Ecology Test 2014 Study Guide (ANSWERS)
advertisement

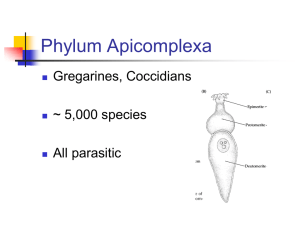
Name:________________________________________Date:_____________________Period:_____ Ecology Test Study Guide- Test Date: 2/27 Words to know: Population- Groups of single species that live together in the same place. Population Trend- How a population changes over time (increase, decrease, stay the same) Food Web- a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains. Predator- an organism that naturally preys on other organisms. Prey- an organism that is hunted and killed by another for food. Producer- An organism that uses the sun for energy Consumer- An organism that eats the food Ecosystem- a biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment. Ecology- The Study of the relationships between organisms, including humans, and the environment. Plankton- the small and microscopic organisms drifting or floating in the sea or fresh water Zooplankton- plankton consisting of small animals and the immature stages of larger animals. Phytoplankton-plankton consisting of microscopic plants. Habitat- the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism. Carrying capacity- the amount a container can hold based on both living and non-living factors Biotic- Living Factors in an environment Abiotic- Non-living factors in an environment. Competition- The interaction between species where the well-being of one is lessened by the other. REMOVED DECOMPOSER Name:________________________________________Date:_____________________Period:_____ Concepts to know: Animalia Phylya (Activity 75, Phylum PowerPoint Notes)1. Describe each phylum and list one example of each of the 9 phyla we studied. Phylum Porifera – – water organism, no tissues or organs, asymmetrical ex: sponge Phylum Cnidaria – – stinging cells, soft body, radially symmetrical, live in water alone or in a group ex: sea anemone, jellyfish, coral Phylum Platyhelminthes – bilaterally symmetrical, flat, worms, 1 digestive opening, can live in other organisms or by themselves. – ex: tapeworm, planarian, nudibranch Phylum Nematoda – round body, symmetrical, digestive system has 2 openings, some live by themselves but prefer to live in other organisms. – ex: roundworm (ringworm) Phylum Mollusca – soft body, many have a hard shell, live in the water or on land. – ex: zebra mussels, squid, cowrie, octopus, snails, clams Name:________________________________________Date:_____________________Period:_____ Phylum Annelida Phylum Arthropoda Phylum Echinodermata Phylum Chordata – has segments, bilaterally symmetrical, live in water or on land, worm. – ex: leech, earthworm, blackworm – hard shell, segmented bodies, paired appendages, live in water or land, exoskeleton. – ex: shrimp, mosquito, beetle, spiders, crustaceans (crabs, lobster) – live in salt water, spiny or leathery skin, tube feet, radially symmetrical – ex: sea star, sand dollar, sea urchin, sun star – internal skeleton, specialized body systems, paired appendages, nerve cord on the back, at some point they have a tail and gill slits. – ex: humans, Nile perch, horses, mammals, birds, fish, reptiles Chordata Classes (People, Birds and Bats)1. Describe the 5 classes in the chordata phylum and give an example of each. Name:________________________________________Date:_____________________Period:_____ Population Trends-(Activity 77-Ups and Downs) 1. Be able to graph population trends using a data table. Population of Alaskan King Crab in the Bering Strait (in Millions) Year 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Crab 200 240 500 180 110 235 360 370 373 Count 2008 205 Crab Count 600 500 Population of Crab 400 300 Crab Count 200 100 0 11999 2000 2 2001 3 2002 4 2003 5 2004 6 2005 7 2006 8 2007 9 2008 10 Years 2. Be able to describe what is happening to a population when looking at a graph. a. What is the population trend of Alaskan King Crab in the Bering Strait from 1999-2008? ABOUT THE SAME (LOOK AT THE FIRST AND LAST DATA b. What is the population trend of Alaskan King Crab in the Bering Strait from 1999-2001? INCREASING (LOOK AT THE DATA FROM POSITIONS 1-3 ABOVE) 3. Be able to describe biotic and abiotic factors that would affect populations. a. What are some biotic factors that would affect this population of King Crab? AS LONG AS YOUR ANSWER REFLECTS LIVING FACTORS AND MAKES SENSE YOU ARE OK! b. What are some abiotic factors that would affect this population of King Crab? AS LONG AS YOUR ANSWER REFLECTS NON-LIVING FACTORS AND MAKES SENSE YOU ARE OK! Name:________________________________________Date:_____________________Period:_____ Food Webs-(Activity 79) 1. What effect do introduced species have on ecosystems? DEPENDS ON WHERE IT IS INTRODUCED IN A FOOD WEB. QUATRANARY CONSUMERS ARE GOING TO EFFECT AN ECOSYSTEM GREATER THAN ANY OTHER. 2. What does the direction of an arrow in a food web indicate (show)? THE DIRECTION OF ENERGY FLOW 3. What happens to energy as you go further up the food chain? ENERGY IS LOST AS YOU GO UP THE FOOD CHAIN. 4. Draw a food web. Include produces (mark P), primary consumers (C1), secondary consumers (C2), tertiary consumers (C3) and quaternary consumers (C4) ANSWERS WILL VARY Competition (Activity 84-Clam Catch) 1. How does competition affect species in an ecosystem? ONE SPECIES WILL BE EFFECTED MORE GREATLY THAN ANOTHER, BUT BOTH WILL NOT BENEFIT FROM THE INTRODUCTION OF ANOTHER SPECIES. 2. How does an introduced species effect competition? IT INCREASES COMPETITION. 3. Be able to interpret a graph of competition. Carrying Capacity- (Activity 85-Is there room for one more?) 1. How do you determine carrying capacity when looking at a graph? IT IS THE POINT AT WHICH THE GRAPH LEVELS OUT AFTER ANY CHANGES. 2. What is the relationship between predator and prey in terms of carrying capacity? IF THE PREDATOR NUMBER INCREASES, SO DOES THE PREY IN ORDER TO COMPENSATE. (OPPOSITE ALSO TRUE). Name:________________________________________Date:_____________________Period:_____ 3. In a lake ecosystem, what are some biotic factors that could affect carrying capacity? AS LONG AS YOUR ANSWER REFLECTS LIVING FACTORS AND MAKES SENSE YOU ARE OK! 4. In a lake ecosystem, what are some abiotic factors that could affect carrying capacity? AS LONG AS YOUR ANSWER REFLECTS NON-LIVING FACTORS AND MAKES SENSE YOU ARE OK! Activity 87- Too many mussels Given an invasive species, speak logically on reasons to control, factors to control, issues surrounding the invasive and why it might be a good thing to let it grow.