drug
advertisement

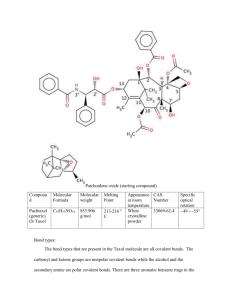
DRUG A substance used in the diagnosis, treatment, or prevention of a disease or as a component of a medication recognized or defined by the U.S. Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. A drug is any chemical or biological substance, synthetic or non-synthetic The New Drug Development Process (Steps from Test Tube to New Drug Application Review) Four categories of drugs used for the treatment of cancers during the past 50 years. Cytotoxic natural products played a major role in conventional chemotherapy until the late 1990s with the advent of molecular targeted therapies using monoclonal antibodies and small molecule kinase inhibitors Natural products in 2007 make a comeback in oncology Drugs recently approved by FDA for the treatment of cancers by category of origin Plant-derived anticancer agents Vinca Alkaloids The first agents to advance into clinical use were the so-called vinca alkaloids are vinblastine and vincristine These Alkaloids were isolated from the Madagascar periwinkle, Catharanthus roseus G. Don. belong to Apocynaceae family. Traditionally the plant was used for the treatment of diabetes. These drugs were first discovered during an investigation of the plant as a source of potential oral hypoglycemic agents. But, while research investigators could not confirm this activity, it was noted that extracts reduced white blood cell counts and caused bone marrow depression in rats, and subsequently it was found that the treatment of mice bearing a transplantable lymphocytic leukemia caused significant life extension. Cont’d Based on the ‘lead compound’ vincristin and vinblastin, researchers synthesized their semi-synthetic analogues, vinorelbine and vindesine These agents are primarily used in combination with other cancer chemotherapeutic drugs for the treatment of a variety of cancers. vinblastine used for the treatment of leukemias, lymphomas, advanced testicular cancer, breast and lung cancers, and Kaposi’s sarcoma, and vincristine, in addition to the treatment of lymphomas, also shows efficacy against leukemias, particularly acute lymphocytic leukemia in childhood. Vinorelbine has shown activity against non-small-cell lung cancer and advanced breast cancer. Cont’d The semi-synthetic vinca alkaloid vinorelbine, synthesized from the leaves of Catharanthus roseus, was first approved in 1989 in Europe for the i.v. treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. In 2001, the drug was approved as soft gelatin capsules for oral treatments of NSCLC Structures Taxol Taxol is known by the generic name Paclitaxel This compound is a complex polyoxygenated diterpenoid isolated from the pacific yew, Taxus brevifolia It was discovered during extensive screening of different plant materials for antineoplastic agents in the late 1960s by a systematic research approach Stages in development paclitaxel as anticancer drug 1962-68 NCI screening of cytotoxic agents from natural products 1967 Antitumor activity detected 1969 Pure paclitaxel isolated 1971 Structure elucidated 1983 Phase I studies initiated 1986 Hypersensitive reaction observed 1988 NCI suggests premedication regimen 1989 Proved effective against ovarian cancer 1991 Proved effective against non-small cell lung cancer 1992 Approved by US FDA for ovarian cancer 1992 Approved by US FDA for breast cancer Total synthesis by Nicolaou and Holton, Independently 1994 Approved in India for ovarian cancer 1995 Approved in India for breast cancer Paclitaxel (Taxol) and Docetaxel (Taxotere) O R2O R1 NH O O Ph O OH HO Taxol OH R1= C6H5; R2= Ac Toxotere R1= O R2= H H AcO BzO O Brief Description of Structure and activity relationship of Taxol Structure and activity relationship (SAR) of Taxol The removal of C-1-hydroxyl reduces the activity The C-2-benzoyloxy is essential for activity. However, some substituted benzoyloxy groups are also acceptable. Removal of the 4-acetyl group reduces the activity. The 4,5,20-oxetane ring is essential for activity The derivatization of the C-7-hydroxyl or change of its stereochemistry has no significant effect on anticancer activity of the molecule. Reduction of 9-ketone slightly increases the activity The 10-acetate has better activity in the case of taxol but in some analogues 10-hydroxyls have better activity Development of Taxol Taxol has poor bioavailability due to its poor solubility in water The widely used technique to solubilize taxol is in a vehicle cremophore EL (polyethoxylated castor oil/ethanol) Nanoparticle taxol in the form of a drug-eluting stent is likely to gain FDA approval Conversion of isotaxel to taxol under physiological conditions Isotaxel is nearly 1800-fold more soluble than taxol Isotaxel itself is an inactive molecule, but, at physiological pH, O–N intramolecular acyl migration takes place and within 12 min it converts into taxol, the active molecule Problems The availability of paclitaxel was a problem due to its poor abundance in the plant. Several research groups now have devised the total synthesis of taxol, but being a complex molecule it is not economic T. brevifolia is a slow-growing plant At age 100 years old, 6-9 m high and have trunk diameter about 25 cm, provide 1 g taxol Demand 100-200 kg per annum (2001) Taxol in Taxus sumatrana (Cemara Sumatra) new source of taxol In screening of plants for source of taxol production, Lince Yarni, 2007 have isolated taxol from Taxus sumatrana (bhs. Cemara Sumatra) Camptothecin In the early sixties, the discovery of camptothecin as an anticancer drug. This naturally occurring alkaloid was first extracted from the stem wood of the Chinese ornamental tree Camptotheca acuminata during the screening of thousands of plants in a search for steroids . Camptothecin Presently, the first generation analogues of Camptotechin, hycamtin (Topotecan) and camptosar (Irinotecan), marketed by Glaxo-SmithKline and Pfizer, respectively, are used for the treatment of ovarian and colon cancers Camptotechin has also been isolated from Ophiorrhiza pumila and Mapia foetida . CPT and its analog Camptotechin is a member of the quinolinoalkaloid group. It consists of a pentacyclic ring structure that includes a pyrrole) quinoline moiety and one asymmetric centre within the a-hydroxy lactone ring with 20(S) configuration Structure and activity relationship O of CPT B A C N The planar pentacyclic ring structure (rings A–E) was suggested to be one of the most important structural features. Earlier, it was reported that the complete pentacyclic ring system is essential for its activity, but recently reported results show that the E-ring lactone is not essential for its activity. However, this ring in the present lactone form with specific C-20 configuration is required for better activity N D E O OH O Camptothecin analogues on A and B ring modifications R3 R4 R2 O A R1 B N C N D E O OH O Future prospects of CPT CPT and its analogues exhibit a broad spectrum of antitumour activity and represent a very promising class of agents The discovery of topoisomerases as new targets for cancer chemotherapy and the mechanism of action of camptothecin put camptothecin back on the frontlines of anticancer drug development Two of the successful drugs, topotecan and irinotecan, have achieved nearly $750 million in annual sales Combestratin A-4 Combretastatins are mitotic agents isolated from the bark of the South African tree Combretum caffrum Combretastatin A-4 is a simple stilbene that has been shown to compete with colchicines for binding sites on tubulin It has been found to be a potent cytotoxic agent which strongly inhibits the polymerization of brain tubulin by binding to the colchicine site CA-4 shows potent cytotoxicity against a wide variety of human cancer cell lines CA-4 is thus an attractive ‘lead molecule’ for the development of anticancer drugs Chemical Structure H3CO OH H3CO OCH3 OCH3 SAR of Combestatin H CO 3 A H3CO OH B OCH3 OCH3 •For a minimal cytotoxic activity, a diaryl system should be separated through a double bond along with a trimethoxy system in one of the rings •Trimethoxy benzene moiety is essential for its activity •The two aryl groups should be separated through a double bond and the cis (Z) isomer is preferred over the trans (E) as cis is much more active than trans Synthetic Analog of Combestatin Future prospects A large number of combretastatins has been synthesized and evaluated, but the main problem associated with this class of compounds is their poor water solubility Therefore, the main emphasis on combretastatins research has been diverted towards watersoluble prodrug One of the prodrugs, that is CA-4 phosphate, is currently in phase II clinical trial in the UK and the USA Podophyllotoxin Podophyllotoxin and deoxypodophyllotoxin are two well-known naturally occurring aryltetralin lignans Podophyllotoxin, a bioactive lignan, was first isolated in 1880 from the North American plant Podophyllum peltatum L Podophyllotoxin was also isolated from several other species like P. emodi Wall (Indian) and P. pleianthum (Taiwan) Other than these, 4-deoxypodophyllotoxin has also been isolated from Anthriscus sylvestris and Pulsatilla koreana It is a potent cytotoxic agent, two of the semisynthetic derivatives of PDT, etoposide and teniposide, are currently used in frontline cancer chemotherapy against various cancers SAR of PDT • Only the A and E rings are essential for its activity • D-ring in lactone form is preferred for better activity. • Modifications at the C-4 position in ring C are mostly acceptable and bulky groups at this position enhance both anticancer and topoisomerase activities OH O O O O H3CO OCH3 OCH3 Podophyllotoxin and analogues Cytotoxicity and DNA topo II inhibition by ananlogous of podophyllotoxin Problems in Cancer therapy Over the years, a number of approaches have been developed for clinical use and a number of anticancer drugs have come out of these as a result. The main problem with these agents is the toxicity associated with them due to their lack of specificity, as these agents also kill healthy cells Other than this, drug resistance is another problem which arises after some time Nowadays, combination therapy is used to combat this problem Dietary chemopreventive compounds in active clinical trials Chemoprotective products found in plant extracts causing molecular changes Chemoprotective products found in plant extracts causing molecular changes ..Cont’d Herbs and spices can modify microorganism which can stimulate growth within organisms that protect against cancer as well as within microrganisms that may serve to increase cancer risk. Culinary herbs and spices generally serve as antioxidants. Inflammation, tumorigenesis, and carcinogen bioactivation influence cancer risk and tumor behavior, but interventions which inhibit these processes can contribute to cancer prevention. Anticancer activity in vitro and Carcinogenesis inhibition effect of Red Fruit extract (Pandanus conoideus Lam) on 7,12-deimethylbenz(a) anthracene (DMBA)-induced rat cancer Mun’im et al. 2006, and 2007 Pandanus Red fruit is a kind of traditional pieces from Papua. By society Wamena, Papua, this fruit is used for seasoning Pandanus conoideus Lam scientific name For Red fruit including plant Families Pandananaceae with pandan-like pandanus trees, but plant height can reach 16 meters with its own branch-free stem height as high as 5-8 m, which strengthened the aerial roots of on the lower trunk Nutritional composition It was the intention of the Red Fruit juices contain lots of antioxidants : • Carotene (12,000 ppm) • Beta-carotene (700 ppm) • Tocopherol (11,000 ppm) In addition to several other substances that increase endurance, among others: oleic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid, dekanoat, Omega 3 and Omega 9 which are all active compounds antidote to the formation of free radicals in the body Results Red fruit extractshows anticancer activity in vitro to HeLa cell. That results suggested that the extract has strong anticancer activity ( LC50 = 23.38 μg/ml ) to Leukimia L 1210 cell and low anticancer activity to HeLa cell ( LC50 = 240 μg/ml ) Observed Tumor Incidence on Organ after incision Histology of lungs tissue with normal alveolus cell, thickness in alveolus cell, cancer cell proliferation, and cancer Conclusions Red fruit extract demonstrated strong anticancer activity in vitro to Leukemia L 1210 cell, but showed weak activity to HeLa cell Based on lung histology examination shows that the extract statistically does not cause significance effect, but at dose 0,21 ml/200g bw can inhibit lungs cancer carcinogenesis DMBA -induced rats Antitumor Effects of Pandanus conoideus in in vitro and in vivo Studies Toshiaki NISHIGAKI1,2, Kunitaka HIROSE3 and Hidekazu SHIGEMATSU1,2 1 Department of Histopathology, School of Medicine, Shinshu University (3-3-1 Asahi, Matsumoto, Nagano 390-8621 Japan) 2 Research Association of Tropical Medicinal Plants (1286-18 Yamato, Azusagawa, Matsumoto, Nagano 390-1701 Japan) 3 Effector Cell Institute (4-7-7 Aobadai, Meguro, Tokyo 153-0042 Japan) Pandanus conoideus (Buah Merah) is exclusively grown in Papua island and its neighbor areas and the inhabitants have been utilizing its extract oil (SBM) as functional food for tens thousands years. The extract found relatively higher quantity of carotenoids which consists of a- and b-carotene as well as a- and b-cryptoxanthin in SBM. bcryptoxanthin is a novel micronutrient to associate with reduced risk of some types of cancers. The researcher evaluated antitumor potentials of SBM in the in vitro and in vivo studies. In the in vitro study, human non-small lung cancer cells, A549 were inhibited on cell proliferation at more than 500 μg/mL of SBM in MTT assay. The in vivo antitumor activity of SBM was evaluated using mouse Sarcoma180, mouse Lewis lung cancer and A549 models. In any animal model assays, SBM demonstrated significant antitumor effects in either tumor volumes or tumor weights. From the experiment using nude mice in A549 assay, antitumor effect of SBM may not be associated with immunological involvement. Buah Merah has higher potentials in prevention of cancers, especially lung cancer Other research Inhibition carcinogenesis combination of Neem (Azadirachta indica) leaves and Curcuma zedoaria Rhizoma extracts on 7,12-DMBA-induced rat cancer(Mun’im et al, 2009) Inhibition carcinogenesis of Brucea javanica leaves extracts on 7,12-DMBA-induced rat cancer (Marisa et al, 2010) Natural products potentiates anticancer activity of conventional anticancer Lev-Ari et al. 2005. Curcumin synergistically potentiates the growth inhibitory and pro-apoptotic effects of celecoxib in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother 59(2): S276-S280. Zhao et al. 2010. Wogonin potentiates the antitumor effects of low dose 5fluorouracil against gastric cancer through induction of apoptosis by downregulation of NF-kappaB and regulation of its metabolism. Toxicol Lett, 197(3): 201-21 Carnesecchi et al. 2004. Geraniol, a component of plant essential oils, modulates DNA synthesis and potentiates 5-fluorouracil efficacy on human colon tumor xenografts. Cancer Lett, 215(1): 53-59. Combination chemoprevention by tomato and garlic in the hamster buccal pouch carcinogenesis model We evaluated the combined chemopreventive effect of tomato paste and aqueous garlic extract against DMBA-induced hamster buccal pouch (HBP) carcinogenesis. Hamsters were divided into 8 groups. Animals in group 1 served as control. Groups 2 through 4 were given tomato, garlic and mixture of tomato and garlic respectively. The right BP of animals in group 5 were painted with 0.5% DMBA three times a week. ipid peroxidation, GSH, GPx, GST, GR and GGT as well as GSH/GSSG ratio were measured in the buccal pouch, liver and erythrocytes at the end of 14 weeks. Diminished lipid peroxidation in the HBP tumours was associated with enhanced levels of GSH and GSH-dependent enzymes. In contrast to the buccal pouch, the liver and erythrocytes of tumour-bearing hamsters exhibited elevated lipid peroxidation accompanied by compromised antioxidant status. Although administration of tomato paste and garlic alone significantly reduced the tumour incidence and tumour burden, combined administration of tomato and garlic was more effective in inhibiting the development of HBP carcinomas as revealed by modulation of the cellular redox status. From these results, we suggest that broader spectrum of chemoprevention with less adverse effects can be attained through effective combination of functional foods Chemoprevention of oral cancer in animal models, and effect on leukoplakias in human patients with ZengShengPing, a mixture of medicinal herbs ZSP, a mixture of six medicinal herbs, has been reported to prevent esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in human patients with dysplasia. This study was designed to investigate the chemopreventive effects of ZSP on oral cancer in animal models and human patients. In DMBA-induced hamster cheek pouch model, ZSP (6 g/kg BW/day by gavage for 10 weeks) significantly reduced the number of visible tumor, the tumor volume, and the incidence of SCC. Two biomarkers associated with cell proliferation, silver stained nucleolar organizer region (AgNOR) and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)-labeling index, were also significantly suppressed by ZSP treatment (P < 0.01). In the 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide-induced oro-esophageal cancer model in mice, ZSP (10% in diet) also significantly reduced the incidence of tongue SCC from 55.2% to 22.2%, and slightly reduced the incidence of esophageal SCC from 34.5% to 22.2% . Furthermore, in a RCT on patients with oral leukoplakia, ZSP (4 x 3 /day for 8–12 months) reduced the size of oral lesion in 67.8% patients, whereas the placebo was effective in 17% patients . Such an effect was associated with significant decrease of AgNOR and PCNAlabeling index. In summary, our studies have demonstrated the chemopreventive effects of ZSP on two animal models of oral cancer, and human patients with oral A systematic review of the effectiveness of Chinese herbal medication in symptom management and improvement of quality of life in adult cancer patients Molassiotis et al. 2009. Comp Ther Med The aim of this systematic review was to assess the effectiveness of Chinese medicinal herbs used concurrently with cancer treatments in terms primarily of toxicity management but also quality of life and survival in adult cancer patients. Forty-nine trials met the inclusion criteria and were reviewed according to standard processes of systematic reviews. These trials included 3992 patients. All studies with the exception of one were of low methodological quality. The vast majority of the studies have shown that Chinese medicinal herbs improved treatment side effects, quality of life, and performance status, and some have provided evidence of tumour regression and increased survival. While no clinical recommendations can derive from such low quality studies, the number of studies reporting positive results is high enough to suggest that Chinese medicinal herbs may have a role in cancer care. However, more methodologically rigorous studies need to be developed as a priority before any firm conclusions can be drawn. Formularium Herbal Indonesia 2011 To promote the use herbal medicinal product in health care center, Ministry of Health publish some regulations, among them are: - Saintifikasi Jamu (Permenkes 003/2010) - Formularium Herbal Indonesia 2011 This formulary is guidance of the use of herbal therapy for physician in Formal Health Care Center Pilot project 2012: 200 Hospitals and Community Health Centers (Puskesmas ) in Indonesia Herbal for Cancer in FHI 2011 Current status Vinca rosea L/ Cataranthus roseus G. Don data requested 2. Annona muricata L data requested 3. Andrographis paniculata (Burm) F. Nees OK 4. Garcinia mangostana L data requested 5. Typhonium flagiforme Lodd data requested 6. Kaemferae rotunda L OK 1. Herbal Potency in Cancer Therapy 1. Antineoplastic Provide anticancer and lead compound 2. Adjuvant/ complement Synergistic effect with conventional anticancer 3. Reduce side effect from chemotherapy or Radiotherapy 4. Reduce cancer symptoms (Palliative) 5. Cancer prevention References Bailly C. 2009. Ready for a comeback of natural products in oncology. Biochem Pharmacol,77: 1447–1457 Fouche et al. 2008. In vitro anticancer screening of South African plants. J Ethnopharmacol, 119: 455–461. Goswami SK, and Das DK, 2009. Resveratrol and chemoprevention . Cancer Lett, 284: 1–6. Hail Jr et al. 2008. Cancer chemoprevention: A radical perspective. Free Rad Biol Med, 45: 97–110. Kaefer CM and Milner JA. 2005. The role of herbs and spices in cancer prevention. Bioorg Med Chem, 13 : 5892– 5908 Li et al. 2011. Implications of cancer stem cell theory for cancer chemoprevention by natural dietary compounds . J Nutrit Biochem, 22: 799–806 Mun'im A, et al. 2006. Uji hambatan tumorigenesis sari buah merah (Pandanus conoideus Lam.) merek M terhadap tukis putih betina yang diinduksi dengan 7,12-dimetilbenz(a)antrasen (DMBA). Majalah Ilmu Kefarmasian, 3(3) Mun'im et al. 2007. Uji Hambatan Karsinogenesis sari buah merah (Pandanus conoideus Lam) dari perdagangan terhadap tikus putih betina yang diinduksi DMBA. Acta Pharmaceutica Indonesia , I, 28-33 Neergheen et al. 2010. Targeting specific cell signaling transduction pathways by dietary and medicinal phytochemicals in cancer chemoprevention. Toxicol, 278 : 229–241 Reddy et al. 2003. Natural products for cancer prevention: a global perspective. Pharmacol Therapeut, 99: 1– 13 Rocha et al. 2001. Natural products in anticancer therapy. Current Opin Pharmacol, 1:364–369. Russo GL. 2007. Ins and outs of dietary phytochemicals in cancer chemoprevention. Biochem Pharmacol, 74: 533–544. Srivastava et al. 2005. Plant-based anticancer molecules: A chemical and biological profile of some important leads. Bioorg Med Chem, 13: 5892–5908