Page of 3 Talking Points Why did you do this Project? Provide a
advertisement

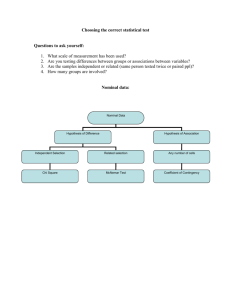
Page 1 of 3 Talking Points Why did you do this Project? Provide a reason or reasons for having chosen the research question you did. You have in interest in _____ You found an article on _____ and it caught your interest You ran across similar research and you thought of a number of things you might change…. What was your research question, hypothesis (s)? Provide your testable question Provide your hypothesis(es) State that for the purposes of conducting research, you re-framed the hypothesis into a ‘null hypothesis’. Why generate a null hypothesis? A Helping hand: While experimental hypothesis are designed to predict whether your experimental manipulation will have some effect or that certain variables will relate to each other, the null hypothesis states the opposite. The null hypothesis is the reverse possibility of the experimental hypothesis and asserts that the prediction made in the experimental hypothesis is wrong and that the predicted effect does not exist. How did you set up your experiment? Provide the rationale behind an experimental design; the roles of control, experimental, and measurable dependent variables. Explain the importance of setting up the design so that you can statistically determine whether anything happened or whether the differences you might see were by chance alone Let the judge know that you designed the study to allow for testing at numerous intervals and that you conducted multiple repetitions to improve on the precision of your results. A Helping Hand: The field of statistics is the science of learning from data. Statisticians offer essential insight in determining which data and conclusions are trustworthy. When statistical principles are correctly applied, statistical analyses tend to produce accurate results. To produce conclusions that you can trust, statisticians must ensure that all stages are correct. Statisticians work to ensure that: The design studies answer the question at hand The data is collected in a trustworthy fashion The data is analyzed appropriately reliable conclusions are constructed What kinds of statistics did you include in your study? Tell the Judge that you used descriptive statistics where possible; means and standard deviations (discuss the importance of taking variance into account. Describe the inferential techniques you used. A Helping hand: You used a t-test to determine whether the means of two groups are statistically different from one another. This analysis is appropriate whenever you want to compare the means of two independent groups. You are Page 2 of 3 assuming that the two groups are normally distributed like, for example, most students in a classroom and that the variability between the two groups is more or less the same. A t-test computes a "t-value". Larger t-values translate into smaller P-values. So the larger the t-value is the more likely the difference is significant. A "critical t-value" is the minimum t-value you need in order to have P < 0.05. If your t-value is greater than or equal to the critical t-value, then you will have a significant difference. The P can then be calculated from the t value. If the value is less than 0.05, the null hypothesis can be rejected. You used a 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) to determine whether the means of three or more groups are statistically different from one another given a single independent variable. This analysis is appropriate whenever you want to compare the means of three or more independent groups. You are assuming that the two groups are normally distributed like, for example, most students in a classroom and that the variability between the two groups is more or less the same. Tell the Judge that the ANOVA is based on comparing the variation between the data samples in different groups to the variation within each particular group sample. If the between variation is much larger than the within variation, the means of different samples will not be equal. If the between and within variations are approximately the same size, then there will be no significant differences between group means. Assumptions of ANOVA: (1) All data groupings involved follow a normal distribution, (2) all groupings have more or less the same variance (or standard deviation), (3) the samples within each group are randomly selected and independent of one another. Inform the judge that the third assumption may not have been as carefully managed, you are working to improve the design. Consider the following 1-way ANOVA results: Page 3 of 3 The F ratio is the ratio of two mean square values. If the null hypothesis is true, you expect F to have a value close to 1.0 most of the time. A large F ratio means that the variation among group means is more than you'd expect to see by chance. This suggests that you might be able to reject the null hypothesis. The P value is computed from the F ratio which is computed from the ANOVA table. If the overall P value is large, the data do not give you any reason to conclude that the means differ. If the overall P value is small, then it is unlikely that the differences you observed are due to random sampling. You can reject the null hypothesis. What did you learn from your research? Report what you discovered during the course of your research. What do the results tell you insofar as any larger issues addressed by your exploration are concerned? You should also use this opportunity to describe any additional research you might pursue.