lesson 1 - How do different metals react - Durham-iPads
advertisement

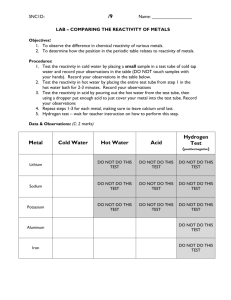
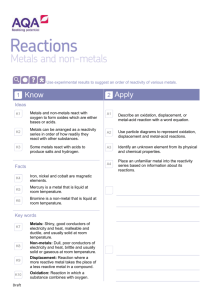
Science Lesson Plan CLASS 8B1 DATE 14th June 2012 TIME 9:00-10:00 THE BIG PICTURE – What will pupils learn by the end of this unit of work? Reactivity THE LITTLE PICTURE – Setting the scene - Lesson 1 – How do different metals react? Learning Objectives Learning outcomes Investigate metal reacting with water State what happens when metals are reacted with water. Analyse the difference in reaction intensity. Construct a series of reactivity. HOMEWORK – STARTER- Give the above LO for the lesson. Stimulate curiosity Demo Na, Li and K – Use open questions to determine the differences in reaction (pupils have already seen this). Alternatively use the ipads and QR reader to view videos of the reaction of caesium and rubidium with water. QR codes are placed on the tables. This is used to stimulate curiosity and allow pupils to question what they will be learning about today. MAIN Take action Pupils to conduct own experiment with Ca, Mg, Cu and Zn in water. They will use the ipads to take a photo of each reaction. They will then use ‘show me’ to produce a presentation about the reactivity of each of the metals in water, it should include: What do they see – are there any differences? How do they differ to the first 3 reactions? Show the presentations on the interactive whiteboard. Differentiation - G&T /SEN G&T could use Mg powder as well as strips – does surface area make a difference? De-Brief (thinking skills)/ PLENARY Pupils in groups decide which metal is the most reactive, and place them in a reactivity series. Where would they place sodium and potassium? Show a full reactivity series. Highlight any metals that have not been seen. Why is Gold at the bottom? Why is Carbon in the series? RISK ASSESSMENT Needed for metals and water expt. FUNCTIONAL SKILLS PLT Independent enquirers – identify Q’s / make predictions/ plan and carry out practical activities to obtain and analyse data/ evaluate exploring ideas and making their own connections work confidently with others/ decide on appropriate Creative thinkers Team workers - distribution of task/ take responsibility for their own contribution / listen to and take account of different views/ through peer review, provide constructive support and feedback organise themselves communicate scientific information / contribute to presentations and discussions evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of themselves and others / setting realistic goals with criteria for success / monitor their own performance and progress, inviting feedback from others and making changes to further their learning. Self-managers Effective participators Reflective learners - ASSESSMENT FOR LEARNING Starter – verbal feedback Main – observation of groups/ feedback from groups/production of work on Show me De-brief /Plenary – verbal – answers to questions/group work Easington Community Science College Easington Community Science College Easington Community Science College






![afl_mat[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005387843_1-8371eaaba182de7da429cb4369cd28fc-300x300.png)