Biol 105
advertisement

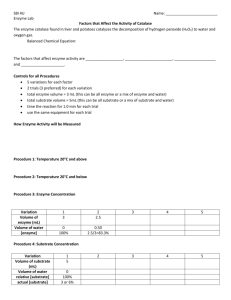
Biol 105: Tutorial 4 (Chapter 5) 1. State the first and second laws of thermodynamics. 1st – energy can be transferred and transformed but can not be created or destroyed 2nd – every energy transfer or transformation increases the entrapy (disorder) of the universe 2. What is meant by the term free energy? 3. - Greactants 4. Compare the energy changes in exergonic and endogonic reactions. exergonic release more energy than they absorb. Endergonic reactions absorb more energy than they release. 5. Give the three parts that make up ATP. the purine base, adenine, linked to the sugar, ribose, linked to a chain of three phosphate groups. 6. Using an example, explain how ATP plays a role in energy coupling. ATP is broken down intp ADP = Pi and releases energy That energy is used to facilitate another reaction Therefore both reactions take place Coupled : energy released by an exergonic reaction is used to facilitate a endogonic rection (endogonic – requires energy) 7. What is an enzyme and how does it work? 8. Explain the term entropy. 9. Briefly explain the induced-fit model of enzyme action? The electrons from the substrate and the enzyme attract each other therefore the enzyme’s active site changes to fit/as does the substrate to fit each other. 10. Clearly explain the relationship between the following: enzyme, substrate and active site. An enzyme has an active site, which is an open space where a substrate can bind. 11. How does an enzyme lower the activation energy of a chemical reaction? 12. Explain how the environmental pH can affect the functioning of an enzyme. 13. Explain the following terms: (a) feedback inhibition; (b) allosteric effector; (c) competitive inhibition. Allosteric Effector – a secondary site where the actual product can bind (or a non competitive inhibitor) which will alter the active site. Competitive Inhibition – replaces the substrate at the active site, therefore the substrate cannot bind. Feedback Inhibition- 1) initial substrate binds into the active site 2) Enzyme 1 is produced 3) intermediate A is produced enzyme 2 4) intermediate B is produced enzyme 3 5) intermediate C enzyme 3 6)intermediate C is produced enzyme 4 7) intermediate D is produced enzyme 5 END PRODUCT. Then realizes there is too much of it, and it bonds into the allosteric site altering the active site then the initial substrate cannot bind into it and production stops 14. Explain how high fever in a patient could affect the functioning of his/her cells. High fever can affect the functioning of a person’s cells because the heat denatures the shape of the enzyme so a metabolic reaction cannot take place and the cell cannot function (multiply) so it dies. 15. Explain why is carbon monoxide toxic. Carbon monoxide is toxic because the carbon monoxide binds to the active site on the hemoglobin (it is a competitive inhibitor) and the oxygen is then unable to bond to the active site, and we need oxygen to breathe