File

Nayri Hatsakorzian
Pharm.D/MPH candidate 2014
College of Pharmacy- Touro University, CA
Acute Coronary Syndrome
Etiology: ruptured plaque that causes a blockage in the coronary artery. o Normally, supply and demand of O2 are equal -in stable angina, atherosclerosis: ↓O2 supply and ↑O2 demand ischemia in coronary arteries angina
SX: chest pain that radiates to neck, jaws, back, shoulders, or arms >30 min. Sweating, n/v, arm tingling, weakness and SOB may occur as well. Pain might be similar to acute angina, but it might last longer with more severity and frequency, and can occur while at rest and without exertion. This pain is not relieved by NTG after one dose hospitalization.
Types of ACS
STEMI: is a clinical syndrome defined by fully occluded artery and characteristic symptoms of myocardial ischemia in association with persistent electrocardiographic (ECG) of ST elevation and subsequent release of biomarkers of myocardial necrosis.
NSTEMI: the artery is not fully occluded, and ECG shows ST depression. Cardiac biomarkers are observed just like STEMI
UA: Chest pain that is sudden and often gets worse over time. It’s a warning sign of possible MI
Pain characteristics include: o More severe compared to stable angina, comes more often o Lasts longer than 15 - 20 minutes o Occurs without cause or exertion (in sleep or sitting quietly) o Does not respond well to NTG
Biomarkers
Troponin: gold standard for myocardial cell injury and MI diagnosis. Testing should be done upon admission and 6-12hours afterwards. Troponin levels can remain high up to 10days post MI or myocardial injury
CK-MB: Creatine Kinase isoenzyme MB mainly found in the myocardium. Detected within 3-8 hours of the onset of chest pain, peak within 12-24 hours, and usually return to baseline levels within 24-48 hours.
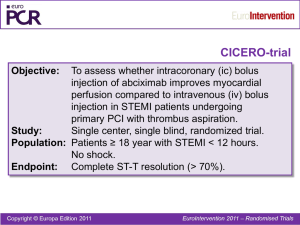
Regional Systems of STEMI Care, Reperfusion Therapy, and Time-to-Treatment Goals
Depends on institution: PCI capable hospital FMC – device time ≤ 90min
Non-PCI capable hospital FMC – device time ≤120 min (fibrinolytic is recommended when anticipated FMC to device time is ≥120 min)
Diagnostic angiogram is performed PCI or CABG or Medical therapy only
When to consider PCI
Ischemic symptoms <12 h
If fibrinolytic therapy is contraindicated then irrespective of time delay
Cardiogenic shock or acute severe HF irrespective of time delay
Persistent ischemia 12-24 hours after symptom onset
Do NOT perform PCI on a non-infarct artery in patients without hemodynamic compromise
Types of PCI
Both BMS or DES are useful
BMS is recommended in patients with: o High bleeding risk o Inability to comply with 1 yr of dual antiplatelet therapy o Anticipated invasive or surgical procedure in the next year
Absolute Contraindications to fibrinolytic therapy
Prior ICH
Known structural cerebral vascular lesion (arteriovenous malformation)
Known malignant intracranial neoplasm (primary or metastatic)
Ischemic stroke within 3 months o Except in acute ischemic stroke
Active bleeding
Significant trauma within 3 months
Intracranial or intraspinal surgery within 2 months
Severe uncontrolled HTN
Streptokinase within 6 months
Relative Contraindications to fibrinolytic therapy
Hx of chronic severe and poorly controlled HTN
Hx of ischemic stroke > 3 months
Dementia, pregnancy, active PUD, oral anticoagulant therapy
Known intracranial pathology other than what covered in absolute contraindication
Traumatic or prolonged (>10min) CPR
Major surgery < 3 weeks
Recent (2-4 weeks) internal bleeding
STEMI- NO PCI (O THANKS SBC)
O
2
2-4L/min via NC o Clinically significant hypoxemia (O
2
saturation < 90%), HF, or dyspnea o Increase rate or change to face mask as needed o Caution with COPD patients or if CO
2
retention is present
Thrombolytic o Need to burst through fully occluded clot o tPA (Activase, Cathflo): 15mg IV bolus 0.75mg/kg over 30 min (max 50mg) 0.5mg/kg over 60min (max 35mg) o Tenectoplase: 30-50mg IV bolus x1 (depends on patient weight < 60kg=30mg) o Fibrinolytic should be initiated when there is a delay of over 120 min to reach PCI
Ischemic symptoms <12h
Evidence of ongoing ischemia 12-24 hrs after symptom onset, large area of myocardium at risk, or hemodynamic instability
Fibrinolytic is not recommended in ST depression (unless posterior MI is suspected)
Heparin or LMWH for at least 48 hours o Heparin D
L
= 60 U/kg IV bolus (max 4000 U) D
M
= 12 U/kg/hr infusion (max 1000 U/hr)
Adjusted to obtain aPTT of 1.5-2.0 times control for 48 hours or until revascularization (approx. 50-70 sec)
If PCI is decided after receiving fibrinolytic therapy dose UFH depending on the administration of GIIb/IIIa inhibitor
Consider Bivalirudin if patient has a history of HIT o Enoxaparin
If patient is <75 yo
30mg IV bolus 1mg/kg SQ Q12h (max 100mg for the first 2 doses)
If patient is ≥ 75 yo
No bolus 0.75mg/kg SQ Q12h (max 75mg for the first 2 doses)
Regardless of age, if CrCl < 30ml/min 1mg/kg Q24h
Duration of enoxaparin is for the index of hospitalization, up to 8 days or until revascularization
If PCI is decided after fibrinolytic therapy 0.3mg/kg IV bolus if last dose of enoxaparin was administered 8-12hrs earlier o Fondaparinux
Initial dose 2.5mg IV, then 2.5mg SQ daily starting following day
Duration is for the index hospitalization up to 8 days or till revascularization
Contraindicated if CrCl<30ml/min
ASA 162-325mg PO X1 STAT o Do not administer Enteric Coated aspirin
NTG for ongoing chest pain, hypertension, and HF o 0.4mg SL q5min up to 3 doses as BP allows o IV should be initiated at 10mcg/min and titrated up as BP allows
Avoid if SBP <90 or >30 below baseline
Avoid in patient with 24-48hrs of PDE5I
ACEI/ARB o Lisinopril 2.5-5mg daily o Captopril 6.25-12.5mg TID o Ramipril 2.5 mg twice daily o Trandolapril test dose of 0.5 mg, titrate up to 4mg daily o Valsartan 20-160mg twice daily
Contraindicated with hypotension, hyperkalemia, and acute renal failure
Morphine Sulfate for pain, anxiety and pulmonary edema. o Initially 4-8 mg IV, 2-8mg IV q 5-15 min if needed
Lower doses in elderly
Caution with patients who are lethargic or having bradycardia
Statin o High dose- Lipitor 80mg daily
Beta blocker: ↓myocardial O
2
demand; ↓HR/BP/contractility o Metoprolol tartrate 25-50mg PO q 6-12hrs, up to 200mg daily as tolerated o Metoprolol tartrate 5mg IV q5 min as tolerated up to 3 doses, then switch to oral with above dosing for at least 48hours then continue with maintenance dosing
Do not initiate if patient is having sinus bradycardia, low SBP, heart block, or cardiogenic shock
Caution in patients with active asthma/COPD
Clopidogrel o If patient is ≤ 75 yo
D
L
D
M
= 300 mg
= 75 mg daily for at least 14 days and up to 1 year in absence of bleeding o If patient is >75 yo
D
L
= 75 mg
D
M
= 75 mg daily for at least 14 days and up to 1 year in absence of bleeding o IF PCI is decided after fibrinolytic therapy is administered:
If patient received loading dose then do not administer additional loading dose prior to PCI
If patient didn’t receive loading dose then:
If PCI ≤ 24 hours after fibrinolytic therapy 300mg prior or at time of PCI
If PCI >24 hours after fibrinolytic therapy 600mg prior or at time of PCI
Maintenance dose is depending on type of stent placed
If DES 75mg daily for at least 1 year
If BMS 75mg daily for at least 1 months and up to 1 year o Caution in patients taking Omeprazole. Omeprazole reduces effects of clopidogrel o Variation in clopidogrel therapy in patients with CYP2C19 genotype o If CABG is decided, clopidogrel should be stopped 5 days prior
UA/NSTEMI- NO PCI (GO HANKS SBC)
GIIb/IIIa inhibitor for ≤ 72 hours o Abciximab (Reopro) 0.25 mg/kg IV bolus 0.125 mcg/kg/min
Max 10 mcg/min
Abciximab should be discontinued at least 12 hours prior to CABG o Tirofiban (Aggrastat)(high bolus dose): 25 mcg/kg IV bolus 0.15 mcg/kg/min
Reduce infusion by 50% if CrCl<30
Should be discontinued 2-4 hours prior to CABG o Eptifibatide (Integrilin) (double bolus): 180 mcg/kg IV bolus 2mcg/kg/min; a second 180 mcg/kg bolus is administered 10min after the 1 st bolus.
Reduce infusion by 50% if CrCl <50
Avoid in hemodialysis patients
O
2
2-4L/min via nasal cannula
Heparin or LMWH for at least 48 hours o Heparin
D
L
= 50-70 U/kg IV bolus to achieve anticoagulant therapy
D
M
= 12 U/kg/min infusion (max 1000 U/hr) o Enoxaparin= 30 mg IV bolus 1 mg/kg SC q 12 hours o Bivalirudin (Angiomax) 0.75 mg/kg IV bolus then 1.75 mg/kg/hr
Additional bolus of 0.3 mg/kg may be given if needed
Reduce infusion to 1mg/kg/hr if CrCl <30
Preferred agent when given with GIIb/IIIa inhibitor in high bleeding risk patients or patients with prior HIT
ASA 325mg PO X1 STAT
NTG SL IV up to 24-48 hours
ACEI start within the first 24 hours of symptoms
MS
Statin (high dose- Lipitor 80mg daily)
Beta blocker start within the first 24 hours of symptoms
Clopidogrel D
L
300-600mg PO X 1; D
M
75mg daily ≥ 1yr or Ticagrelor
STEMI/UA/NSTEMI- PCI (GO HANKS SBC)
GIIb/IIIa inhibitor for o Abciximab or Eptifibatide
O
2
2-4L/min via nasal cannula
Heparin or LMWH for at least 48 hours o Heparin D
L
= 60 U/kg IV bolus (max 4000 U) D
M
= 12 U/kg/min infusion (max 1000 U/hr) o Enoxaparin= 30 mg IV bolus, then 1 mg/kg SC q 12 hours o Bivalirudin (Angiomax) 0.75 mg/kg IV bolus then 1.75 mg/kg/hr
Additional bolus of 0.3 mg/kg may be given if needed
Reduce infusion to 1mg/kg/hr if CrCl <30
Reduce infusion to 0.25mg/kg/hr if Hemodialysis
Preferred agent when given with GIIb/IIIa inhibitor in high bleeding risk patients o Fondaparinux is not recommended as sole anticoagulant in PCI because of risk of catheter thrombosis
ASA 325mg PO X1 STAT
NTG SL IV up to 24-48 hours
ACEI start within the first 24 hours of symptoms
MS (this is given for the chest pain)
Statin (high dose- Lipitor 80mg daily)
Beta blocker start within the first 24 hours of symptoms
Clopidogrel D
L
300-600mg PO X 1 (as early as possible or at the time of PCI); D
M
75mg daily o Prasugrel D
L
=60mg x1; D
M
= 10mg
TRITION-TIMI 38 trial showed higher efficacy than clopidogrel in composite primary outcome (death from cardiovascular causes, MI, stroke), and occurrence of stent thrombosis.
Prasugrel is contraindicated in patients with:
Prior stroke or TIA
≥ 75 years old
Weighing <60 kg
No renal dose adjustment is necessary
If CABG is decided, prasugrel should be stopped 7 days prior o Ticagrelor D
L
=180mg x1; D
M
= 90mg twice daily
Recommended maintenance dose of ASA with ticagrelor is 81mg due to increase risks of bleeding with higher doses of ASA
A nonthienopyridine, reversible, direct-acting oral antagonist of the P2Y
12
receptor that does not require transformation to an active metabolite.
No renal dose adjustment is necessary
PLATO trial concluded lower death and stent thrombosis when compared to Clopidogrel, but higher risks of stroke and episodes of ICH
If CABG is decided, ticagrelor should be stopped 5 days prior
References:
O’Gara et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA Guideline for the Management of ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. JACC. 2013. Vol.
61, No. 4:e78-140. Downloaded From: http://content.onlinejacc.org/
2012 ACCF/AHA Focused Update of the Guideline for the Management of Patients With Unstable Angina/Non −ST-
Elevation Myocardial Infarction (Updating the 2007 Guideline and Replacing the 2011 Focused Update): A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines.
Downloaded from http://circ.ahajournals.org/
Dipiro et al. Pharmacotherapy- A Pathophysiologic Approach. 7 th ed, 2008.