AP Biology Test 2 Study Guide: Chapters 3 & 4
advertisement

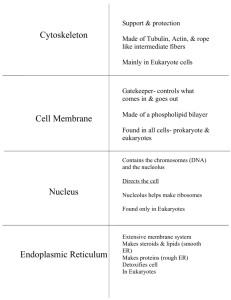
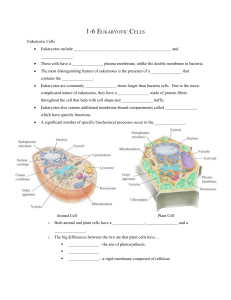
AP Biology Test 2 Chapters 3 & 4 What atom do organic compounds always contain What’s the purpose of functional groups Different functional groups and what atoms make them up Specific monosaccharides and polysaccharides Difference between cellulose, starch, and chitin What types of eukaryotes contain chitin Which of the four organic molecules is hydrophobic Saturated vs unsaturated Phospholipid structure and function What are steroids What are enzymes What makes up cell membranes? What does the cell membrane look like? 4 levels of protein structure What happens when a protein is denatured? What could cause a protein to be denatured? DNA vs RNA Isomers Surface area to volume ratio What type of molecules can pass through the cell membrane? Structure of cell membrane Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Which domains are prokaryotes and which are eukaryotes Animal Cells vs. Plant Cells Chromatin vs. chromosomes. What’s the difference, and when would each be present? Know all organelles structure and function for plants and animals, including the contractile vacuole which is found in some single celled organisms Tay-Sachs disease Cytoskeleton. I won’t ask you the difference between the three fibers, but you need to know what they are, and as a whole what is their purpose? Extracellular matrix Cilia and flagella Plasmodesmata Put in order the steps of the path of a protein from the DNA sequence to export from the cell Free Response 1) Surface area to volume ratio for cells. As a cell increases in size, what happens to the surface area: volume ratio? As a cell increases in size, which increases faster, surface area or volume? Why is a low surface area: volume ratio bad for cells? What can cells do to avoid having a low surface area: volume ratio? 2) Polymers and their monomers and the subunits of each monomer. Triglyceride and phospholipid subunits. Know and be able to explain the reactions that join monomers together and break monomers apart. Know the type of bond that links proteins together.