10 – 2 Cell Division
advertisement
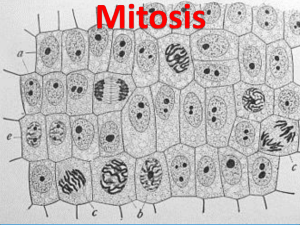
10 – 2 Cell Division Mitosis Chromosomes DNA is passed on in chromosomes Every organism has a specific # of chromosomes: fruit flies 8 humans 46 Before division called sister “chromatids” Chromatids are attached with a centromere and become … Chromosomes are only visible during cell division The Cell Cycle During the cell cycle, a cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form 2 daughter cells, each of which then begins the cell cycle again. 1. Interphase = growth 2. Mitosis = division Events of the Cell Cycle Interphase centrioles Period of growth Hereditary material is in the form of chromatin 3 stages: G1 - “growth” Increase in cell size in # of organelles, and in # of proteins S – “synthesis” nucleolus DNA replication (chromatin is doubled) G2 – “growth” Continued cell growth chromatin Mitosis Begins Mitosis is when a cell divides into two new cells. Mitosis is one of the shortest parts of a cells life. However, it has the most stages. CELLSALIVE.COM Mitosis (1. prophase) Mitosis – period of cell division 4 stages: Sister chromatid Prophase – “prepare” Longest phase of mitosis Chromatin coils up and forms chromosomes Duplicated chromosmes are made up of 2 identical sister chromatids connected at the centromeres centromere Identical Sister chromatid Mitsosis (1. prophase) Prophase (continued) Nucleolus and nuclear membrane fade away, causing the nucleus to disappear. Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell Centrioles – cylindrical structures made of microtubles Spindle fibers form between the centrioles spindle Spindle – Pulls the sister chromatides apart. *the spindle attaches to the chromosome at the centromere* centriole Mitosis (2. Metaphase) Metaphase “middle” Chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers at their centromere Chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell (equator) Mitosis (3. Anaphase) Anaphase – “apart” Sister chromatids are pulled apart by centrioles. Mitosis (4. Telophase) Telophase – “tear into two” Chromatids reach the opposite sides (pole) of the cell Chromosomes uncoil or unwind (chromatin) Spindle fibers begin to break down Nucleolus reappears New nuclear membrane forms around each new set of chromosomes Plasma membrane begins to separate into 2 new nuclei Cytokinesis Division of cytoplasm In animals: “cleavage furrow” pinches the plasma membrane to divide the cytoplasm In plants: “cell plate” forms to divide the cytoplasm Cell division-again! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q6ucKWII Fmg