Design in electronics - Zoe-s-wiki
advertisement

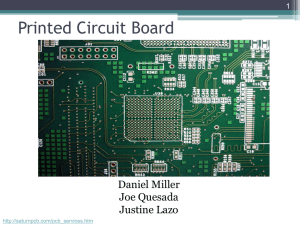
Design & Technology Design in electronics A well-designed and manufactured product starts with good planning and documentation including a design brief [design brief: a set of instructions given to a designer by a client. ] and specification [specification: a statement that tells the designer exactly what the product has to do and what the design requirements are. ]. Circuits are first modelled using a prototype board, before being assembled into a PCB [PCB: Printed Circuit Board ]. Evaluation and testing needs to be built in at critical control points [critical control points: the predefined points in a manufacture system where quality control checks take place. ] such as initial design, breadboard and PCB phases, and at the manufacturing stage. And you need to be familiar with the ways that CAD[an error occurred while processing this directive] is used in the electronics design process. The design procedure A design procedure is a series of steps which guide you through any electronic design-and-make process. Sticking to the procedure will help deliver a first-class product. Following a design process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Choose an area of study Write down in a few words the purpose of the project Prepare a desin brief Write down a specification Carry out research Use graphics, computer software and other techniques to generate design ideas 7. Select the best design for further development Once you have defined the purpose of your project, there are two important documents you need to write. These are: the design brief - a short statement of the problem to be solved. The brief should outline the design problem you are tackling, perhaps including one or two of the envisaged design features. Next comes the design specification . This is a longer decument, including full details of the functional and design features of the finished electronic product - as well as information on weight and size, maintenance, cost and safety. The specification for an electronic product should include electronic factors such as component details, maximum working voltages, maximum currents, and temperature or frequency ranges. Ergonomics and aesthetics The factors which make a product efficient, safe and comfortable to use are called ergonomics. Considerations of style - the things which make a product look and feel good - are called aesthetics. You need to consider both ergonomic and aesthetic factors when planning your designs. When designing circuits, for example, ensure that switches and other control components are placed so that they can be easily reached, and that output components such as LEDs can be easily seen. A product's style is a more subjective matter, as different people may have different ideas of what looks good. Think about contemporary style, about what is currently fashionable, when designing your product. You may not want to follow the fashion - but you still need to know what it is! Circuit modelling Circuits can be modelled to make sure they work the way you want them to. Circuit modelling can be done either using a computer modelling application, or on a prototype board - also called a breadboard or veroboard - a board covered with small sockets into which components can be plugged and connected up. The graphic shows a breadboard with holes connected in two long rows at the top and bottom, and columns of five linked holes elsewhere. Electronic components and wires can be simply plugged into the board in order to make any required circuit connections. The top and bottom rows act as power supply channels for the circuit. breadboard, showing pattern of holes and connections for prototyping circuits A breadboard prototype for a 555 monostable timer circuit might look like this: breadboard showing a 555 timer circuit layout Printed circuit boards (PCBs) Once it has been established that the circuit functions as intended, the next step is usually to make a printed circuit board. PCB showing copper connections running beneath the board Making a PCB The first step is to draw the circuit on to a mask. This is a kind of filter which protects the 'positive' parts of the diagram (the connections between components) and exposes the 'negative' parts (all the rest). The mask is then placed on the board which has a thin coating of copper, and the circuit diagram transferred onto the board using an etch-resist pen. (An alternative technique uses a photosensitive board which is covered by the mask and then exposed to light.) The circuit is then etched onto the board using iron (III) chloride in an etching tank; this removes all the unwanted copper, leaving the req uired tracks and pads in place on the board. NB - this should only be done under a teacher's supervision. Next, a small PCB drill is used to drill out the center of the pads. Finally the components are pushed through the board and soldered in place. The graphic below shows a mask [mask: a filter or partial covering which protects some parts of a plate, while allowing the remaining parts to be exposed to acid or light. ] for a 555 monostable timer circuit, ready for transferring to a board. Note that masks are normally shown from the component side - that is, as though the board was transparent and viewed from the side from which the components are pushed through. PCB mask of 555 timer circuit With the components installed, the board would look like this: PCB with 555 timer circuit components Soldering In electronics the main method of joining circuits is soldering. Electrical solder is made from an alloy of 65 percent tin and 35 percent lead. It also has a flux running through its core. The flux is needed to ensure that the solder makes a good joint between the components and the tracks and wires on the PCB. Evaluation and testing Evaluation and testing is about making sure that the product stays on track with the design specification [specification: a statement that tells the designer exactly what the product has to do and what the design requirements are. ]. You should plan to evaluate and test your project at a number of key stages of design and manufacture. These stages are referred to as critical control points. The critical control points for evaluation and testing an electronic product are: 1. Initial design phase. Check that you have used the correct value components, and that the various systems work together. These checks can be done using a computer-simulation package. 2. Breadboard phase. Use the breadboard [breadboard: a prototype circuit made from a plastic board with holes in which the components are inserted, linked by conductor traces on the underside. Also called a veroboard. ] to check whether the circuit works properly. Test each part of the circuit using a multimeter or logic probe. 3. PCB layout. Check that the components are in the correct positions and that you have used the optimum track layout. Make sure that components are located neatly and that joints are well-soldered. 4. Manufacturing and packaging phase. After manufacture, check that the product conforms to its specification. During packaging, check that the product fits securely in the package, and that any conducting parts are insulated. 5. Finally, the analysis phase. Look back over the design and making process. Analyse how well it went, noting down any modifications and improvements you would make if you were to do it again. These notes are an important part of your design portfolio. Keep notes! Make a note of each stage in your design process. If possible, illustrate your notes with digital photographs and/or graphics. Here are some of the things you should include in your notes: The source of your design ideas and how you adapted these ideas into the intended product. The design specification for the product. Your design developments. These should include the circuit designs with annotated notes, circuit diagrams, any computer program simulation work, evidence of bread boarding and testing and the design of your packaging etc. The testing procedure and evaluation. ICT in electronics design There are many advantages to using computers in electronics design. They speed up the design process, enabling changes to be made very quickly. They enable circuits and products to be modelled before manufacture. And they make it easy and cheap to store and edit design specifications, and then download them onto machines for manufacturing. Computer software specially written to facilitate product design is called CAD[an error occurred while processing this directive] software. 555 timer circuit diagram produced using CAD software Several different CAD packages can be used to build up and test circuits on screen, so that you can try out a circuit before making it, or design a PCB [PCB: Printed Circuit Board ] or vero-board. Crocodile Clips, Livewire, and PCB Wizard are three common circuit-modelling packages. Designers also use CAD to make accurate 2D and 3D drawings of circuits and products, and for solid modelling [solid modelling: use of digital drawings based on geometric shapes, used for solid objects such as car components. ] to show how products will look when finished. Different colours and textures can be added to the model and the product can be rotated to show different views. Computers are often used to design electronic logic gates for PIC circuits [PIC circuits: circuits controlled by a PIC (Programmable Interface Controller) - a device which can be programmed by a computer to control complex circuits ]. PIC programs are usually built up from a computerised flow chart [flow chart: a graphic outline of the sequence of operations needed to complete a task ], and then be burnt or downloaded onto a PIC chip. Now try a Test Bite Back to Revision Bite