Synaptic transmission
advertisement

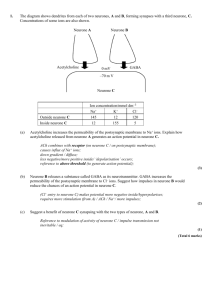
Volume 28, Number 2, November 2015 Activity Synaptic transmission Martin Rowland The following questions relate to the article by Dr Helena Bailes on pages 2–5 of the November 2015 issue of BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES REVIEW. You can either read the article and then attempt these questions, or attempt the questions as you read the article. In addition to information in the article, you will need to use your knowledge and understanding of neurones, nerve impulses and synapses. Before you attempt each question, identify which of the assessment objectives (AOs) the question is testing. This will help you to determine what skills you must demonstrate in your answers. The command word of each question (e.g. ‘Give’, ‘Explain’ or ‘Evaluate’) will give you a clue about which AO is being tested. The wording of the assessment objectives below applies to all GCE examination boards setting examinations in colleges and schools in England. AO1: Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of scientific ideas, processes, techniques and procedures AO2: Apply knowledge and understanding of scientific ideas, processes, techniques and procedures: o in a theoretical context o in a practical context o when handling qualitative data o when handling quantitative data AO3: Analyse, interpret and evaluate scientific information, ideas and evidence, including in relation to issues, to: o make judgements and reach conclusions o develop and refine practical design and procedures. Finally, use the space provided for each of your answers as an indication of how much you are expected to write. Philip Allan Publishers © 2015 www.hoddereducation.co.uk/biologicalsciencesreview Questions 1 Give the three major components of a single neurone. (1 mark) 1 ................................................. 2 ................................................. 3 ................................................. 2 Describe three differences between the structure of a motor neurone shown in Figure 1 of the article and that of a sensory neurone. (3 marks) Difference 1 ....................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................ Difference 2 ........................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................ Difference 3 ........................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................ 3 (a) Describe the structure of the myelin sheath shown in Figure 1 of the article. (3 marks) ....................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................... (b) Explain the function of a myelin sheath around an axon. (2 marks) ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ 4 A motor neurone with a length of 58 cm passes an impulse at a rate of 80 m s−1. Calculate how long it takes this impulse to travel the length of the neurone. Show your working. (2 marks) Answer.............................. Philip Allan Publishers © 2015 www.hoddereducation.co.uk/biologicalsciencesreview 5 Explain what is meant by the ‘all or none’ property of an action potential. (2 marks) ................................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................... 6 The gap between adjacent cells in an electrical synapse is 5 nanometres. Express this distance in metres, using standard form. (1 mark) .............................. 7 Contrast the structures of an electrical synapse and a chemical synapse. (2 marks) .............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... 8 Explain one advantage of an electrical synapse over a chemical synapse. (2 marks) ................................................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................................... 9 Explain the term voltage-gated ion channel. (2 marks) ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... .............................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................. 10 The graph shows the changes in membrane potential, sodium ion conductance and potassium ion conductance at a point of the membrane of an axon as it generates an action potential. Philip Allan Publishers © 2015 www.hoddereducation.co.uk/biologicalsciencesreview (a) Give the evidence from the graph that supports the hypothesis that depolarisation results from an influx of sodium ions and repolarisation results mainly from the exit of potassium ions. (3 marks) .................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................... (b) Give two effects the refractory period during nerve impulse transmission. (2 marks) 1 ................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................... 2 ................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................... 11 A nerve impulse can cross a synapse in only one direction. Explain why. (3 marks) ……....................................................................................................................... ……....................................................................................................................... ….......................................................................................................................... ….......................................................................................................................... ….......................................................................................................................... …......................................................................................................................... The diagram shows three sensory neurones that can stimulate a motor neurone. The table shows the effects of stimulation of the motor neurone by different combinations of the three sensory neurones. Philip Allan Publishers © 2015 www.hoddereducation.co.uk/biologicalsciencesreview Neurone Action potential in neurone Sensory neurone A Sensory neurone B Sensory neurone C Motor neurone (4 marks) Explain the results shown in the table. ................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................. 12 (a) Use information from Figure 4 of the article in BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES REVIEW to describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted across a cholinergic synapse. (4 marks) ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ....................................................................................................................... (b) Atracurium is a drug that can be used as a muscle relaxant during surgery. It has a structure similar to that of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Use your understanding of synaptic transmission to suggest how the administration of atracurium during surgery causes relaxation of skeletal muscles. (2 marks) ……....................................................................................................................... ……....................................................................................................................... ……....................................................................................................................... ……....................................................................................................................... ……........................................................................................................................ Philip Allan Publishers © 2015 www.hoddereducation.co.uk/biologicalsciencesreview Outline answers Each point expected in the answer is given, followed by (1), indicating that 1 mark would be awarded. An alternative answer within each marking point is indicated by a solidus (/). Where there are more marking points than marks available, the maximum mark is also indicated. Where a specific term is required, it is underlined in the marking point. Elsewhere, provided it is clearly expressed, the content of each marking point can be awarded in an answer that uses other forms of wording. Q Marking points Mark 1 Axon and cell body/soma and dendron/dendrites (1) 1 2 In a motor neurone, the cell body/soma is at one end of the cell but in a sensory neurone it is along length of neurone (1) A motor neurone has many short dendrites but a sensory neurone has a single dendron (1) 3 In a motor neurone, dendrites emerge from the cell body/soma but in a sensory neurone dendrites emerge from the dendron (1) 3(a) Made of many Schwann cells (1) Each (Schwann) cell is wrapped many times around the axon (1) 3 max So axon covered/insulated by many layers of the (Schwann) cell’s surface membrane/lipid bilayer (1) Gaps between (Schwann) cells are nodes of Ranvier (1) 3(b) 4 Increases rate of impulse transmission/speed of impulse transmission (1) Since depolarisation can occur only at the nodes (of Ranvier)/saltatory conduction of impulses (1) 2 7.25 ms (2) 2 If the answer is wrong, allow 1 mark if working shows either 5 1000 8000 × 58 or 58 8000 × 1000 The amplitude of the action potential/its amplitude (1) Is independent of the intensity of the stimulus that produced it (1) 2 If neither point is made, allow 1 mark for: action potential either occurs fully or not at all (1) 6 5 × 10−9 m (1) 7 The synaptic gap in an electrical synapse is about 5 nm whereas in a chemical synapse it is 20–50 nm (1) 1 In an electrical synapse, a single channel protein passes through the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes whereas in a chemical synapse different channel proteins occur in the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes (1) 8 2 Allows faster transmission of impulses (1) Philip Allan Publishers © 2015 www.hoddereducation.co.uk/biologicalsciencesreview Since the channel proteins allow the direct diffusion of ions between presynaptic and postsynaptic cells (1) 9 Proteins that enable ions to pass through cell surface membranes/through phospholipid bilayers (1) 2 2 That are activated by changes in voltage/potential difference (1) 10(a) Depolarisation causes the rise in membrane potential and repolarisation causes the fall in membrane potential (1) 3 Rise in conductance of sodium ions allows rapid diffusion of sodium ions into axon, causing rise in membrane potential (1) Rise in conductance of potassium ion channels allows diffusion of potassium ions out of axon, causing fall in membrane potential (1) 10(b) Ensures impulse travels in only one direction (1) 2 Limits frequency of impulses (1) 11(a) Neurotransmitter only released by presynaptic neurone (1) So neurotransmitter diffuses down a concentration gradient to postsynaptic membrane (1) 3 Receptors for neurotransmitter only present on postsynaptic membrane (1) 11(b) When stimulated only by sensory neurone A or sensory neurone B, threshold of motor neurone not reached (1) 4 max Since neither A nor B releases sufficient neurotransmitter to cause opening of sodium ions channels in motor neurone (1) When stimulated by both sensory neurone A and sensory neurone B, threshold of motor neurone exceeded and sodium ion channels open (1) Effect of stimulation by neurone A and neurone B is called summation (1) Stimulation of motor neurone by sensory neurone C prevents summation/threshold being reached by causing opening of chloride ion channels (1) 12(a) Arrival of action potential at presynaptic membrane causes opening of voltage-gated calcium ion channels (1) 4 max Calcium ions enter axon terminal via ion channels down diffusion gradient (1) (Entry of calcium ions) causes synaptic vesicles to move to, and fuse with, presynaptic membrane (1) Acetylcholine binds to receptor proteins in the postsynaptic membrane, causing sodium ion channels to open (1) Entry of sodium ions causes depolarisation of postsynaptic membrane (1) 12(b) Atracurium binds to acetylcholine receptors on postsynaptic membranes/on membrane around muscle cells (1) 2 So acetylcholine can’t bind and muscles cannot be stimulated to contract (1) Philip Allan Publishers © 2015 www.hoddereducation.co.uk/biologicalsciencesreview This resource is part of BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES REVIEW , a magazine written for A-level students by subject experts. To subscribe to the full magazine go to http://www.hoddereducation.co.uk/biologicalsciencesreview Philip Allan Publishers © 2015 www.hoddereducation.co.uk/biologicalsciencesreview