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Which taxon includes the most specific characteristics? _____________________________________________ Which taxon includes the broadest characteristics? ________________________________________________ Which taxon includes more species, an order or a family? ___________________________________________ Which taxon includes only organisms that can successfully interbreed? ________________________________ If two organisms belong to the same family, what other taxonomic groups must they share? _______________ Which two organisms on the chart above are most closely related? Explain how you know. ________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. To which taxa (more than one taxon) do all four organisms belong? ____________________________________ 8. What is the order, family, and genus of a human? ___________________________________________________ 9. Using the information in the chart, what can you conclude about the classification taxa of an organism with the scientific name Rana temporaria? In other words, which kingdom, phylum, class, order, and genus, must this species belong to? __________________________________________________________________________ 10. Explain how the shape of the diagram to the left and the diagram below could be helpful to students trying to understand how the science of taxonomy works. _________________________________ _________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 11. True or False: Organisms belonging to the same Phylum will always belong to the same Kingdom? __________ 12. True or False: Organisms belonging to the same Family will belong to the same Genus? ________ 13. True or False: Classes are less diverse than Families? _______ 14. True or False: Orders are more inclusive than species? ______ BE CAREFUL!! DON’T BE TRICKED!! Organisms can be further broken into groups beyond the species level. For example, dogs, while they all belong to the same genus and species, Canis familiaris, can be divided into breeds. In the plant world, plants of same genus and species can be further organized by varieties. Check out this example below: All live oaks belong to the genus, Quercus. All live oaks belong to the species, virginiana. Therefore, they all share the same scientific name, Quercus virginiana. However, there are different varieties of live oaks like Bay live oak (Quercus virginiana var. maritima.), Texas live oak (Quercus virginiana var. fusiformus), and Sand live oak (Quercus. virginiana var. geminata). Now carefully answer this question. 15. Which tree is most closely related to Bay live oaks (Quercus virginiana var. maritima)? A. Batis maritima B. Carpinus caroliniana var. maritima C. Quercus Falcata var. pagodaefolia D. Clematis virginiana 16. Directions: Compare and contrast these six kingdoms by filling the columns with check marks beside the characteristics that define each kingdom. Then use your chart to complete the Venn diagrams that follow. KINGDOMS CHARACTERISTICS EUBACTEIA ARCHAEBACTERIA PROTISTA FUNGI PLANTAE ANIMALIA PROKARYOTIC EUKARYOTIC UNICELLULAR MULTICELLULAR AUTOTROPHIC HETEROTROPHIC HAS A CELL WALL HAS A NUCLEUS ALL MEMBERS REPRODUCE ASEXUALLY PHOTOSYNTHETIC FEED ON OTHER ORGANISMS 17. Plants vs Fungi vs Animals 18. Protists vs Plants vs Animals 19. Dichotomous Keys: Can you name these fish? Use the key below to write their name in each box. 20. Describe in detail what a Glass-eye snapper looks like according to the dichotomous key above: _____________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________