cell cycle

Cell Cycle and Mitosis Videos, 2015 www.discoveryeducation.com
username nbrown@mayfieldschools.org
password discoveryeducation
“The cell cycle and mitosis: Introduction” 8 segments. Standard deviants
Biology review series, 2002 —2004, Cerebellum. (module one)
1 Where do cells come from? _______________________________
2 The path cells must follow is called the _________ ___________.
3 During asexual cell divisions, one cell divides into two cells that are genetically
_______________________.
4 The name for asexual cell division of a eukaryotic cell is called
_____________________.
5Some terms you need:
Nucleus-
Nucleolus
Nuclear membrane
Chromatin
DNA
Chromatids/chromosomes
Sister chromatids
Centromere
Cytokinesis
Daughter cells
6 Before animal cells, like human cells divide, they are termed “2n”. a. What does 2n mean for cells in general? B. What does 2N mean for human cells?
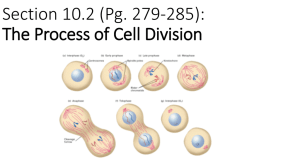
7 Sketch a diagram for the cell cycle.
8. What are the parts of the major Segment of the cell cycle called
“interphase”?
9. What are the parts of the major segment of the cell cycle called “mitosis”?
10. What happens after mitosis is complete?
11. During interphase, DNA content of diploid (2N during G1) cells changes from 2n to 4n. What does this mean?
12. What events are most important during the G1 segment of interphase?
13. What events are most important during the S segment of interphase?
14. What events are most important during the G2 segment of interphase.
15. The reason that that cells in S phase have their DNA called chromatin , instead of chromosomes, is that
_______________________________________________________________
______________________.
16. Mitosis is the actual splitting of the _____________________ of the cell. At the start of mitosis, the cell is ____n due to the copying of DNA during S phase.
At the end of mitosis, because the nucleus has divided, the two daughter cells produced are _____n again, just like the original mother cell!
17. a. During the 1 st part of mitosis, called P____________________, the chromatin becomes visible and is called
_____________________________________. Because during S phase the chromatin was duplicated, the chromosomes present during prophase are called sister chromatids. B. Explain how sister chromatids are analogous to
Siamese twins. (use the term centromere in your explanation).
18. The nuclear membrane has been broken down prior to prophase, then the mitotic spindle forms between the centrioles (in animal & fungal cells)/centrosomes (protists & plant cells). A. Draw an animal cell during mitosis, labeling the: Centrioles, spindle, , cytoplasm, and cell membrane. B.
Pro- means __________.
19. a. Draw a cell having 2 red and 2 blue pairs of sister chromatids (so 2n=4 before S phase, but 4n=8 after S phase and before cytokinesis) at Metaphase of mitosis. Label: cell membrane, cytoplasm, centrioles, spindle fibers, equator, and a pair of sister chromatids. B. Meta- means ______________________
20. a. Use the siamest twin analogy to explain what happens to the DNA of the cell during anaphase. B. Draw a 4n animal cell having 2 blue and 2 red pairs of sister chromatids during anaphase, labeling: spindle, centrioles, cytoplasm, centromeres, and chromatids. C. Explain why this cell is still 4n.
21. a. During telophase, the separated duplicated chromosomes are placed into two new ___________________. B. During cytokinesis in animal cells, the cell is split into 2 new ____________________________ cells via development of a cleavage _______________________. During cytokinesis of plant cells, the cell is split into 2 new ____________________________ cells via development of a cell ____________________. The two new cells are
_______n and are genetically _______________________.
22. Write an analogy for remembering the parts of the cell cycle AND cytokinesis.
23. The only animal cells that do NOT reproduce by mitosis are
_______________ cells, called _______________ in males and
____________________ in females These cells undergo sexual cell division called _______________________________.
KEY Cell Cycle and Mitosis Videos, 2015 www.discoveryeducation.com
username nbrown@mayfieldschools.org
password discoveryeducation
“The cell cycle and mitosis: Introduction” 8 segments. Standard deviants
Biology review series, 2002 —2004, Cerebellum. (module one)
1 Where do cells come from? __division of pre-existing cells____
2 The path cells must follow is called the cell cycle
3 During asexual cell divisions, one cell divides into two cells that are genetically identical to the cell that divided and to each other
4 The name for asexual cell division of a eukaryotic cell is called _mitosis_.
5Some terms you need:
Nucleus —in eukaryotic cell, a membrane enclosed organelle enclosing the DNA
Nucleolus —part of the nucleus where ribosomes are made
Nuclear membrane —membrane surrounding the nucleus
Chromatin —the less densely packed form of chromosomes—not visible by a light microscope and existing during interphase.
DNA —a double helical molecule that is the molecule controlling heredity
Chromatids/chromosomes —each is constructed of a single long double helix of DNA wrapped tightly around proteins that coil it into a form that can be seen with a light microscope; each contains a particular group of genes. Exists during the mitotic phase of the cell cycle.
Sister chromatids —the two identical copies of a double helix that are generated during S phase
Centromere —the location where sister chromatids are connected until the end of metaphase.
Cytokinesis —the division of the cytoplasm after the end of the mitotic phase, generating 2 daughter cells
Daughter cells —the two genetically identical cells produced after the completion of a mitotic cell cycle and cytokinesis
6 Before animal cells, like human cells divide, they are termed “2n”. a. What does 2n mean for cells in general? B. What does 2N mean for human cells? a. 2 for 2 sets and n for the number of chromosomes in 1 set, diploid b. For human cells, each cell contains one set of 23 chromosomes from the person’s mother and another set of 23 chromosomes from the person’s father, so 2n for humans = 46.
7 Sketch a diagram for the cell cycle. See textbook or study guide
8. What are the parts of the major Segment of the cell cycle called
“interphase”? G1, S, G2
9. What are the part s of the major segment of the cell cycle called “mitosis”?
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase
10. What happens after mitosis is complete? Cytokinesis splits the cytoplasm so that two daughter cells form
11. During interphase, DNA content of diploid (2N during G1) cells changes from 2n to 4n. What does this mean? Every chromosome is copied, so that 4 sets of chromosomes exist in the cell.
12. What events are most important during the G1 segment of interphase?
Growth and development
13. What events are most important during the S segment of interphase?
Replication of each chromosome
14. What events are most important during the G2 segment of interphase.
More growth and development and preparation of the cell for entry to the mitotic phase.
15. The reason that that cells in S phase have their DNA called chromatin , instead of chromosomes, is that DNA is more loosely packed around proteins during replication than during mitosis —it isn’t visible by a light microscope during S phase.
16. Mitosis is the actual splitting of the _replicated genome(nucleas)_ of the cell. At the start of mitosis, the cell is 4n due to the copying of DNA during S phase. At the end of mitosis, because the nucleus has divided, the two daughter cells produced are _2n again, just like the original mother cell!
17. a. During the 1 st part of mitosis, called Prophase, the chromatin becomes visible and is called _chromatids or chromosomes_. Because during S phase the chromatin was duplicated, the chromosomes present during prophase are called sister chromatids. B. Explain how sister chromatids are analogous to
Siamese twins. (use the term centromere in your explanation). Both are identical copies joined together
18. The nuclear membrane has been broken down prior to prophase, then the mitotic spindle forms between the centrioles (in animal & fungal cells)/centrosomes (protists & plant cells). A. Draw an animal cell during mitosis, labeling the: Centrioles, spindle, , cytoplasm, and cell membrane. See textbook & illustration at the end of this key B. Pro- means early or before__________.
19. a. Draw a cell having 2 red and 2 blue pairs of sister chromatids (so 2n=4 before S phase, but 4n=8 after S phase and before cytokinesis) at Metaphase of mitosis. Label: cell membrane, cytoplasm, centrioles, spindle fibers, equator, and a pair of sister chromatids. See textbook & illustration at the end of this key
B. Meta- means middle
20. a. Use the siamese twin analogy to explain what happens to the DNA of the cell during anaphase. The identical copies have their connection removed so that they are freed from each other B. Draw a 4n animal cell having 2 blue and 2 red pairs of sister chromatids during anaphase, labeling: spindle, centrioles, cytoplasm, centromeres, and chromatids. See textbook C. Explain why this cell is still 4n. both sister chromatids are still present in one cell!
Cell membrane
G2 4n=8
Metaphase 4n=8
Anaphase 4n=8
G1, 2n=4
Cytoplasm
Centrioles
Cell membrane spindle
After telophase and cytokinesis, 2 daugher cells each 2n=4
21. a. During telophase, the separated duplicated chromosomes are placed into two new ___________________. B. During cytokinesis in animal cells, the cell is split into 2 new ____________________________ cells via development of a cleavage _______________________. During cytokinesis of plant cells, the cell is split into 2 new ____________________________ cells via development of a cell ____________________. The two new cells are
_______n and are genetically _______________________.
22. Write an analogy for remembering the parts of the cell cycle AND cytokinesis.
23. The only animal cells that do NOT reproduce by mitosis are
_______________ cells, called _______________ in males and
____________________ in females These cells undergo sexual cell division called _______________________________.