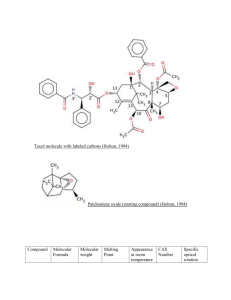
The chemistry of taxol
advertisement

Patchoulene oxide (starting compound) Compoun d Molecular Formula Molecular weight Melting Point Paclitaxel (generic) Or Taxol C47H51NO14 853.906 g/mol 213-216 C Appearance CAS at room Number temperature White 33069-62-4 crystalline powder Specific optical rotation - 49 -55 Bond types: The bond types that are present in the Taxol molecule are all covalent bonds. The carbonyl and ketone groups are nonpolar covalent bonds while the alcohol and the secondary amine are polar covalent bonds. There are three aromatic benzene rings in the molecule however the molecule is non-aromatic. While 45 out of the 47 carbon atoms in the molecule are sp3 hybridized the remaining two are sp2 hybridized. Functional groups: There are many functional groups on this molecule. The groups that are duplicated are noted in the parentheses: Phenyl (3), Amide, Alcohol (3), Carbonyl (2), Ester (3), Epoxide ring and an Alkene. Chiral centers: There are eleven chiral centers in the Taxol molecule. In the structure pictured the chiral centers are numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 13, 2' and 3'. Nine of the eleven chirality centers can be found in what can be called the ABCD ring framework. The A is the hexene ring; the B is the eight carbon ring that together with A comprise an unfused bicyclo ring; C is a six carbon ring that is fused with B and D is referring to the epoxide. Synthesis: The synthesis for Taxol is very long and complicated. The Holton Taxol total synthesis will be the particular synthesis that is elaborated. The Holton synthesis was the first complete synthesis of Taxol that was published in 1994, by Robert A. Holton and colleagues at Florida State University. The reaction is in fact so complex that there is a long list of the groups that were required as they were protecting groups. Benzyloxymethyl, Carbonate, cyclic carbonate, 2-methoxy-2-propyl, tert-butyldimethylsilyl, triethylsilyl, and trimethylsilyl to name a few. The Holton team began with a patchoulol. One reason Holton and his team chose to start the synthesis with patchoulene oxide is the structure of the compound already contains three quarters of the carbons that are needed to comprise the ABCD ring framework. Two important reactions in the total synthesis are enolate oxidation by sulfonyl oxaziridines and a Chan rearrangement. The enolate oxidation happens in the tenth step in the synthesis when a ketone in the number nine position becomes an enolate by oxidation with (+)-camphorsulfonyl oxaziridine. This gives a -hydroxyketone. The importance of this step of the reaction lies in ABCD framework. This sets the stage for the formation of the C ring. The first step in the formation of the C ring is the Chan rearrangement. This is the rearrangement of a carbonate ester in the presence of a strong base (lithium tetramethylpiperidide) to make a -hydroxy ester. There are many more steps in the reaction but few are more important than those that form the ring framework. The mechanism is enantioselective in that synthesizing Taxol from (-)-patchoulene oxide will give the (+)-Taxol enantiomer. The other enantiomer ((-)-Taxol enantiomer) can be obtained by synthesizing Taxol from (-)-borneol. The synthesis is complete, however, initially, Dr. Holton himself claimed that the process was not commercially viable. A big reason for this is that the reaction is an example of linear synthesis, where each subsequent step in the reaction significantly reduces the yield until the final product is exponentially less that all the required reactants. After a series of months the Holton team managed to refine the process, of each step, so that the average chemical yield reached 93 %. Attached is a copy of a summary for the retrosynthesis of Taxol from patchoulene oxide.