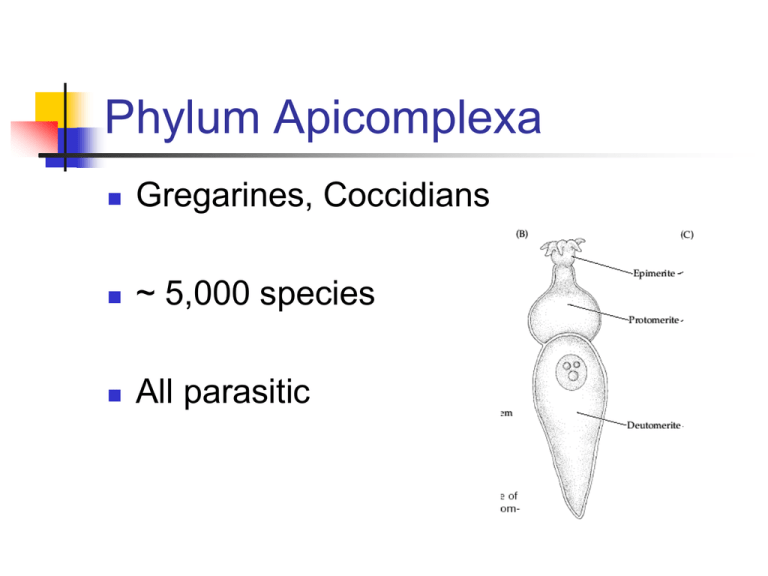
Phylum Apicomplexa
Gregarines, Coccidians
~ 5,000 species
All parasitic
Apical complex
Organelles for attaching parasite to host
cell
Hooks/suckers
Plasmodium vivax
Causes malaria
Kills 1-3 million / year
Mostly in Africa
Vector = mosquito
http://www.cdc.gov/malaria/about/biology/
Malaria: important world-wide
disease
•
•
•
> 300-500 million infections / year
> 1 million deaths / year
Distinctive fever pattern – cyclic 48 hours
Gregarine: gut parasites of
many invertebrates
Best known from arthropods
sporozoite
spores
In beetle
Phylum Dinoflagellata
~ 4,000 species described
Most unicellular, some are filamentous
or colonial
Some planktonic, some symbiotic (w/
corals, other cnidarians)
Red tide caused by
dinoflagellates
Discolored area of ocean with billions of
dinoflagellates
Produce toxins, kill everything.
Two flagella: armor or not
Ceratium
Ceratium sp.
Noctiluca
Dinoflagellates
Freshwater and marine
Osmoregulation by pusules
Tubules that open to outside
Autotrophic and heterotrophic
Switch
Many photo pigments
Repro
Asexual
Sexual: haploid cells divide, produce
daughter cells = gametes
Forms cyst, resting stage
Phylum Rhizopoda: amebas
~ 200 species
Most free-living, some endosymbiotic,
some pathogenic
Pseudopodia in all
Entamoeba histolytica
Amebic dysentery
4 nuclei - cyst found in fecal smear
Difflugia
Phylum Actinopoda
~4,240 species
Radiolarians, Heliozoans, etc.
Most w/internal siliceous skeletons
Planktonic and benthic
Heterotrophic mostly (phagocytosis)
Binary fission, budding, sex rare
Actinopoda
“ray feet” = axopodia
Slender pseudopodia
Actinosphaerium
Actinosphaerium
Foraminifera
~ 40,000 species
All aquatic habitats
Some planktonic, most benthic
Tests form chalks, marble, limestone
Chalk cliffs of Dover
Phylum Diplomonadida
Plasma membrane rigid from three
microtubular roots
Most phagotrophic, feed on bacteria
Asexual, most form cysts
Giardia
No mitochondria, ER, or Golgi bodies
Warm climates mostly
In severe infections every cell in gut is
covered by a parasite.
Coating of inside of intestine interferes
with absorption
Giardia lamblia
Phylum Chlorophyta
“Green algae” - green chloroplasts
Like plants
Some colonial
Some have lost photosynthesis =
heterotrophs
Volvox
Phylum Opalinida
Many rows of cilia - different than in
ciliates
Reproduction is longitudinal (like
flagellates), not transverse (ciliates)
~ 150 species
Endosymbiotic in frog and toad gut
Phylum Opalinida
Sexual repro by synamy
Asexual = binary fission
Opalina
Protist Phylogeny
Origins ~ 2.5 bya
Evolution of eukaryotes?
Serial Endosymbiotic Theory (SET)
Serial endosymbiotic theory