Critical Care Process Paper
advertisement

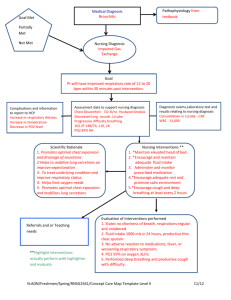
Medications (see attached) IV Sites/Fluids/Rate Right TL IJ NS@ 30hr Student Name: Kim Posey Age: 56 Gender: F Client Initials: M.M Room # ICU 24 CODE Status: Full Code Date: 2-4-13 Admit Date: 1-30-13 Allergies: ACE Inhibitors, PCN Diet: FEEDING TUBE PEPTAMEN BARIATRIC 40ml/HR Activity: bed rest Braden Score : 17 Monitoring: Invasive/NonInvasive State specific monitoring device and specific values with each device 5 Lead EKG (see attached paper) PQRST, heart rate and rhythm, VENT Vent Mode: AC FiO2: 60 TV: 600 RR:16 PEEP: 7.5 *Patient was extubated @ 945am ECG Interpretation (see attached) Chief Complaint: Difficulty in breathing Admitting Diagnosis(es): Respiratory Failure, COPD, HAP State lab values and identify trends. 141 │105 │47 (H) 176 (H) 4.4 │23 │ 1.460 (H) ___8.2 7.7 (L) ___Mg 14.0(H) 264 PO4 27.0 (L) State other appropriate lab results PH- 7.31(L) PCO2- 50.9 (H) HCO3- 25.3 State diagnostic test results Medical/Surgical Diagnosis(es): Respiratory Failure and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 1.Describe the patient’s condition, including signs/symptoms that led to this Admission: The patient was brought into hospital from a nursing home with c/o trouble breathing. When ambulance arrived at facility the patient was alert c/o trouble breathing and coughing. They know WBC increased D/T HAP, UTI H&H decreased- dx of anemia BUN/CREAT: due to patient having stage III kidney disease, CHF, ABGS’ compensated Respiratory acidosis GLUCOSE: patient is diabetic (Pagana & Pagana, 2011) Past Medical/Surgical History Relevant to this admission CHF Bronchitis with chronic hypoxic and hypercapnic respiratory failure, Chronic UTI Hypercapnic encephalopathy HTN Multiple Sclerosis Seizure disorder Kidney disease stage III Morbid Obesity Depression HX of 5 Trach’s Anemia this patient from past that when this happens she deteriorates fast. In route to the hospital her breathing became worse and became sleepy. Patient stats were in the 60’s and the patient was intubated in the emergency department. The patient is currently on a ventilator and sedated, at this point the patient is stable on vent, she continues to be sedated and in soft wrist restraints. The sedation medication was turned down and the patient is becoming more awake. The Respiratory doctor was in to see patient and decided to extubated patient. The doctor was expected to put in a trach because the patient has a history of trach’s. Once patient was extubated, she was placed on 50% aerosol mask at 7 liters, and was titrated down to 4liters and switched to nasal cannula. 2. Briefly describe the pathophysiology related to the patient’s diagnosis and current medical/surgical condition. The patient has an extensive respiratory history, bronchitis with chronic hypoxic and hypercapnic respiratory failure, history of 5 trach’s, and the patient has MS. Since MS affects muscles, it will affect the diaphragm which would cause the patient to be unable to take in deep breaths, accessory muscles become weak and lungs less compliant. Also the patient being morbidly obese can cause restriction to breathing, diaphragm, cannot expand. Unable to get a sufficient amount of O2, the patient is retaining more CO2 which cause respiratory acidosis which can cause respiratory failure. Which can flare up COPD and also leaving the patient vulnerable to getting pneumonia, also pneumonia could have cause the respiratory failure (Black, J.M., & Hawks, J.H., 2009) 3. Describe the patient’s head to toe assessment findings and explain how they relate to the pathophysiology. Include the vital signs. Patient is morbidly obese, pale, rhonchi throughout lungs; patient on vent is starting to be more alert with decreasing profonol. She has weakness in extremities, foley cath draining clear yellow urine; bowel sounds x4, PERRLA. She understands questions and can shake her head yes or no, has TI LJ in right neck, EGT placed. Patient being morbidly obese can cause breathing restriction, rhonchi throughout lungs is from Respiratory failure and from CHF, weakness is from the MS, she is wheelchair bound when at SNF, patient is pale from being anemic. Once off vent and put onto mask and then nasal cannula Treatments/ Medical and Nursing Interventions Foley Cath Turn Q 2 Strict I&O Daily WT Albuterol and Atrovent Q6hrs & PRN Barrier Cream Bilateral Soft Wrist Blood Transfusion @ 1120 patient is noted to have dyspnea which is related to respiratory failure, COPD and pneumonia, 4. Integrate the current laboratory, diagnostic test results, hemodynamic parameters medications, medical and nursing interventions, and other treatments into the pathophysiology and explain how it is affecting this patient’s outcome/current condition. ****Please see attached paper***** Primary Nursing Diagnosis with Relational Statement Impaired Gas Exchange R/T altered oxygen-carrying capacity of blood, having respiratory failure Definition (State definition and source) Unable to have CO2 and O2 gas exchange (Doenges, Moorhouse, & C, 2009) AEB: Defining characteristics specifically exhibited by your patient that support primary nursing diagnosis Patient has history of Bronchitis with chronic hypoxic and hypercapnic respiratory failure, COPD, Anemia, Patient in Compensated Respiratory Acidosis, patient on vent Short Term Goal Relevant to Nursing Diagnosis Patient will demonstrate improved ventilation by end of shift Outcome Criteria (Must be specific and measurable) Patient will demonstrate improved ventilation by end of shift Met- patient was breathing over vent and vent was pulled and put onto 4L NC Patient ABG’s will come back into normal limits by end of shift Not Met- patient ABG’s are from the ED, no new ABG’s have been drawn as of yet Patient will do cough and deep breathing exercises Q1 hr Met, encouraged patient to do coughing and deep breathing exercises, 6 Nursing Diagnosis with Relational Statement 1. Anxiety R/T difficulty breathing 2. Fatigue related to infection secondary to MS 3. Risk for dysfunctional ventilator weaning process related to respiratory failure 4. Activity intolerance R/T MS and respiratory failure 5. Risk for fluid volume excess related towards chronic kidney disease stage 3 6. Impaired mobility R/T MS explained importance of these exercises Patients Pulse Ox stats will stay above 93% throughout the rest of my shift Met, patient pulse ox was mid 90’s Identify nursing interventions that you implemented with this patient. Evaluate patient progress towards achieving outcome criteria as a result of nursing interventions. Monitor Client on Vent to see if patient is breathing on own and update doctor on patient status Patient was breathing over vent and vent was pulled Monitor respiratory rate, depth, and effort Alveolar hypoventilation and associated hypoxemia lead to respiratory failure Once pt. was off vent respiratory status was monitored closely respirations were around 20, patient did have dyspnea at times Restrict use of hypnotic sedatives or tranquilizers. Respiratory depression and CO2 narcosis may develop Patient propfonol was weaned down Administer Oxygen as indicated it helps aid in hypoxemia Once patient was weaned off vent, a 50% aerosol mask at 7 liters was put on to patient and weaned down to 4 L on nasal cannula Encourage and assist with deep-breathing exercises, turning and coughing to help improve lung ventilation and reduce or prevent airway obstructions associated with accumulation of mucus. Encouraged patient with deep breathing exercises and use of IS, turned Q2hrs (Doenges, Moorhouse, & C, 2009) Secondary Nursing Diagnosis with Relational Statement Ineffective air way clearance related to inability or ineffective cough Short Term Goal Relevant to Nursing Diagnosis Maintain patent airway with breath sound clear during my shift Definition (State definition and source) Outcome Criteria (Must be specific and measurable) Unable to effectively clear airway (Doenges, Moorhouse, & C, 2009) AEB: Defining characteristics specifically exhibited by your patient that support primary nursing diagnosis Being on vent Having to be suctioned Has anxiety Rhonchi throughout lungs What I Would Do Differently Ask more questions about the vent settings Got more hands on with the suctioning Ask how they determine when and how to wean a person off the ventilator Ask the doctor to see if he wanted a new ABG after patient had been off ventilator Patient will be able to cough out secretions by end of shift *Met, after ET was removed patient was coughing and bringing up sputum Patient O2 stats will stay above 93% throughout shift patient O2 stats ranged in mid 90’s Patient will understand the importance of clearing airway by end of shift *Patient understands that she needs to keep her airway clear from secretions Identify nursing interventions that you implemented with this patient. Evaluate patient progress towards achieving outcome criteria as a result of nursing interventions. Assess airway patency-obstruction may be caused by accumulation of secretions Patient was checked on frequently lungs were asculated Monitor ET tube placement- tube may slip into right main stem bronchus Tube placement checked Encourage Cough and deep breathing exercises- help cough up secretions Patient doing coughing and deep breathing exercises Perform suctioning on as a needed bases- many traumatize air way and mucosa Patient was suctioned as needed (Doenges, Moorhouse, & C, 2009) Current lab work shows that the patient is in compensated respiratory acidosis which is leading to her respiratory failure. She also has HAP which could have been the precursor to the patient for going into respiratory failure. These two things are making it difficult for the patient to breathe and to have adequate perfusion in the lungs. The patient had to be placed on a vent to stabilize the patient and get the respiratory system under control. The breathing treatment the patient is receiving is to help aid in opening up the alveoli to help improve ventilation. The patient is also receiving the antibiotic to help with the pneumonia. Blood transfusion is to help bring up the patient blood count and with that will help carry more oxygen throughout the body. The nursing intervention applied towards this patient is for improving the patients breathing and ventilation. The interventions are meant to help to make sure the patient is getting enough oxygen in the body. Since the patient started to breath over vent, the Respiratory doctor decided to take patient off the vent. After taken off the vent the patient was put on a 50% aerosol mask at 7 liters and was titrated down to 4 liters nasal cannula by the end of my shift, Patient pulse ox was ranging in mid 90’s good enough to keep patient on nasal cannula. Since the vent was helping the patient breath it was able to stabilize her breathing more efficiently and by that, they were able to wean her off the vent. There was no current ABG’s ordered only ABG was from the patient was in the ED. With the patient having MS this also affects the respiratory system because decrease muscle strength and inability full expand diaphragm to breathe in, and breathe in the O2 needed. Also at the nursing home the patient is wheel chair bound because of the MS. Since patient is diabetic also, her blood glucose can become out of control because of stress, infection and respiratory status. References Black, J.M., & Hawks, J.H. (2009). Medical-Surgical Nursing: Clinical Management for Positive Outcomes (8th ed.). St. Louis: Saunders Elsevier. Doenges, M. E., Moorhouse, M. F., & C, M. A. (2009). Nursing Care Plans Guidelines for Individualizing Client Care Across the Life Span. Philadelohia: F.A Davis Company. Pagana, K., & Pagana, T. (2011). Mosby's Diagnostic and Laboratory Test reference. St. Louis: Elsevier Science Health. Skidmore-Roth, L. (2011). 2011 Mosby's Nursing Drug reference. St. Louis: Elsevier, Mosby.