Climate Change
advertisement

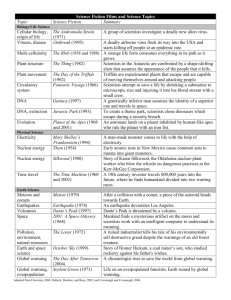
Climate Change One of the most controversial topics in today's media is the issue of climate change. Scientists, politicians, and environmentalists have been debating the causes and effects of changing climatic patterns for several decades, and recent popular concern about global warming has made the topic of climate change a political, economic, and scientific hotbutton issue. While climatic variation is an historical constant (no two years are ever identical in weather), large-scale climate change poses significant challenges for maintaining plant and animal life as we know it on the planet today. Is the climate skewing warmer due to human behaviors, or is climate change merely a natural cyclical process? It is answers to these questions that scientists seek and debate among themselves and in the public arena. While weather is the daily pattern of atmospheric changes, climate may be defined as the constant range of temperature, humidity, and weather patterns in a particular region of the world. Scientists consider climatic consistency crucial for the stability of the world's ecosystems. Slow and nondrastic changes in climate allow many plant and animal species to adapt to new environmental conditions and survive. However, rapid climate changes may have devastating effects on biological and botanical life. The current issue of global warming, the most dramatic change in climate in contemporary history, revolves around the ability of plant and animal species to adapt quickly enough to survive radical changes in climate and whether or not humans will be able to slow down, or even stop, the speed of global warming by their consumption behaviors. An understanding of the Earth's environmental system is crucial for comprehending the current debates regarding climate change. The atmosphere of the "Blue Planet" is constantly in flux, heavily influenced by radiant heat and moisture emitted from the world's oceans, land masses, and vegetation. While geologists and paleontologists have demonstrated that climate change has been dramatic throughout the Earth's history and that the current ecosystems of the planet have not existed consistently throughout time, scientists who study the current ecosystems of the Earth have been taken by seemingly rapid, and potentially devastating, changes to the current climate systems. Although there are a variety of theories about how and why this is occurring, mainstream scientific hypotheses blame global warming, caused by a combination of ecosystem destruction and greenhouse gas emissions, for a seemingly breakneck pace of climate change. Scientists utilize many methods for measuring climate change. Aside from the vast quantities of data gleaned from obvious developments in the weather, climate specialists look at ocean temperatures, ice accumulations, and satellite imagery, as well as evidence from historical documents, to determine the types of climate changes, the rates, and the impacts of climate change on the living environment. Botanical and biological evidence is then used to reinforce proposed assumptions. Scientists then examine a variety of forces that may be causing climate change. These factors are controversial and difficult to pin down, but include extraterrestrial and terrestrial causes, both natural and human-made. Climate change may be determined in part by a variety of natural forces that are beyond the ability of humans to control. Volcanic and tectonic activities are responsible for aspects of climate change, particularly over very long periods of time, but also in short historic bursts. For example, a violent volcanic eruption of Mount Tambora on the Indonesian island of Sumbawa in 1815 was responsible for significant climate change throughout the world for the next few years. Solar energy, too, has an incredible impact on climate change, both over millions of years as well as in relatively short bursts. All of these forces are beyond human abilities to alter; in these cases, climate change is an untouchable inevitability. However, scientists argue that there are several other factors influencing climate change that are within the realm of human control. Unprecedented levels of greenhouse gas emissions, including chlorofluorocarbons, methane, carbon dioxide, and ozone, have resulted in radical changes of weather, water temperatures, and glacial ice melt. Moreover, human alterations of the world's ecosystems, including deforestation, desertification, and toxic refuse dumping into the world's water and land, have resulted in changes of feedback between ecosystems and increased heat radiation on the planet. Major changes in the Earth's climate have been recorded since the Industrial Revolution, leading many scientists to propose that global warming has been accelerated due to humans' unprecedented destruction of the natural environment and usage of fossil fuels. Over the past 1,000 years, the 20th century was the warmest of all centuries, and the final decade of that century was the warmest decade of the 20th century. Such statistics, coupled with evidence of dramatic glacial ice melts, dead zones in warming seas, and increased incidences of killer weather systems, have shone a spotlight on issues of climate change in the media. However, not all scientists believe that climate change is a result of human activity. Instead, some view it as a natural process that is cyclical in nature, and the result of astronomical and geological events far beyond the control of humans. Others reject out of hand the notion that global warming is occurring. One of those people is Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change member John R. Christy, who famously declined to share the 2007 Nobel Peace Prize with the IPCC and former vice president Al Gore precisely because he does not believe that scientific evidence points to global warming. While it remains to be seen if climate change rates will slow down or accelerate in the near future, it is clear that the issue of climate change will continue to captivate scientists in their quest to better understand the Earth and its environment for many decades to come. MLA Stockdale, Nancy L. "climate change." World Geography: Understanding a Changing World. ABC-CLIO, 2014. Web. 21 Sept. 2014. 1. What questions about climate change are scientists trying to answer? 2. Why is a consistent climate important? 3. What are the mainstream hypotheses about the rapid changes in climate? 4. What methods do scientists use to measure climate change? List several. 5. What natural forces can cause climate change? 6. What human activities influence climate change? List several. 7. What do climate records reveal about the 20th century? 8. Do all scientists believe climate change is a result of human activity? Explain. 9. What is your opinion on climate change? Explain.