File - Greta`s Digital Portfolio
advertisement
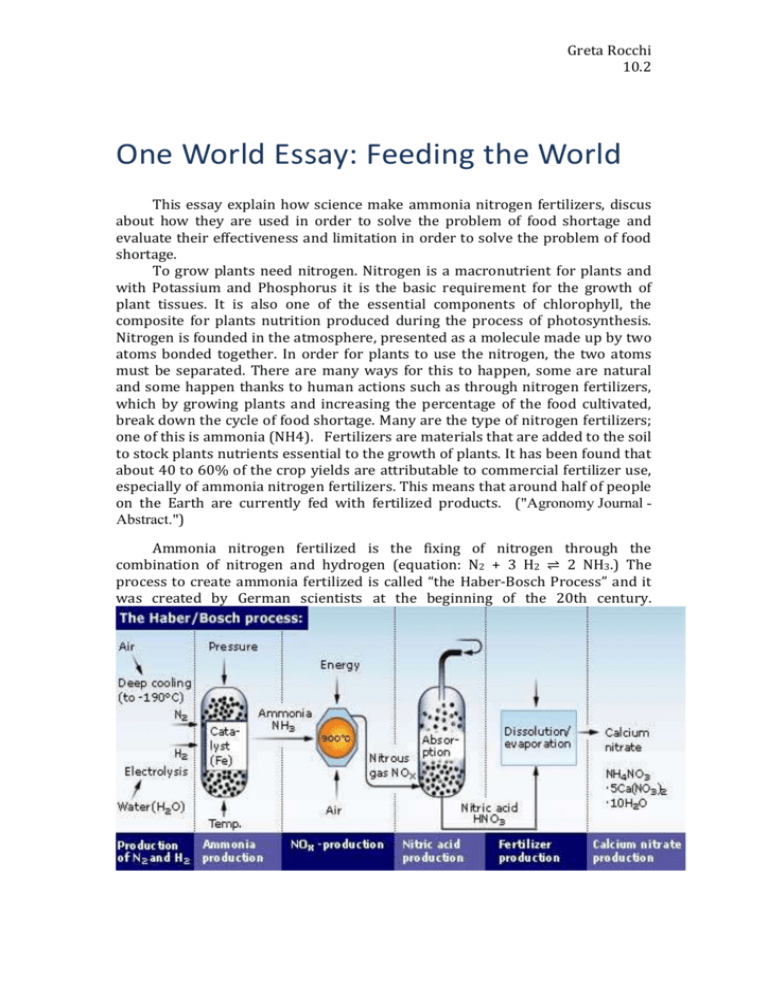
Greta Rocchi 10.2 One World Essay: Feeding the World This essay explain how science make ammonia nitrogen fertilizers, discus about how they are used in order to solve the problem of food shortage and evaluate their effectiveness and limitation in order to solve the problem of food shortage. To grow plants need nitrogen. Nitrogen is a macronutrient for plants and with Potassium and Phosphorus it is the basic requirement for the growth of plant tissues. It is also one of the essential components of chlorophyll, the composite for plants nutrition produced during the process of photosynthesis. Nitrogen is founded in the atmosphere, presented as a molecule made up by two atoms bonded together. In order for plants to use the nitrogen, the two atoms must be separated. There are many ways for this to happen, some are natural and some happen thanks to human actions such as through nitrogen fertilizers, which by growing plants and increasing the percentage of the food cultivated, break down the cycle of food shortage. Many are the type of nitrogen fertilizers; one of this is ammonia (NH4). Fertilizers are materials that are added to the soil to stock plants nutrients essential to the growth of plants. It has been found that about 40 to 60% of the crop yields are attributable to commercial fertilizer use, especially of ammonia nitrogen fertilizers. This means that around half of people on the Earth are currently fed with fertilized products. ("Agronomy Journal Abstract.") Ammonia nitrogen fertilized is the fixing of nitrogen through the combination of nitrogen and hydrogen (equation: N2 + 3 H2 ⇌ 2 NH3.) The process to create ammonia fertilized is called “the Haber-Bosch Process” and it was created by German scientists at the beginning of the 20th century. Greta Rocchi 10.2 As it is shown if the picture above ("1928: Proximity to the Market." ) the first thing that happens in the process is the production of nitrogen (N2) from air, and of hydrogen (H2) from a hydrogen source such as water or derived form natural gas like methane. Afterword these two elements are bonded with ammonia (NH3) at a temperature between 300 and 900 °C. This is called nitrogen fixation. The process takes place in a compression tank where pressure, temperature and an iron catalyzer cause the nitrogen and hydrogen to combine with the ammonia. The ammonia is than changed into nitric acid before fertilizer can be manufactured. Ammonia fertilizers are either soled as salts or as liquid solutions. They are tossed or sprayed on agricultural fields. As NH3 carry positive charges, it is adsorbed onto soil particles. Than the bacteria and fungi found in the soil change NH3+ to the NO3- in order for the plants to be able to use it . This process occurs rapidly (beginning within 2 to 3 days) when the soil temperature starts climbing above 50°F. The roots of the plants absorb the NO3- from the soil. Most of the nitrogen collected by the plants is used to produce proteins, in the form of enzymes, and nucleic acids. Nitrogen is automatically transported through the plant from older tissue to younger tissue. This explains way sometime we see leaves that are yellowing than others. The yellow leaves are the older leaves that due to the underdevelopment or destruction of chloroplasts suffer of deficient in nitrogen. Fertilizers are responsible for sustaining one-third of the Earth's population as they favorite plants’ growth, such as crops, which consequently prevent from food shortage. They favorite the growth of plants as they encourages and strengthen roots and foliage growth as well as bigger and healthier blooms, repaired depleted soils and enable plants to take in more water and nutrients. All this things allow a plant to grow tastier and succulent vegetables, to be more resistant to pests, diseases, and other adverse conditions and also to grow rapidly, which can generate bigger yields. Furthermore it has been proved that the application of ammonia fertilizers are on off-season plantations can increase the biomass of the plants, while also having a beneficial effect on soil nitrogen levels during the summer season. Even though the food produced by ammonia fertilizers are genetically modified food (GMO), they are not noxious to humans. This because ammonia is an aqueous solution, it is miscible with water and it can be expelled by boiling. Although, the application of ammonia fertilizers doesn’t only provide major quantity of food to the global population that constantly increase. Ammonia fertilizers also cause harmful negative effects, especially on the environment that surrounds us. An over application of the ammonia fertilizers, also known as Nitrogen deficiency, can provoke negative environmental effects; plants may not produce flowers or fruit, they can get burned, which causes them to shrivel and than to die. Ammonia fertilizers can have negative economical effects too that would effect the growers, mainly consisting on the waste of time and money. On the other hand ammonia fertilizers had positive economical effects, by allowing and improving agriculture in some developing nations where otherwise it would be impossible because of natural factors, such as aridity and drought of the soil. Greta Rocchi 10.2 Fertilizers can also provide to the expansion of pollution. Since most plants utilize less than one-half of the ammonia nitrogen fertilizer applied by growers, much of the remaining nitrogen fertilizer leaches into the soil, air and water and pollutes aquifers, rivers, lakes and oceans. other defects of the ammonia fertilizers is that the process for their production requires a great use of gases and energy. Through the Haber process, for a production of approximately 500 million tons of mostly ammonia nitrogen fertilizer per year, 3–5% of world natural gases and 1–2% of the world's annual energy supply is consumed. As the worldwide population increases, also the needs of food increase as well as the development of science techniques to solve the problem. It has been estimated that the global production of ammonia for 2012 is 198 million tones, a 35% bigger amount than the estimated 2006 global output of 146.5 million tones. ("Nitrogen Use Efficient Crops.") Ammonia fertilizers a healthy growth and make plants thrive. They provide food to a growing world population and develop agriculture in developing nations. The world needs more food, and therefore nations are increasing the use of fertilizers in their agriculture no matters there can be some negative effect due to their application. As we can see in the table below ("Environmental Issues and Options."), China is the top user of fertilizers followed by the US. We know that China as well as the US are the two countries with the major population density in the world. This is an evidence that fertilizers are efficient for the increasing of the food production in order to feed national population. Total N Countr Amt. used for feed/pasture use y (Mt pa) (Mt pa) China 18.7 3.0 U.S. 9.1 4.7 France 2.5 1.3 German 2.0 1.2 y Brazil 1.7 0.7 Canada 1.6 0.9 Turkey 1.5 0.3 UK 1.3 0.9 Mexico 1.3 0.3 Spain 1.2 0.5 Argenti 0.4 0.1 na Greta Rocchi 10.2 Works Cited "1928: Proximity to the Market." 1928: Proximity to the Market. Hydro, 22 Aug. 2007. Web. 24 Nov. 2012. <http://www.hydro.com/en/About-Hydro/Ourhistory/1918---1928/1928-Proximity-to-the-market/>. "Ammonia." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 23 Nov. 2012. Web. 24 Nov. 2012. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ammonia>. Laura Reynolds. "How Are Nitrogen Fertilizers Made?" GardenGuides. Garden Guides.com, n.d. Web. 24 Nov. 2012. <http://www.gardenguides.com/90326nitrogen-fertilizers-made.html>. Livestock's Long Shadow. "Environmental Issues and Options." N.p., 29 June 2009. Web. 24 Nov. 2012. <PDF>. "Nitrogen Use Efficient Crops." Home. Arcadia, n.d. Web. 24 Nov. 2012. <http://www.arcadiabio.com/nitrogen>. "Market Study: Fertilizers (UC-3005)." Ceresana. Ceresana Market Intelligent Consulting, Nov. 2011. Web. 24 Nov. 2012. <http://www.ceresana.com/en/market-studies/chemicals/fertilizers/>. "Record Drought Leaves Food Banks Dry â RT." Record Drought Leaves Food Banks Dry â RT. Questionmore, 24 Nov. 2012. Web. 24 Nov. 2012. <http://rt.com/usa/news/drought-food-bank-hurricane-459/>. Stewart, W.M.; Dibb, D.W.; Johnston, A.E.; Smyth, T.J. "Agronomy Journal Abstract." Home. Agronomy Journal, 2005. Web. 24 Nov. 2012. "The Role Of Nitrogen In Plants." House and Garden Nutrients RSS. Hause and Garden, n.d. Web. 24 Nov. 2012. <http://www.house-garden.us/articles/therole-of-nitrogen-in-plants/>. <https://www.agronomy.org/publications/aj/abstracts/97/1/0001>.