QUESTIONS - Learning
advertisement

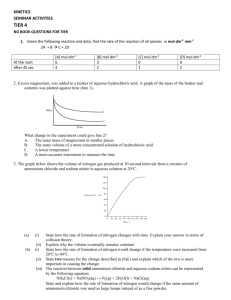
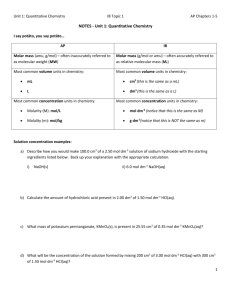
Acids and Bases Worksheet 1 : 1. A solution has a concentration of [H+] 5 x 10-3 mol.dm-3. Calculate the pH of this solution. (5) 2. What ion is always formed when acids dissolve in water? A B NH4+ SO42- C D NO3H3O+ (2) 3. Which one of the following 0.1 mol.dm-3 acid solutions has the highest pH? A B sulphuric acid hydrochloric acid C D nitric acid ethanoic acid (2) 4. The stronger a base, the greater will be its ability to A B donate electrons. combine with electrons. C D combine with protons. donate protons. 5. Consider the following equation of a chemical equilibrium reaction: NH4+ + OH- ⇌ NH3 + H2O The acids in this reaction are A B H2O and OHNH4+ and OH- C D NH4+ and H2O NH3 and OH- 6. Which one of the following can be classified as an amphiprotic substance? A B HSO4S042- C D C032NH4+ 7. When concentrated sulphuric acid is dissolved in distilled water, the following reaction takes place: H2S04 + 2H20 ⇌ 2H30+ + S042(a) Would you classify sulphuric acid as a strong or weak acid? Give a reason for your answer. (3) (b) Rewrite the equation given above and indicate the conjugate acid-base pairs involved in this reaction. (4) Worksheet 2 1.1 A learner tries to obtain the concentration of household vinegar (ethanoic acid solution) by titrating it against a solution of sodium hydroxide. She makes the following statement: ‘...at the endpoint, neutralisation has just been completed, and therefore the pH of the solution will be seven’. The learner's statement is incorrect. With the aid of a chemical equation, supply a correct explanation. [8] 1.2 A standard solution of sodium hydroxide is prepared by dissolving 4,5 g of NaOH in distilled water and by making the solution up to a volume of 250 cm3. 25 cm3 of this NaOH solution is then titrated with sulphuric acid solution of known concentration. The endpoint of the titration is reached when 22,5 cm3 of sulphuric acid has been added. The reaction is represented by the following unbalanced equation: NaOH + H2SO4 ⇌ Na2SO4 + H2O 1.2.1 1.2.2 1.3 Calculate the concentration (in mol.dm-3) of the H2SO4 solution. (9) What volume of pure water must be added to 100 cm3 of a 0,60 mol.dm-3 solution of NaOH to dilute it to 0,15 mol.dm-3? (4) When 50 cm3 of a solution of sodium hydroxide solution is added to 45 cm3 of oxalic acid of concentration 0,002 mol.dm-3, the temperature rises and the solution is neutralised according to the reaction 2NaOH + (COOH)2 ⇌ 2(COONa)2 + 2H2O 1.3.1 1.3.2 Classify this reaction as exothermic or endothermic. (a) 1.3.3 1.3.4 (2) Which of the indicators phenolphthalein, bromothymol blue and methyl orange is best for this reaction? (b) Give a reason for your answer. (4) Calculate the original concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution. (6) Calculate the mass of oxalic acid dihydrate ((COOH)2.2H2O) that was required to make up 250 cm3 of the original solution. (4) 2 1.4 A certain mass of potassium hydroxide was added to 250 cm3 of pure water. 25 cm3 of the alkali solution was neutralised by 10 cm3 of a 0,20 mol.dm-3 solution of sulphuric acid. 1.4.1 1.4.2 1.4.3 1.5 Give a balanced equation for the reaction that takes place between the alkali and the acid. (3) Calculate the mass of potassium hydroxide dissolved in the 250 cm3 of pure water. (10) Calculate the pH of the original sulphuric acid solution. (3) One gram (1,00 g) of pure marble (CaCO3) was dissolved in 50 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid. After the marble had reacted completely, 25 cm3 of a solution of caustic soda (NaOH) of concentration 0,1 mol.dm-3 were used to neutralise the excess acid. The following equations represent the reactions taking place. A 2 HCl(aq) + CaCO3(s) ⇌ CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) B HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) ⇌ NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) 1.5.1 1.5.2 1.5.3 1.5.4 1.5.5 Name a suitable indicator that could be used in reaction B. (2) How many moles of CaCO3 were dissolved in the hydrochloric acid? (3) Calculate the number of moles of HCl(aq) that reacted with the CaCO3. Calculate the concentration of the original hydrochloric acid. (7) Calculate the mass of NaOH in 25 cm3 of the NaOH solution. 3 (5) (2) Worksheet 3 1.1 When ammonium sulphate, (NH4)2S04 is dissolved in water, the pH of the solution is approximately 6,5. Which one of the following equations offers the best explanation for this? (A.) (NH4)2S04 ⇌ 2NH4+ + S042- (B.) 2NH4+ + H2O ⇌ NH3 + H3O+ (C.) 2H2O ⇌ H3O+ + OH- (D.) S042- + 2H2O ⇌ H2SO4 + 2OH- 1.2 During a certain neutralisation reaction, 1 mole of base is used for every 2 moles of acid. Which one of the following pairs can possibly be the base and the acid respectively? Sodium hydroxide and oxalic acid A Barium hydroxide and ethanoic acid B Sodium carbonate and sulphuric acid C Potassium hydroxide and nitric acid. 1.3 Which one of the following pairs would be a conjugate acid-base pair? HSO4- and NH3 A HSO4- and SO42B HSO4- and NH4+ C SO42- and NH4+ 1.4 2 Which one of the following salts below, when added to 10 ml of distilled water, will decrease the pH of the solution? Na2CO3 A NaCl B K2CO3 C NH4Cl A quantity of ammonium chloride is dissolved in water. 2.1 Is this solution acidic, basic or neutral? (2) 2.2 To explain your choice in 2.1, write down the reaction of the ammonium ion in aqueous solution. (4) 2.3 Indicate ONE conjugate acid-base pair in the reaction in 2.2. (2) 2.4 What is an ampholyte? Write down the formula of an ampholyte appearing in the equation in 2.2. (4) 3 Hydrocyanic acid (HCN) is considered to be a WEAK acid, when dissolved in water. 3.1 Differentiate between STRONG and WEAK acids. (4) 3.2 Write the equation for the dissolution of hydrocyanic acid indicating the movement of protons when the solution is in equilibrium. (4) 3.3 10 ml of hydrocyanic acid is added to 10 ml of hydrochloric acid. Both acids have the same concentration. 3.3.1 Which of the two solutions would act as the acid and why? (4) 3.3.2 Calculate the pH of a 0,003 mol.dm-3 solution of hydrochloric acid. 4 (4) Calculate the pH of a solution of Ba(OH)2 if it contains 3,426 g base per 800 cm3 solution. 4 (8)