L7 - Rock Cycle handout
advertisement

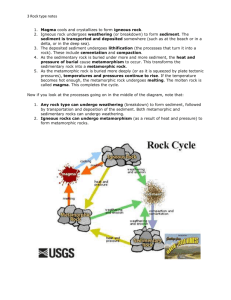
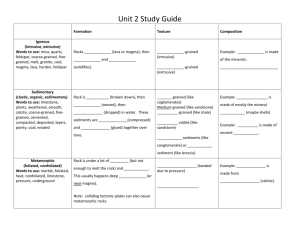
The Rock Cycle – Types Magma Rocks are created from magma (below ground) and lava (above ground) There are 4 forces, which affect rocks: 1. Cooling 2. Weathering and Erosion 3. Heat and Pressure 4. Heat causing melting Igneous Rock Formed when magma (or lava) is cooled Cooling can occur underground, above ground, or under water Characteristics: crystal structures and metallic minerals o e.g. granite Intrusive – granite occurs below the surface Extrusive – cooling occurs near the surface; minerals such as basal, gold, silver Igneous rock may be subjected to heat, heat and pressure, or weathering and erosion Sedimentary Rock When rock experiences weathering and erosion, it is broken down eventually into fine particles called sediment Through compaction and cementation these sediments form sedimentary rock Characteristics: fine particles, layering of particles, and fossils of sea animals o e.g. sandstone Fossil fuels are associated with this type of rock (e.g coal, oil, natural gas, salt, and potash) Sedimentary rock will also experience heat, heat and pressure, or weathering and erosion Metamorphic Rock When rocks are exposed to heat and pressure their structure will transform into metamorphic rock – “changed” rock o e.g. marble Metamorphic rock will also experience heat, heat and pressure, or weathering and erosion to form other types of rock Metamorphic, igneous, and sedimentary rocks can sometimes melt and form magma