NAKURU DISTRICT SEC. SCHOOLS KCSE TRIAL
advertisement

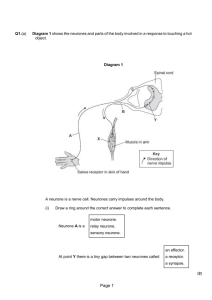
NAKURU DISTRICT SEC. SCHOOLS K.C.S.E TRIAL EXAMINATIONS2015 Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E) MARKING SCHEME BIOLOGY PAPER 2 (1 mark) 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 2(a) (b) Emulsification ; Bile juice; (i) sodium taurocholate ; (ii) sodium glycocholate ; Bile is produced in the liver ; Surface area of digestion would be reduced hence the rate of digestion ; - Absorption process would be reduced ; (2 x 1) (1 mark) (1mark) (1 mark) (1 mark) (2 marks) Sickle cell anaemia ; (i) Advantage – individual having this condition rarely suffer from malaria (ii) disadvantage – suffocation due to insufficient supply of oxygen to the (respiring) body tissues ; Parental phenotypes Person A Person B Parental Genotype HbA HbA X HbS HbS ; Gametes HbA HbA HbS HbS; fusion F 1 Generation HbAHbS HbAHbS Phenotypes; All have sickle cell traits, Genotypes; All are HbAHbS; 3(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) HbAHbS HbAHbS Pathway followed by a nerve impulse that gives rise to a reflex action 1- motor neurone 2 – relay neurone/intermediate neurone The arrows point towards neurone 1 from 2 and 3 Grey matter Impulse reaching the dendrite end of relay neurone causes the synaptic vesicles to release a acetylcholine/transmitter substance; into the synaptic cleft, the acetylcholine/transmitter chemical diffuses across the cleft; and causes the depolarization of the neurone 4(a) (2 marks) (1 mark) (1 mark) (3 marks) (4 marks) Guinea fowls Vultures Termites Grasshoppers Leopard Grass (1 mark) Gazelles 1 : Award a mark for every trophic level (b) (c) (d) 5(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Grass Grass Grass Vultures Grasshoppers Termites Guinea fowls; Guineas Fowls; A- Photosynthesis ; B – Respiration Provision of food to plants organisms when convert light energy into chemical energy to make their own food which is later consumed by animals ; A – chloroplast ; B – Mitochondrion ; Glycolysis ; Kreb’s cycle; This is the point when the rate of photosynthesis is equal to the rate respiration ; 6(a)(i) 3.00 p.m or 1500 – pH (ii) 3.00 p.m of 1500 – dissolved oxygen (b)(i) pH increased between 06.00 to 09.00; because of increased rate of photosynthesis ; in aquatic plants, which consumed more carbon(IV) oxide gas dissolved in water; (ii) pH decreased between 2100 to 2400; of carbon (IV) oxide which was being produced; by the respiring; water plants, but was not being used for photosynthesis; (c) Increasing light intensity increases the rate of photolysis/photosynthesis hence increased production of oxygen gas while decreasing light intensity decreases the rate of photolysis; hence reduce production of oxygen gas; Acc. Photosynthesis instead of photolysis (d) Have dissected/branched leaves which provide a large surface area of light absorption and gaseous exchange; Leaves have chlorophyll which is very sensitive to light; (e) Some nitrate fertilizer would get into the river water; thus causing rapid growth of many water plants; Many water plants, photosynthesize food under high light intensity using a lot of carbon (IV) oxide gas thus raising pH value; and produce a lot of Oxygen, increasing the concentration of oxygen; The very many water plants also respire rapidly under low light intensity thus producing large volume of carbon (IV) oxide gas which greatly lowers the pH of water ; 7 (a) 15 marks Roots extensively developed/roots superficial; to provide large surface area for water absorption; Rej. Fibrous roots Roots grow deep/long roots; to reach water table/source deep in the ground; Acc. Fleshy stem/tissues/leaves Succulent/possession of water storage tissues; to store water/to survive drought Possession of waxy/thick cuticle; to reduce transpiration; Hairy leaves; sunken stomata; reduce leaf size/spines/scales/thorns/leaves modified to needle like/reduced number of stomata; Xerophytes 2 Rolled leaves/folding leaves’ shedding leaves; reversed stomatal rhythm; Short life cycle/quick growth after rains; to make use of the available water quickly; Rej. Flowering alone Rej. Long/short roots alone (b) 8 Hydrophytes 20 marks Aerenchyma tissue/air spaces intercellular spaces;/long fibrous roots; for buoyancy/to float on water; Poorly developed support tissues/sclerechyma; Upper epidermis leaves have more stomata than lower Epidermis; for gaseous exchange/increased rate of transpiration; poorly developed conducting tissues/xylem and phloem; plants obtain water by diffusion; Acc. Stomata on upper surface only Total 8 Max 7 The process of mitosis occurs in cells its important in cell multiplication; for growth; and asexual reproduction; in some species Its occurs in one nuclear division/divisional process; It is divided into five phases; A diplopid mother/parent cell; enters into interphase; during interphase the cell exhibits a very high rate of respiration; to produce large amounts of energy; for the process; genetic material replicates; to maintain chromosomal number in daughter cells. New organelles are synthesized (for the cells); The cell then enters prophase; during this phase centrioles migrate; to opposite poles; and form spindle fibres; the nuclear membrane dissolves/break down; to free the chromosomes into the cytoplasm; the chromosomes shorten and thicken; to prevent brewage during separation; Each chromosome is seen to have chromatids/sister chromatids; The cell enters metaphase; during metaphase chromosomes are free in the cytoplasm; and the spindles attach to the centromeres(of chromosome); Chromosomes align themselves at the equator of the spindle/cell; The cell then enters anaphase; during anaphase spindles shorten/contract; sister chromatides separate; at the centromere; and migrate to oppose poles; The spindles then disappear; the cell membrane begins to constrict; in animals; while in plants; a wall plate/cell wall is deposited; The cell then enterstelophase; During telophase chromatids reach opposite poles; and a nuclear membrane forms around each set; They cytoplasm divides into two; to form two; diploid; daughter cells; The Chromosomes become less distinct; 𝟑𝟔 𝒙 𝟏 Total marks = = 18 maximum marks 𝟐 NB: Marking stops at a point where a student does not follow the sequence 3