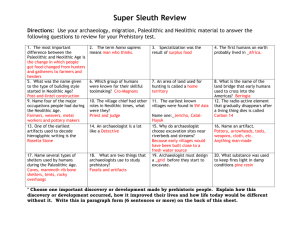
6th Grade SS Unit 1 2015-16
advertisement

DPS Unit Map 6th Grade SS Unit 1: Geography & First Human Societies 5 Weeks Stage 1: Examine and Unpack Standards These unpacked standards are expected in every Durham Public Schools classroom. UNIT STANDARDS Social Studies 6.H.2.3 - Explain how innovation and/or technology transformed civilizations, societies and regions over time. 6.G.1.1 Explain how the physical features and human characteristics of a place influenced the development of civilizations, societies and regions. 6.G.1.2 - Explain the factors that influenced the movement of people, goods, and ideas and the effects of that movement on societies and regions over time. 6.G.1.4 - Explain how and why civilizations, societies and regions have used, modified and adapted to their environments. 6.G.2.1 - Use maps, charts, graphs, geographic data and available technology tools to draw conclusions about the emergence, expansion and decline of civilizations, societies and regions. Common Core/Literacy RH.6-8.1 - Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources. RH.6-8.2 - Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of the source distinct from prior knowledge or opinions. WHST.6-8.1.A - Introduce claim(s) about a topic or issue, acknowledge and distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and organize the reasons and evidence logically. Transfer Students will be able to independently use their learning to… Demonstrate an understanding of geography and the development of a civilization Making Meaning UNDERSTANDINGS ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Students will understand that… 1. How does geography influence the way 1. Innovation or technology can be temporary or people live? long lasting and have positive or negative 2. What is history? consequences. 3. How do people adapt to their environment? 2. Physical features and human characteristics may influence the emergence, expansion and decline of civilizations, societies and regions. 3. Scarcity of resources can often be motivating factors in influencing the movement of people, goods and ideas. 4. Civilizations and societies adapt to the environment in order to meet needs. Acquisition KNOWLEDGE SKILLS Students will know… Students will be able to… 1. Humans may adapt their behavior as their 1. Demonstrate an understanding of geography environment changes. and the development of a civilization 2. Regions are the basic unit of study in geography. 2. Interpret and draw conclusions from maps, 3. Factors that motivate the movement of people, charts, graphs and geographic data. goods and ideas. 3. Cite textual evidence to support analysis of 4. Physical features of a place may include climate, primary sources. landforms, soils, and vegetation. 4. Present a claim about an issue, distinguish 5. Innovation and technology includes more than the claim from alternate claims, and just inventions. Innovation can include organize evidence logically. thoughts, processes and procedures. Key Vocabulary Tier 3 Vocabulary Words Domesticate, Archaeology, Agrarian, Artifact, Culture Tier 2 Vocabulary Words Migration, Location, Population, Place, Scale, Technology, Region, Movement, Hemisphere, Physical Map, Key/Legend, Political Map, Longitude, Latitude Curriculum, Instruction and Assessment Page 1 of 4 DPS Unit Map 6th Grade SS Unit 1: Geography & First Human Societies 5 Weeks Notable Individuals, Places, Events, and Documents Stone Ages, Otzi, Neolithic, Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Lucy Stage 2: Calibrate Rigor and Design Assessment Evaluative Criteria for Assessment District Provided Assessment Tasks Rubric Criteria Addressing the prompt Cite Evidence (from text – primary or secondary sources) 1 The product does not address the goal of the performance task. There is no evidence to support the answer. No attempts to explain how the evidence Explain addresses the prompt have been made. Conventions Many grammatical errors exist that obscure meaning. Curriculum, Instruction and Assessment 2 The product partially addresses the goal of the performance task. Examples are provided that loosely support the answer. The attempts to explain how the evidence addresses the prompt are unclear or insufficient. Some grammatical errors exist, but do not obscure meaning. 3 The product addresses the goal of the performance task. Examples are provided that fully support the answer. The explanation of the evidence is clear and insightful. No grammatical errors exist. Performance Task (Option 1) Goal - Students will work in small groups to create presentations that identify and compare cultural adaptations to geographic environments. Role – Geographers Audience – Classmates Situation – Students will begin by participating in a discussion about the different areas of their school building, the characteristics of each area (physical, social environment for students, etc.) and how they adapt to each environment. Next, students will choose a region of the world and research how people in that region of the world adapt to their environment. Product – Students will create presentations that compare people’s methods of adapting to their environments and present these methods to the class. Performance Task (Option 2) Part 1 - Students will create a comic strip that shows the changes in people's lives from the Paleolithic age to the Neolithic age. The comic strip should include, but not be limited to the following topics: 1. food supply - how does the type of food eaten changed as well as how it is acquired 2. shelter - what are the changes? 3. tools/weapons - what are the changes? 4. jobs - transitioning from hunter/gatherer to farming; what jobs need to be done in order to survive? 5. religion - the fact they go from no religion to an idea of religion/afterlife in the Neolithic age The comic strip should have dialogue, illustrations, captions that show knowledge of the above topics. Part 2 - Writing Explain the challenges of being a hunter/gatherer and why it would be beneficial to begin farming as done in the Neolithic age. You need to include an opening statement, an explanation as to why it is challenging to be a hunter/gatherer, the benefits of farming, closing statement Page 2 of 4 DPS Unit Map 6th Grade SS Unit 1: Geography & First Human Societies 5 Weeks Other Evidence – Embedded Stage 3 Learning Events Teacher designed Teacher designed DPS 6-8 RACER & ACES + C Rubric PLC designed Minute by Minute Assessments Speech, Debate or Socratic Seminar Text-Dependent Constructed Response Questions PLC-Created Text or Concept Specific Common Formative Assessments Stage 3: Plan and Deliver Instruction This instructional pacing and sequencing represents one best practice option. Professional Resources Instructional Resources Resources for Unit Concepts: Teachers to Watch: Summary of Key Learning Events, Opportunities, and Instruction Standard(s) Support 6.G.2.1 http://goo.gl/sbou0h http://goo.gl/PLCVJV The first few days of the school year may need to be used to introduce students to class and school procedures. This unit will begin with map skills. Students will explore maps and discuss the different types of maps (i.e. physical, political, climate, population, etc) and their purposes. Students should identify the four main parts of a map (title, key, scale, compass). 1 # of Days 3 Focus of Lesson Map Skills 2 5 Five Themes of Geography 6.G.1.1, 6.G.1.2, 6.G.1.4 3 7 The Paleolithic Era and the 6.H.2.3 Curriculum, Instruction and Assessment http://goo.gl/lJaAcz We will then continue our study of the geography. Students will locate and label the continents, the oceans, equator, and prime meridian. This is foundational information which they will use in our global study throughout the year. Then students will study each of the five themes of geography, defining the terms and then applying them. For example, students may use absolute location (longitude and latitude) to locate points on a map while using a school map and relative location for the same end goal. After a literary passage (type “country profile” into cbbc site below and choose) about a certain region, they may differentiate between the physical and human (cultural) characteristics of a place in a t-chart. This is a great opportunity to also mention key vocabulary about specific landforms (i.e. peninsula, island, etc.) while discussing physical characteristics. Movement can be addressed discussing how people, goods, and ideas spread throughout the globe. Human-Environment interaction may be illustrated with a comparison of a section of land 100 years ago and that of today. Region may be studied using the four corners of the room as different regions that students may go to depending on the topic (i.e. birth city, favorite sport, etc). http://goo.gl/VSiYYz Page 3 of 4 DPS Unit Map 6th Grade SS Unit 1: Geography & First Human Societies First Humans 4 5 The Neolithic Era 6.H.2.3 5 5 Review and Assessment All Curriculum, Instruction and Assessment 5 Weeks http://goo.gl/Bxg5il Students will begin their study of the beginning of human societies. It will aid students in their understanding if key vocabulary words (i.e. migration, archaeologists, artifacts, etc.) are discussed at this time. Students should examine the mass migration of humans. Students will describe characteristics of the nomadic lifestyle of the Paleolithic Era and explain why people lived in this style. They will examine the techniques, technology, and development of society that fit with this way of life. http://goo.gl/FFyzh3 Students will move on to the emergence of agrarian societies in the Neolithic Era. They will examine the techniques, technology, and development of society that fit with this way of life during the Neolithic Age. Students should be able to compare and contrast the Neolithic and Paleolithic Eras. Next students can explore the life of Otzi the Iceman, the preserved mummy of the man that lived over 5300 years ago during the Stone Ages. As students study the items left with Otzi and his story, they should be able to analyze the artifacts and evidence to come up with their own theory on Otzi’s demise. Students will also be able to explain why Otzi and his belongings are artifacts of the Stone Ages and draw conclusions from this evidence. Complete Performance Task listed above Page 4 of 4