Sci Template5.4.E
advertisement
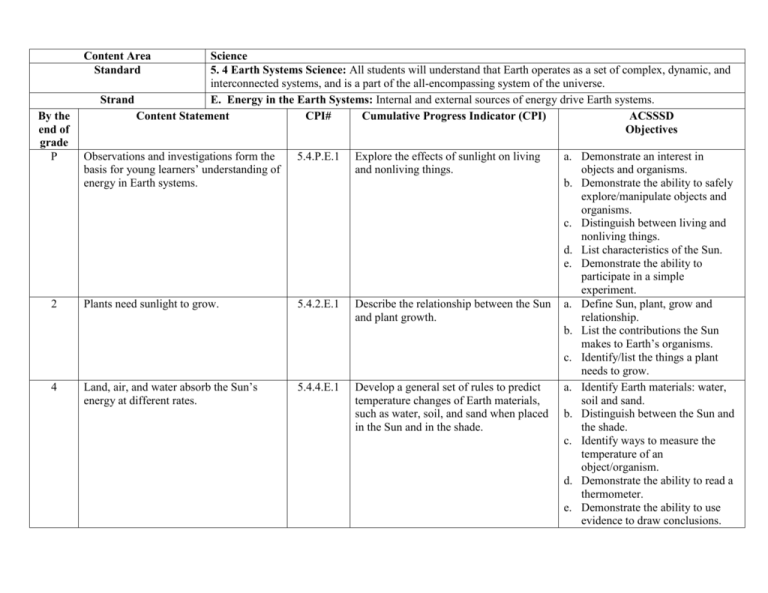
Content Area Standard By the end of grade P Science 5. 4 Earth Systems Science: All students will understand that Earth operates as a set of complex, dynamic, and interconnected systems, and is a part of the all-encompassing system of the universe. E. Energy in the Earth Systems: Internal and external sources of energy drive Earth systems. Strand Content Statement CPI# Cumulative Progress Indicator (CPI) ACSSSD Objectives Observations and investigations form the basis for young learners’ understanding of energy in Earth systems. 5.4.P.E.1 Explore the effects of sunlight on living and nonliving things. 2 Plants need sunlight to grow. 5.4.2.E.1 Describe the relationship between the Sun and plant growth. 4 Land, air, and water absorb the Sun’s energy at different rates. 5.4.4.E.1 Develop a general set of rules to predict temperature changes of Earth materials, such as water, soil, and sand when placed in the Sun and in the shade. a. Demonstrate an interest in objects and organisms. b. Demonstrate the ability to safely explore/manipulate objects and organisms. c. Distinguish between living and nonliving things. d. List characteristics of the Sun. e. Demonstrate the ability to participate in a simple experiment. a. Define Sun, plant, grow and relationship. b. List the contributions the Sun makes to Earth’s organisms. c. Identify/list the things a plant needs to grow. a. Identify Earth materials: water, soil and sand. b. Distinguish between the Sun and the shade. c. Identify ways to measure the temperature of an object/organism. d. Demonstrate the ability to read a thermometer. e. Demonstrate the ability to use evidence to draw conclusions. 6 The Sun is the major source of energy for circulating the atmosphere and oceans. 5.4.6.E.1 Generate a conclusion about energy transfer and circulation by observing a model of convection currents. 8 The Sun provides energy for plants to grow and drives convection within the atmosphere and oceans, producing winds, ocean currents, and the water cycle. 5.4.8.E.1 Explain how energy from the Sun is transformed or transferred in global wind circulation, ocean circulation, and the water cycle. 12 The Sun is the major external source of energy for Earth’s global energy budget. 5.4.12.E.1 Model and explain the physical science principles that account for the global energy budget. a. Identify the Sun, atmosphere and ocean. b. List characteristics of the Sun, atmosphere and ocean. c. Demonstrate the ability to collect data/evidence during an observation. d. Demonstrate the ability to draw conclusions from data/evidence. e. Explain energy transfer and circulation. f. Explain how a convection current works. a. Identify the Sun, wind, ocean, atmosphere, water and plant. b. List characteristics of the Sun, wind, ocean, atmosphere, water and plants. c. Explain how the Sun produces/provides energy. d. Explain the process of global wind circulation. e. Explain how ocean waters circulate. f. Explain the water cycle. a. Explain how the Sun produces/provides energy to the Earth. b. Demonstrate an understanding of how a budget works/is balanced. c. Demonstrate the ability to construct a simple model. d. List the physical science principles related to Earth’s energy budget. e. Identify sources of incoming energy to the Earth. f. Identify ways energy is lost from the Earth. g. Explain why the energy flow into and out of Earth’s entire ecosystem should stay in balance.