Test yourself
advertisement

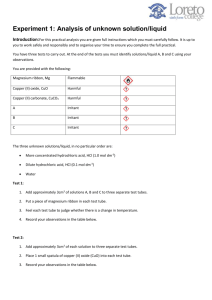
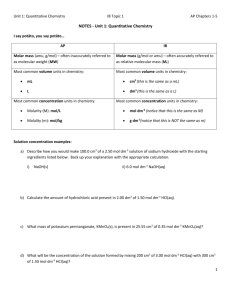
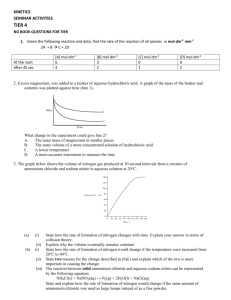
Test yourself : Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 7 : Acid and Bases Section 1 A. Acid and Bases 1. Complete the general equations below. 2. a. Acid + alkali ___________________________________________ b. Acid + reactive metal ___________________________________________ c. Acid + metal carbonate ___________________________________________ d. Acid + metal oxide ___________________________________________ e. Alkali + ammonium salt ______________________________________________ Based on question 1, complete the chemical equation below. a. HCl + NaOH ________________________________________________ b. H2SO4 + Mg ________________________________________________ c. 2HNO3 + ZnCO3 ________________________________________________ d. H2SO4 + CuO ________________________________________________ e. NaOH + NH4Cl ________________________________________________ B. Concentration of Acid and Bases 1. Calculate the concentration in g mol-1 of 0.5 mole potassium hydroxide in 5.0 dm3 solution. [Relative atomic mass; H.1;K.39;O,16] 2. Find the concentration of 2.0 mol dm-3 sodium chloride solution in g dm-3 [Relative atomic mass : Cl, 35.5; Na, 23] 3. 4.0 g of sodium, hydroxide is dissolved in water to make up 500 cm 3 of solution. Calculation the molarity of sodium hydroxide solution obtained. [ Relative atomic mass : H,1; Na, 23; O,16] 4. Calculate the number of moles of copper (II) sulphate in 250 cm 3 of 1.5 mol dm-3 copper (II) sulphate solution. 5. What is the volume of 2.0 mol dm-3 sodium chloride solution needed to prepare 250 cm3 of 0.2 mol dm-3sodium chloride solution? C. Neutralisation 1. What is the volume of 0.2 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid needed to neutralize 25 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 potassium hydroxide solution? 2. What is the mass of zinc oxide needed to neutralize 50 cm3 of 0.5 mol dm-3 sulphuric acid? [ Relative atomic mass: Zn, 165; O,16] 3. What is the molarity of 25 cm3of sodium hydroxide solution that is needed to neutralize 10 cm3 of 0.2 mol dm-3 sulphuric acid? Section 2 1 The table below shows the description and observation for two experiments involving two solutions: Hydrogen chloride in solvent X Hydrogen chloride in solvent Y Experiment (a) Description Observation HCl in solvent X HCl in solvent Y I Reaction of hydrogen chloride in solvent X and solvent Y with calcium carbonate lumps. Effervescence occurs. A colourless gas is liberated. No change occur II Electrolysis of hydrogen chloride in solvent X and solvent Y Ammeter shows reading Ammeter does not show reading. Name a suitable compound for Solvent X : ............................................................................................................. Solvent Y: ................................................................................................................ [2 marks] (b) (i) Which of the solution shows acidic properties? .................................................................................................................... (ii) What is the role of solvent in (b) (i) that enables the solution to show acidic properties? .................................................................................................................... [2 marks] (c) (i) Effervescence occurs when hydrogen chloride in solvent X react with calcium carbonate. Name the gas liberated. ................................................................................................................... (ii) Describe a chemical test to identify the gas liberated in (c) (i) .................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................... (iii) Write ionic equation for the reaction in (c) (i). .................................................................................................................... [4 marks] (d) Hydrogen chloride in solvent X can conduct electricity but hydrogen chloride in solvent Y cannot conduct electricity. Explain why. .................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................... [2 marks] (e) Calculate the mass of hydrogen chloride gas, HCl to prepare 100 cm3 of 0.5 mol dm-3 HCl acid. [Given that the relative atomic mass of H = 1, Cl = 35.5 , C = 12, Ca = 40 , O = 16 ] [3 marks] 2 The diagram shows the set up apparatus for the titration of sodium hydroxide solution with hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid 1moldm-3 50 cm3 of 1 moldm-3 sodium hydroxide solution and phenolphthalein 1.0 moldm-3 hydrochloric acid is added to 25 cm3 of 1.0 moldm-3 sodium hydroxide solution and phenolphthalein is used as an indicator . a) (i) Name the reaction between sodium hydroxide solution and hydrochloric acid. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [ 1 mark ] (ii) Name the salt produced in the experiment. (b) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [ 1 mark ] State the colour change in the conical flask at the end point. (c) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [ 1 mark] Write a chemical equation for the reaction occurs in the conical flask. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… [ 1 mark] (d) (i) Calculate the volume of 1.0 moldm-3 hydrochloric acid needed to exactly neutralise 25 cm3 of 1.0 moldm-3 sodium hydroxide solution. [2 marks ] (ii) The experiment above is repeated by replacing 1.0 moldm-3 hydrochloric acid with 0.5 moldm-3 sulphuric acid. Predict the volume of sulphuric acid required to complete neutralise the sodium hydroxide solution. ………………………………………………………………………………………………… [ 2 marks ] (e) Calculate the maximum mass of the salt formed in this experiment. [Given that the relative atomic mass of Na = 23, Cl = 35.5 ] [ 2 marks ] (f) State one of the uses of the salt formed in daily lives. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [ 1 mark ]