Social Studies U.S. Regional Characteristics Northeast: almost
advertisement

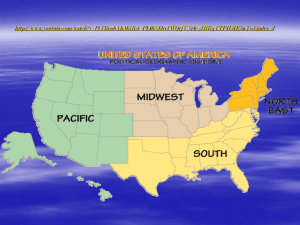
Social Studies U.S. Regional Characteristics Northeast: almost entirely humid continental climate (snowy, cold winters and warm, humid summers) economy is heavily dependent on banks, investment firms, and insurance companies education contributes to the economy – home to respected universities like Harvard, Yale, and Princeton. home to Pittsburgh – important for the steel industry cool shallow waters off the North Atlantic contribute to the fish and lobster industry most densely (tightly packed) populated region Includes much of the BosWash megalopolis home to the earliest British colonies residents are sometimes called Yanks includes sheltered ports and harbors for shipping has poor farmland (rocky soil) short growing season makes farming difficult home to one sixth of the country’s population home to the “Big Apple” and “City of Brotherly Love.” mostly mixed forest South: includes the state with 6 of the 30 most populous cities in the U.S. large areas of wide coastal plains has good conditions for growing cotton, tobacco and citrus fruits includes the city of Atlanta, which has grown to be a transportation hub in the region population growth due to climate, business opportunities, recreation, and retirement has a trade and travel connection to Mexico, Central, and South America oil refineries and petrochemical plants contribute to the economy includes much of the Appalachian Mountains includes the nation’s capital includes much of the “sunbelt” includes the areas experiencing more hurricanes than any other has larger areas of wetlands than any other region the country’s fastest growing (population) region seceded from the nation, causing the civil war longest growing season highest annual precipitation includes the Mississippi River Delta borders the Gulf of Mexico has a large population of African Americans mostly mild humid subtropical climate Midwest: home to one of the most productive farming regions in the world farm products include corn, wheat, soybeans, and dairy waterways leading from the Atlantic (i.e. Saint Lawrence Seaway) contributed to the region’s development includes the “motor city” – Detroit Missouri River Great Plains has a continental climate in the east and is dry in the west home to the largest group of freshwater lakes in the world home to the Central Lowlands includes the “windy city” – Chicago, one of the busiest shipping ports and 3rd largest in the U.S. home to the city considered as the “gateway to the West” – St. Louis home to much of “Tornado Alley” has large deposits of coal called the heartland or breadbasket of the U.S. West: largest region has the most diverse land of any region (many different types of land) is home to 8 different climates zones has land that is used for ranching and herding more than any other region immigration has created significant Asian and Hispanic populations is sparsely populated in the eastern part of the region includes the Great Basin most mineral (gold, silver, copper, etc.) resources last part of the U.S. to be populated by people of European decent has the most significant population of Native Americans home to the most populous state in the U.S. major industries include computer software and entertainment lack of water resources have required irrigation project like dams and canals Sierra Nevada and Cascades Mtns. includes the “mile high” city - Denver only region to share borders with two other countries fishing and forestry are important economic activities in the Northern Pacific part of this region Rocky Mountains borders Pacific Ocean Mount McKinley – highest Mtn. in N. America (20, 320 ft.) Social Studies Canada Regional Characteristics East All on or near the sea (maritime) Immigration from the British Isles Forestry and fishing are important industries Limited farming (short growing season) Most people live in coastal cities Heartland Most populous region (1/2 of the country total) Most urbanized region (cities) Industrial and business center French believe their province should be given special status Regionalism can be a problem West Grasslands (prairie) include a rich wheat growing area Rockies attract visitors to parks Rich in minerals, oil and natural gas Significant trade with Asian countries North Near the Arctic Circle (frigid) Includes land created for native Inuit people Forest and tundra Limited winter sunlight Many isolated towns and villages