Rubric
advertisement
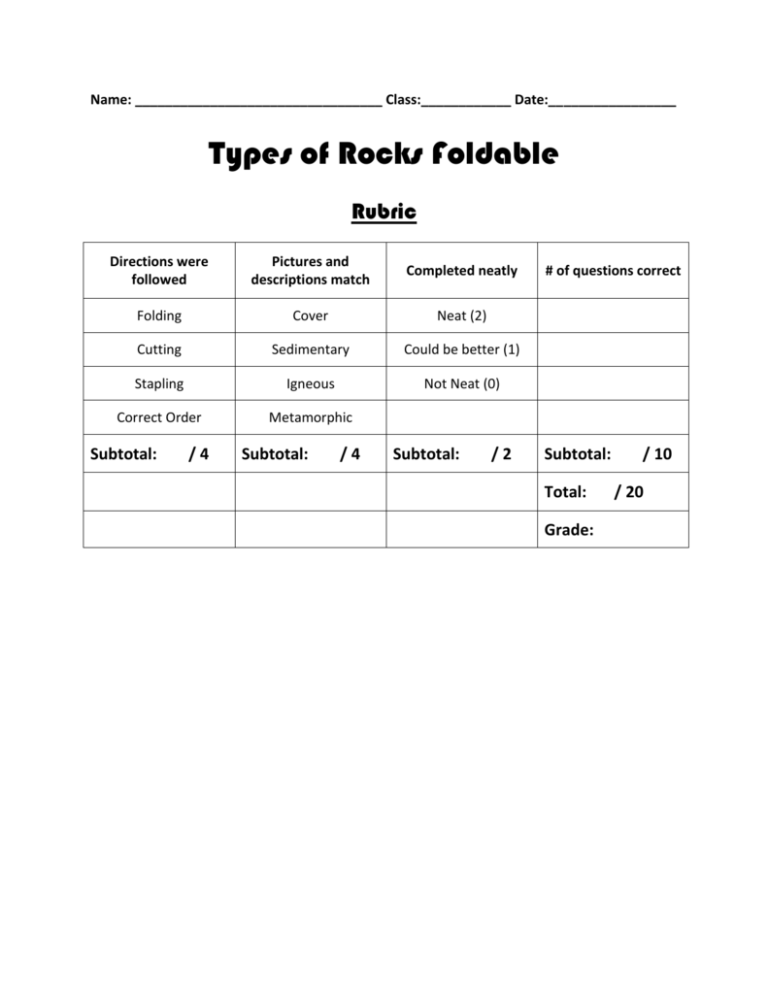
Name: _________________________________ Class:____________ Date:_________________ Types of Rocks Foldable Rubric Directions were followed Pictures and descriptions match Completed neatly Folding Cover Neat (2) Cutting Sedimentary Could be better (1) Stapling Igneous Not Neat (0) Correct Order Metamorphic Subtotal: /4 Subtotal: /4 Subtotal: /2 # of questions correct Subtotal: Total: Grade: / 10 / 20 Types of Rocks Foldable Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4. Fold the construction paper like a hamburger. Cut along the fold. Now you should have two pieces of paper. Line up the two sheets and fold it in half like a hamburger. Use one staple to staple the middle along the fold. Be sure to catch the inside paper in the staple. 5. Cut out the pieces from the other paper and glue them onto the appropriate pages. a. Front Page – Cover b. Second and Third Pages – Sedimentary Rocks c. Fourth and Fifth Pages – Igneous Rocks d. Sixth and Seventh Pages – Metamorphic Rocks 6. Answer the questions below in complete sentences on the lined paper. Questions: 1. What is the rock cycle? 2. Which rock groups can form from metamorphic rocks? 3. In the rock cycle, igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks can all become magma again. What step in the rock cycle causes this to happen? 4. Do all rock fragments or sediments follow the same path in the rock cycle? Explain. 5. What is the main characteristic that makes igneous rocks so different from sedimentary and metamorphic rocks? Explain. 6. What is one role of plate tectonics in the rock cycle? 7. What takes place when water or wind loosen and carry rock fragments? 8. Which process occurs when sand particles settles out of the water or wind and deposit sediments? 9. If igneous rocks cool rapidly on or near the surface of the Earth, then what would the rocks’ texture be like? 10. How are sedimentary and metamorphic rocks similar? Different? 2 Major Types 1. Intrusive – formed beneath the surface when magma hardens; coarse grained and has large crystals 2. Extrusive – formed above the surface when lava hardens; fine grained and has small or no crystals 2 Major Types 1. Foliated – grains are arranged in flat layers or bands 2. Nonfoliated – grains are arranged randomly Formation Processes Weathering Erosion Deposition Compaction Cementation Formation Processes Heat and Pressure Formation Processes Melting and Cooling Sedimentary Rocks Metamorphic Rocks 1. Clastic - rock fragments (ex: sandstone and shale) 2. Organic – remains of plants and animals (ex. Coal and some limestone) 3. Chemical – minerals dissolved in water and crystalized (ex. Some limestone and rock salt) Igneous Rocks 3 Major Types Name: Types of Rocks









