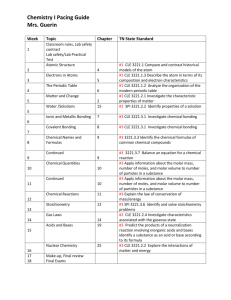
Regular Chemistry Syllabus

Regular Chemistry Syllabus
Instructor: Julie Stansberry email: stansberryj@hcboe.net
Text: Chemistry (Prentice Hall) website: mhhsw.hcboe.net phone (423)581-1600 ext 1170 words listed in italics in the spi will be taught in a different chapter
Unit 1- Atomic Structure
week 1.Atomic Structure
5.1 Models of the atom
4.1 Defining the atom
4.2 Structure of the atom
4.3 Distinguishing among atoms
Demo: Cathode ray tube
Lab: Law of Definite composition
Timeline: Models of the Atom
vocabulary: Democritus, Dalton’s atomic theory, Thomson, Rutherford, Chadwick, Planck,
Bohr, quantum mechanical model, nucleus, proton, neutron, electron, orbit, energy levels, probability, atomic number, mass number, isotope, ion, oxidation number, cation , anion, and neutral atom
Ch 5.1,4 test spi 3221:
1.1 Compare and contrast the major models of the atom (eg Democritus, Thomson,
Rutherford, Bohr, and the quantum mechanical model.
1.2 Interpret the periodic table to describe an element’s atomic makeup week 2. Nuclear Chemistry
25.1 Nuclear radiation
25.2 Nuclear transformations
25.3 Fission and fusion of atomic nuclei
25.4 Radiation in your life
vocabulary: radioactivity ,electromagnetic radiation spectrum, carbon-14 dating, radioisotopes, alpha, beta, positron, gamma, half-life, transmutation, transuranium elements, parent nuclide, daughter, chain reaction, decay series, fission, fusion, moderator, control rod, geiger counter, film badge, scintillation counter, and film badge
Ch. 25 Test
spi 3221:
t/e.1 Distinguish among tools and procedures best suited to conduct a specified scientific inquiry math.3 Interpret graphs that depict real-world phenomena
2.4 Classify a property of change of matter as (physical, chemical, or) nuclear
3.8 Describe radioactive decay through a balanced nuclear equation and through the analysis of half-life
3.9 Compare and contrast nuclear fusion and fission week 3. Electrons in the Atom
5.2 Electron arrangement in atoms
5.3 Physics and the Quantum Mechanical Model
Lab: Flame Test
vocabulary: valence electron, core electrons, electron configuration, noble gas configuration, orbital notation, core configuration, valence configuration, atomic orbital, aufbau principle, energy levels, Hund’s rule, Pauli’s exclusion principle, photons, and quantum
Redox reactions
20.1 Oxidation and reduction
20.2 Oxidation numbers
Demo: Potato Clock
Demo: coin plating
vocabulary: reduction, oxidation, oxidation number
Ch 5, 20 Test
spi 3221 1.5 represent an electron’s location in the quantum mechanical model of an atom in terms of the shape of electron clouds (s and p orbitals in particular), relative energies of orbitals, and the number of electrons possible in the s,p,d, and f orbitals week 4. The Periodic Table
6.1 Organizing the elements
6.2 Classifying the elements
6.3 Periodic trends
Demo: Reactivity of Sodium and Calcium
Lab: Mini Hindenburg (properties of hydrogen)
Project: Investigate an element
vocabulary: alkali metals, alkali earth metals, atomic radius, electronegativity, halogens, noble gas, inner transition metal, transition metal, representative element, metal, nonmetal, metalloid, and periodic law
Ch 6 Test
spi 3221.1.3 Describe the trends found in the periodic table with respect to atomic size, ionization energy, electron affinity, or electronegativity week 5. Ionic and metallic bonding
7.1 Ions
7.2 Ionic bonds and ionic compounds
7.3 Bonding in metals
vocabulary: chemical formula, electron dot structure (lewis dot structure), formula unit, ionic bond, ionic compound, metallic bond, octet rule, valence electron
-Covalent Bonding
8.1 Molecular compounds
8.2 The nature of covalent bonding
8.4 Polar bonds and molecules
vocabulary: covalent bond, dipole, dispersion forces, double covalent bond, hydrogen bonds, molecular compound, molecule, nonpolar covalent bond, polar covalent bond, polyatomic ion, single covalent bond, triple covalent bond, unshared pair (nonbonding electrons), van der waals forces (intermolecular forces)
Lab: Saponification
Ch 7,8 test spi 3221
1.4 determine the lewis electron-dot structure or number of valence electrons for an atom of any main-group element from its atomic number or position on the periodic table
3.1 Analyze ionic and covalent compounds in terms of how they form, (names) chemical formulas, (percent composition and molar mass)
UNIT 1 Exam (1/4)
UNIT 2A- Interactions of matter
week 6. Hydrocarbon Compounds
22.1 Hydrocarbons
22.2 Unsaturated hydrocarbons
22.3 Isomers
vocabulary: hydrocarbon, alkane, alkene, alkyne, straight-chain, branched-chain, condensed structural formula, alkyl group, unsaturated compounds, saturated compounds, isomers,
-Functional groups
23.1 Intro to functional groups
23.2 Alcohols and ethers
vocabulary: alcohol, aldehyde, ester, ether, carboxylic acid, amine, and ketone
activity: organic models ch 22,23 test
spi 3221.3.1 Analyze (ionic and) covalent compounds in terms of(how they form), name, chemical formula, (percent composition and molar mass) week 7. Chemical names and formulas
9.1 Naming ions
9.2 Naming and writing formulas for ionic compounds
9.3 Naming and writing formulas for molecular compounds
9.4 Naming and writing formulas for acids and bases
9.5 The laws governing formulas and names
vocabulary: acid, binary compound, monatomic ion, and polyatomic ion, subscript ch 9 test
spi 3221.3.1 Analyze ionic and covalent compounds in terms of how they form, names, chemical formulas, (percent composition, and molar mass) week 8. Chemical reactions
11.1 Describing chemical reactions
11.2 Types of chemical reactions
11.3 Reactions in aqueous solutions
Lab: Observing Chemical Changes
vocabulary: chemical equation, coefficient, balanced equation, combustion, combination
(composition, synthesis), decomposition, single-replacement, double replacement, soluble
(aqueous), and precipitate
Ch11 test spi 3221
3.2 Identify the reactants, products, and types of different chemical reactions: composition (synthesis, combination), decomposition, double replacement, single replacement, and combustion
3.3 Predict the products of a chemical reaction
3.4 Balance a chemical equation (to determine molar ratios)
UNIT 2A Exam (1/2)
UNIT 2B
week 9. Scientific measurement
3.1 Measurements and their uncertainty
3.2 The international system of units
3.3 Conversion problems
3.4 Density
Lab: Density
vocabulary: measurement, scientific notation, accuracy, precision, accepted value, experimental value, error, percent error, dimensional analysis, conversion factor, density
-Chemical quantities
10.1 The mole
10.2 Mole-mass and mole-volume relationship
10.3 Percent composition and Chemical formulas
Lab: Aspirin
vocabulary: Avogadros number, representative particle, molar mass, molar ratio, STP, molar volume, percent composition, percent yield
Ch3,10 test spi 3221
Inq.4 evaluate the accuracy and precision of data
Math.4 Apply measurement unit relationships including Avogadro’s number, (molarity,
molality), volume, and mass to balance chemical equations
Math.5 Use concepts of mass, length, area, and volume to estimate and solve real-world problems
3.1 Analyze ionic and covalent compounds in terms of how they form, names, chemical formulas, percent composition, and molar mass.
3.5 Convert among the following quantities of a substance: mass, number of moles, number of particles, molar volume at STP
3.6 Identify and solve stoichiometry problems: volume at STP to mass, moles to mass, (and molarity) week 10. Stoichiometry
12.1 The arithmetic of equations
12.2 Chemical calculations
12.3 Limiting reagent and percent yield
Lab: Rice Krispie
vocabulary: actual yield, excess reagent, limiting reagent, mole ratio, stoichiometry, and theoretical yield ch 12 test spi 3221
3.4 balance a chemical equation to determine molar ratios.
3.6 Identify and solve stoichiometry problems: volume at STP to mass, moles to mass,
(and molarity) week 11. Acids, bases, and salts
19.1 Acid-Base theories
19.2 Hydrogen ions and acidity
19.3 Strengths of acids and bases
19.4 Neutralization reaction
19.5 Salts in solutions
Demo: properties of acids, bases, and salts
Lab: Analysis of vinegar
vocabulary acidic solution, basic (alkaline) solution, amphoteric, buffers, monoprotic acid, diprotic acid, triprotic acid, end point, hydronium ion, neutral solution, neutralization reaction, pH, strong acid, strong base, weak acid, weak base, strong electrolyte, weak electrolyte, nonelectrolyte, titration ch 19 test spi 3221 t/e.1 distinguish among tools and procedures best suited to conduct a specified scientific inquiry
Math.2 Perform operations on algebraic expression (logarithms)
3.2 Identify the reactants, products, and types of chemical reactions (double replacement)
3.7 Classify substances as acids or bases based on their formulas and how they react with various indicators
UNIT 2B Exam (3/4)
UNIT 3-Matter and Energy
week 12. Scientific investigation
1.3 Thinking like a scientist
Activity: Scientific Method
Activity: Bubbles
1.4 Problem solving in chemistry
Paper: Discuss the similarities and differences of the purpose and outcome of the
Scientific Method versus the Engineering Design Process
Vocabulary: matter, chemistry, organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, biochemistry, technology, biotechnology, pollutant, biodiesel, agriculture, scientific method, observation, hypothesis, experiment, manipulated variable, responding variable, theory, scientific law, and numeric word problem
week 13. Matter and change
2.1 Properties of matter
2.2 Mixtures
2.3 Elements and Compounds
Activity: Classifying matter
2.4 Chemical reactions
vocabulary: element, diatomic element, compound, mixture, homogeneous mixture, heterogeneous mixture, solution, alloy, colloid, suspension, atom, molecule, pure substance, phase change, physical property, chemical change, chemical property, product, reactant, chemical symbol, shape, volume, mass, definite, indefinite, energy, compress, expand, melting, freezing, boiling (vaporizing), evaporating, condensing, subliming, and deposing
Ch 1.3, 1.4, 2 Test
spi 3221:
Inq1 Select a description or scenario that reevaluates and/or extends a scientific finding
Inq2 Analyze the components of a properly designed scientific investigation
Inq5 Defend a conclusion based on scientific evidence
Inq6 Determine why a conclusion is free of bias
Inq7 Compare conclusions that offer different, but acceptable explanation for the same set of experimental data t/e1 Distinguish among tools and procedures best suited to conduct a specified scientific inquiry t/e.2 Evaluate a protocol to determine the degree to which an engineering design process was successfully applied.
2.1 Distinguish among elements, compounds, solutions, colloids, and suspensions
2.4 Classify a property of change of matter as physical, chemical, (or nuclear)
2.5 Compare and contrast heat and temperature in chemical and physical processes
2.6 Investigate similarities and differences among solids, liquids, and gases in terms of energy and particle spacing week 14. Thermochemistry
17.1 The flow of energy- heat and work
17.2 Measuring and expressing enthalpy changes
17.3 Heat in changes of state
13.4 Changes of state
lab-Specific heat of a metal
vocabulary: heat of fusion, heat of vaporization, phase change, temperature change, thermochemistry, heat, law of conservation of energy, surroundings, system, endothermic, exothermic, joule, calorie, specific heat, calorimeter ch. 13.4,17.1-.3 test
spi 3221.3.10 Relate the laws of conservation of mass/energy to thermal changes that occur during physical, chemical, or nuclear processes week 15. The behavior of gases
14.1 Properties of gases
14.2 The gas laws
14.3 Ideal gases
14.4 Gases: mixtures and movement
Lab: Bicarbonate in antacid
vocabulary: Barometer, Boyle’s law, Charles’s law, combined gas law, Dalton’s law of partial pressure, diffusion, Gay Lussac’s law, ideal gas law, ideal gas law constant, partial pressure ch 14 test spi 3221 math.1 use real numbers to represent real-world applications (eg slope, rate of change, probability and proportionality) math.2 perform operations on algebraic expressions and informally justify the selected procedures
2.7 predict how changes in volume, temperature, and pressure affect the behavior of a gas week 16. Solutions
16.1 Properties of solutions
16.2 concentrations of solutions
16.3 colligative properties
16.4 calculations involving colligative properties
Demo: supersaturated solution
Lab: making ice cream
vocabulary: boiling point elevation, concentrated solution, concentration, colligative property, dilute solution, freezing point depression, immiscible, miscible, molality, molal constants, molarity, dissociation, molecular solvation, saturated solution, unsaturated solution, super saturated solution, solubility, seed crystal, surface area, vapor pressure, agitation, ppm, ppb, percentage m/m or v/v, solute, and solvent ch 16 test
spi 3221.2.2 Identify properties of a solution: solute and solvent in a solid, liquid, or gaseous solution; procedure to make or determine the concentration of a solution in units of ppm, ppb, molarity, molality, percent composition; factors that affect the rate of solution; and colligative properties
2.3 Classify a solution as saturated, unsaturated, or supersaturated based on its composition and temperature and a solubility graph.
UNIT 3 Exam
week 17 - review
*if time permits: The Chemistry of life ch 24