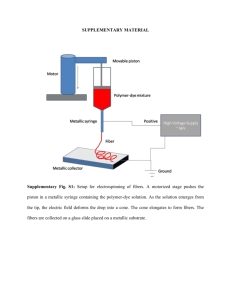
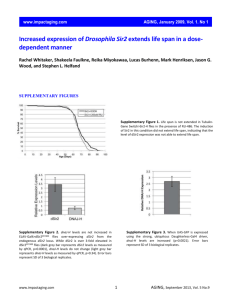
Supplement 2
advertisement

Supplementary Figure S1. Representative tissues and samples used in this study from Campeiostachys nutans accession “Xiahe No. 2” used in this study. (A) callus cells. (B) plumule (seven days after seed germination). (C) whole seedling (three weeks after seed germination). (D) tufted leaves in the tillering stage. (E) flag leaves in the heading stage. (F) stems (less lignified young stems, moderately lignified stems, and highly lignified old stems). (G) young inflorescences (10 days before fertilization). (H) inflorescences (five days before fertilization). (I) old inflorescences (five days after fertilization). Supplementary Figure S2. Gene ontology (GO) classification of assembled C. nutans unigenes. In total, 43,882 unigenes with BLASTx matches were assigned to three main categories: biological process, cellular component, and molecular function. Supplementary Figure S3. Clusters of Orthologous Groups (COG) classification. In total, 22,636 of the 66,514 sequences with Nr hits were grouped into 25 COG classifications. Supplementary Figure S4. The statistics of SSR length distribution. In total, 195 types of motifs were identified in the SSRs. Supplementary Figure S5: Gene ontology (GO) term enrichment status for SSR repeatcontaining unigenes in C. nutans. (A) molecular function. (B) cellular component. (C) biological process. The scale shows the p-value cutoff levels for each biological process. A deeper color denotes a more significant biological pathway. Supplementary Figure S6: Gene ontology (GO) term enrichment status for the SSR repeatcontaining unigenes in two dicots. (A) molecular function, (B) biological process of SSR repeat-containing unigenes in V. sativa. (C) molecular function, (D) biological process of SSR repeat-containing unigenes in M. sativa. There are no significant results for “Cellular Component” in the two species. The scale shows the p-value cutoff levels for each biological process. A deeper color denotes a more significant biological pathway. Supplementary Figure S7. EST-SSR marker variations at the Cn-32, Cn-192, Cn-468 and Cn-476 loci of 16 C. nutans accessions. Each accession includes three individual plants. The corresponding detailed information for the 16 C. nutans accessions is shown in Supplementary Table S1. The letter ‘M’ denotes the molecular markers, which are 200 bp, 150 bp, and 100 bp (top to bottom) in Cn-32 and Cn-192, and 150 bp and 100 bp in Cn-468 and Cn-476 (top to bottom). Supplementary Figure S8. Phylogenetic analysis of 16 C. nutans accessions. Pop 1 through Pop 16 represent the 16 C. nutans accessions. The corresponding detailed information for the 16 C. nutans accessions is shown in Supplementary Table S1.