Social Studies Intro Chapter Outline
advertisement

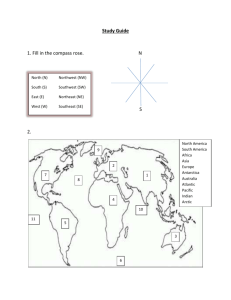
Introduction: Reviewing Geography A. Understanding the Global Grid a. What are latitude and longitude? i. _______________ lines run east and ___________, or horizontally around the earth. ii. Latitude lines measure distance ____________ or south of the equator. 1. Latitude lines are also called ________________. 2. The ___________________ is a parallel located at 0 degrees latitude. 3. The _________________________________ is located at 23 ½ degrees north latitude. 4. The _________________________________ is located at 23 ½ degrees south latitude. iii. ______________________ lines run north and south, or vertically. 1. They are also called ______________________. 2. They measure the distance east and ______________ from the Prime Meridian, which is located at 0 degrees longitude. 3. They also connect the North and ___________ poles. iv. Together, the latitude and longitude lines form the ______________ _____________. v. __________________________ location is the exact location of a place expressed by latitude and longitude. b. What are directions? i. North, south, east, and west are the main directions, or _____________________ directions. ii. The cardinal directions can be found on a map using the ______________________ rose. iii. The spikes between the cardinal directions on the compass rose show ____________________________, or in-between directions. 1. Intermediate directions help us describe ___________________ location, which is when we describe one place in relation to another. For example, you could say that Virginia is southwest of Delaware. c. What is a map scale? i. All maps are smaller than the real area that they show, so to figure out the real distance between places, most maps include a ___________________, which shows the relationship between distances on a map and real distances. (see p.H14) d. Why do maps include symbols? i. A map _______________________ is a drawing that stands for real things. ii. Some examples of symbols often used on maps are: 1. _____________________________________ 2. _____________________________________ 3. _____________________________________ e. What do locators show? i. A ______________________ is a small map set into the main map. It shows where the area of the main map is located. B. Using Maps to Find Geographic Information a. What is a political map? i. Political maps show _____________, states, and countries. 1. They also use lines to show __________________________. 2. An example of a political map would be a map of ___________________________. b. What are physical maps? i. A _____________________ map shows the characteristics of the ______________________ environment, such as landforms. 1. ____________________ is shading on a map to show mountains or hilly areas. ii. An ___________________________ map is a physical map that uses colors to show the elevation, or height, of land above sea level. 1. The height is usually measured in feet or meters. 2. An example of a physical map would be a map of ___________________________. c. What is a historical map? i. A ____________________________ map shows information about past events and where they occurred. 1. An example of a historical map would be a map of ___________________________. d. What is a road map? i. A ____________________ map shows you how to get from one place to another. Introduction: Land and People of the United States Lesson 1: America’s Land A. America’s Land a. The United States has several kinds of landforms. i. Landform: a shape on Earth’s surface ii. Some landforms in the United States are __________________, plains, _________________, and basins. b. Mountains i. Mountains protect settlements by making them difficult to reach. ii. America’s longest mountain range is the ________________________________, which stretches from Alaska to _____________________. iii. The highest mountain range is the _______________________________ in the West. iv. Our country’s highest mountain, ________________________________, is located in the Pacific Ranges. v. The lowest mountain range is the __________________________________________, which stretches from Maine to Alabama. vi. Many of the mountains in the US are rich in natural resources, such as minerals and forests. c. Plains i. The __________________________________ are a vast area of flat land stretching between the Appalachian and Rocky Mountains. 1. The Interior Plains have our country’s largest river system, which includes the Great Lakes and the ________________________________ River. ii. The __________________________________, in the west, are drier than the rest of the area, but it has rich soil, which makes it ideal for growing _____________ and wheat. iii. The ______________________________ has sandy beaches, wetlands, and rich farmland. d. Plateaus and Basins i. The Western Plateaus and Basins region stretches from Washington State to ___________________. 1. It is the driest region of the US ii. The ___________________________ Plateau, in the south, has some of the most unusual landforms in our nation, including natural bridges, the _____________________________, and huge, flattopped rocks. e. America’s Climate i. Different parts of our nation have different climates, which is the weather an area has over a number of years. 1. Climate includes a place’s general ______________________, and amount of precipitation. ii. Climate varies for many reasons. 1. Example: A region’s distance from the _______________________ affects its climate. a. Places near the equator are warmer. iii. The East is ______________ and receives more than 20 inches of precipitation per year, while the West is ______________, and gets less than 20 inches of precipitation. f. United States Vegetation i. There are five vegetation regions of the United States. 1. ______________________: needleleaf trees, broadleaf trees, ferns, fungi, mosses. 2. ______________________: bluestem grass, buffalo grass, gamma grass. 3. ______________________: cactuses, desert palm, sagebrush, wildflowers. 4. ______________________: rubber, mahagony, tropical palm, ferns, orchids. 5. ________________________: mosses, shrubs, wild flowers, low-growing grasses. Lesson 2: Environment B. Environment a. Natural Resources i. The _______________________ is all the surroundings in which people, plants, and animals live. ii. Natural resources can be _____________________ or nonrenewable. 1. Renewable resources, such as trees, can be replaced. 2. Nonrenewable resources, such as minerals, cannot be replaced. a. Fossil fuels, such as _____________, oil, and _____________________________ are also nonrenewable. b. Ecosystems i. Our environment is divided into many smaller special environments called _____________________, which is all the living and nonliving things in a certain area. 1. Pond ecosystem: Made up of soil, water, tiny plants called algae, insects, fish, and frogs ii. Six major ecosystems 1. _________________________________ 2. _________________________________ 3. _________________________________ 4. _________________________________ 5. _________________________________ 6. _________________________________ iii. Ecosystems are in a biological balance, meaning that the living and non-living things in an ecosystem affect one another. 1. Sometimes _____________________, which is unclean matter, can threaten this balance. C. Changing Our Land a. We change the land in many ways, for example, we change the ___________________ when we _______________________________________________. b. Cities i. ___________________________ is the development and growth of cities. ii. Less than a century ago, most people in the US lived in ___________________ areas, meaning they lived in the country. iii. _______________ are central places, which often help businesses grow. When businesses grow, more people begin to move to _____________________ areas, or cities, for better paying jobs. c. Conservation i. ____________________________ is the protection and careful use of natural resources. ii. One way that we conserve is by __________________, which is the reuse of materials. 1. Recycling saves natural resources and energy. Lesson 3: The American People “Give me your tired, your poor, your huddled masses yearning to breathe free.” – Emma Lazarus, 1883 D. Many Different People a. The above quote appears on the ________________________________, which is a symbol of freedom to millions of __________________________, which is a person who leaves one country to go and live in another. b. Immigrants from all over the world have made contributions to the United States, and their differences have brought a great deal of __________________, or variety, to our country. i. Diversity can be seen in the many religions, languages, values, and traditions that are found in our nation. c. Part of our nation’s diversity is due to its many different ________________________________, which is a group of people who share the same customs and language. Many also have a common history. d. Today, the largest number of immigrants come from _______________ and ____________________________. i. People whose ancestors are from Spanish or Portuguesespeaking countries in the Western Hemisphere are called _______________________, or Latinos. 1. An ____________________________ is a relative who lived before you. E. Government a. Our nation’s government is responsible for protecting the diverse people who make up the United States. b. The _________________________ of the United States is the plan for our country, which serves the people by providing ways to make, carry out, and ______________________ the laws of our land. i. Our Constitution calls for a ______________________ republic, meaning that people choose representatives to run the ______________________, or national government. 1. A representative is a person chosen to speak or act for others. ii. Every four years, voters in the United States elect a __________________________. 1. Fact: Every president except ___________________________________ worked and lived in the White House, which was designed by James Hoban, an Irish-born immigrant. c. Citizenship i. _____________________ of the United States have many rights and responsibilities. 1. A citizen is a person who is born in a country or who chooses to become a member of that country by law. ii. The basic rights of citizens are protected by the first ten _________________________ to the Constitution, called the _____________________________. 1. These rights include freedom of speech, freedom of religion, and freedom of assembly. iii. Citizens responsibilities include: 1. _________________________________ 2. _________________________________ 3. _________________________________ 4. _________________________________ 5. _________________________________ 6. _________________________________ Lesson 4: Our Nation’s Economy F. Our Nation’s Economy a. Citizens benefit from the American ____________________________________ system, which allows equal opportunity for people to own and operate their own businesses. i. Each business person makes their own economic decisions, such as what to make, how much to produce, and how much to charge. ii. People who form and run a business are called _______________________________. 1. They use their ideas and savings to start a business. 2. They need skilled and hard-working people to produce their goods and services. 3. They are an important part of free enterprise and make our economy strong and growing. b. The laws of the United States help and protect both businesses and __________________________. i. A consumer is a person who buys and uses goods and services. ii. Our laws help consumers by making businesses list what is in the products we eat. G. Preserving Our History a. ________________________________, people who study the past, examine clues and records that peple have left behind. i. They use this information to understand why people do what they do, and then write books to keep history alive. ii. Historians also study both ______________________ sources and ________________________ sources. 1. A ____________________________ source is information that comes from the time being studied. a. Example: A letter, official document, or photograph 2. A _______________________ source is an account written by someone who did not witness the event being studied. a. Example: Someone living now who is writing about the Revolutionary War. H. Regions of the United States a. Most nations are divided into ______________________. i. The _________ regions of the United States are examples of how each region is a mixture of physical and cultural features. 1. Each region has its own environment, for example. 2. Each region shares a history and other features. ii. The six regions of the United States are: 1. _________________________________ 2. _________________________________ 3. _________________________________ 4. _________________________________ 5. _________________________________ 6. _________________________________ b. Our nation also has __________________________ regions, which are areas where people share the same language, beliefs, and customs. i. Example: The Gullah people of coastal South Carolina and Georgia make up a cultural region. 1. They speak a language like that of Sierra Leone in Africa and tell African folktales and make Africanstyle handicrafts. c. ___________________________ regions are another kind of region, which are formed when many people are affected by a natural resource or product of an area. i. Examples: Corn belt of the Middle West, Silicon Valley in California