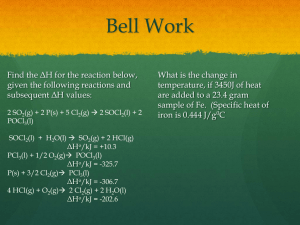
Gas Law Problems 2. If a gas at 25.0 °C occupies 3.60 liters at a
advertisement

Gas Law Problems 2. If a gas at 25.0 °C occupies 3.60 liters at a pressure of 1.00 atm, what will be its volume at a pressure of 2.50 atm? (Use Boyle’s Law) P1V1 = P2V2 P1=1.00 atm V1= 3.60 L P2= 2.5 atm V2=? (1.00 atm) (3.60 L) = (2.5 atm) ( V2) 3.60 atm L = 2.5 atm V2 2.5 atm 2.5 atm V2 = 1.44 L 3. A balloon is inflated to 5L at 20°C. What will be the new volume of the balloon if it is put in a freezer at 0°C? . (Use Charles’ Law) V1 = V2 T1 = T2 V1= 5 L T1= 293 K V2= ? T2= 273 K 273 K 5L = V2 (273 K) 293 K 273 K 1365 L = V2 293 V2 = 4.66 L 4. A gas occupies 1.56 L at 1.00 atm. What will be the volume of this gas if the pressure becomes 3.00 atm? (Use Boyle’s Law) P1V1 = P2V2 P1=1.00 atm V1= 1.56 L (1.00 atm) (1.56 L) = (3 atm) ( V2) 1.56 atm L = 3 atm V2 3 atm 3 atm V2 = 0.52 L P2= 3 atm V2=? Gas Law Problems 5. A cylinder of chlorine gas is stored in a concrete-lined room for safety. The cylinder is designed to withstand 50.0atm of pressure. The pressure gage reads 35.0 atm at 23.2C. An accidental fire in the room next door causes the temperature in the storeroom to increase to 87.5C. What will the pressure gage read at this temperature? (Use Gay-Lussac’s Law) P1 / T1 = P2 / T2 P1 = 35 atm T1 = 23.2 C P2 = ? T2 = 87.5C 35 atm / 23.2*C = P2 / 87.5*C (87.5*C) 35 atm / 23.2*C = P2 / 87.5*C (87.5*C) 3062.5 atm / 23.2 = P2 P2 = 132.00 atm 6. A gas occupies 11.2 liters at 0.860 atm. What is the pressure if the volume becomes 15.0 L? (Use Boyle’s Law) P1V1 = P2V2 P1 = 0.86 atm V1 = 11.2 L P2 = ? V2= 15 L (0.86 atm) (11.2 L) = (P2) ( 15 L) 15L 15 L P2 = 0.642 atm 7. If you took a balloon outside that was originally at 20°C at 2 L in volume, and it heated up to 29°C, then what would its new volume be? (Use Charles’ Law) V1 = V2 T1 = T2 V1= 2 L T1= 293 K 302 K 2L = V2 (302 K) 293 K 302 K 604 L = V2 293 V2 = 2.06 L V2= ? T2= 302 K Gas Law Problems 8. A 40.0 L tank of ammonia has a pressure of 1000 mmHg. Calculate the volume of the ammonia if its pressure is changed to 500 torr while its temperature remains constant. P1V1 = P2V2 P1 = 1000 torr V1 = 40 L P2 = 500 torr V2= ? (1000 torr) (40 L) = (V2) ( 500 torr) 500 torr 500 torr 40000 L = V2 500 V2 = 80 L 9. Chlorine gas occupies a volume of 1.2 liters at 720 torr pressure. What volume will it occupy at 1 atm pressure? (Use Boyle’s Law) P1V1 = P2V2 P1 = 1 atm V1 = 1.2 L P2 = 0.95 atm V2= ? (1 atm) (40 L) = (V2) ( 0.95 atm) 0.95 atm 0.95 atm 40 L = V2 0.95 V2 = 42.11 L 1 atm = 101.3 kPa = 101,325 Pa = 760 mm Hg = 760 torr Use these conversion factors (dimensional analysis) to solve 8 and 9. Gas Law Problems