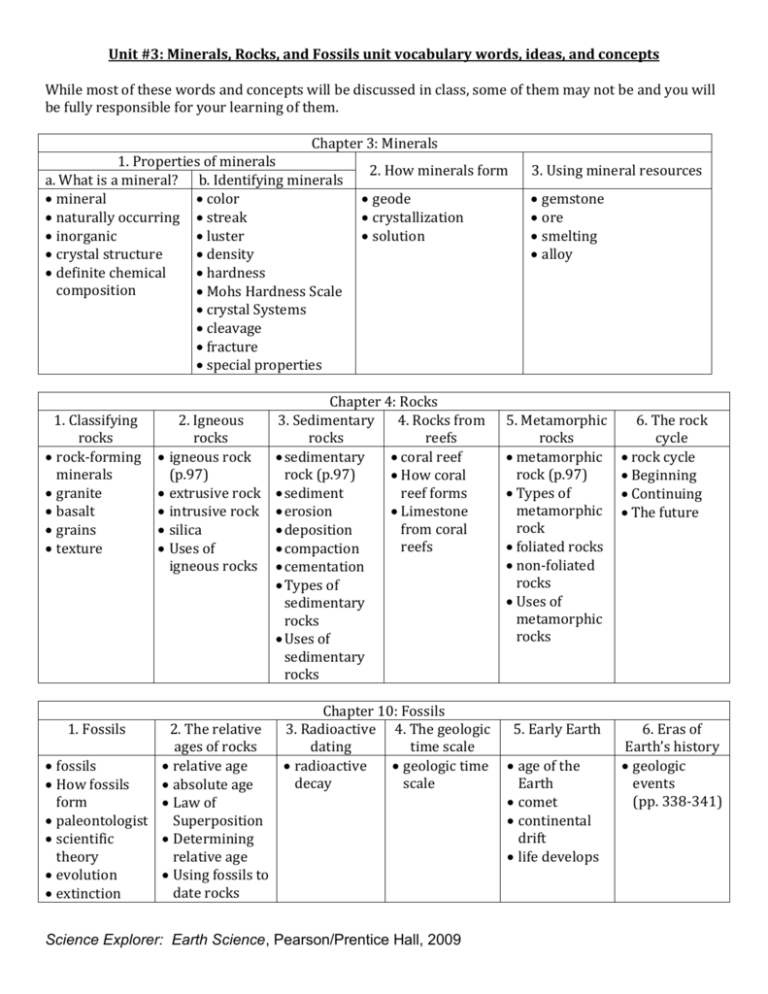
Unit #3: Minerals, Rocks, and Fossils unit vocabulary words, ideas, and concepts
While most of these words and concepts will be discussed in class, some of them may not be and you will
be fully responsible for your learning of them.
Chapter 3: Minerals
1. Properties of minerals
a. What is a mineral? b. Identifying minerals
mineral
color
naturally occurring streak
inorganic
luster
crystal structure
density
definite chemical
hardness
composition
Mohs Hardness Scale
crystal Systems
cleavage
fracture
special properties
1. Classifying
rocks
rock-forming
minerals
granite
basalt
grains
texture
1. Fossils
2. Igneous
rocks
igneous rock
(p.97)
extrusive rock
intrusive rock
silica
Uses of
igneous rocks
2. The relative
ages of rocks
fossils
relative age
How fossils
absolute age
form
Law of
paleontologist
Superposition
scientific
Determining
theory
relative age
evolution
Using fossils to
date rocks
extinction
2. How minerals form
geode
crystallization
solution
Chapter 4: Rocks
3. Sedimentary
4. Rocks from
rocks
reefs
sedimentary
coral reef
rock (p.97)
How coral
sediment
reef forms
erosion
Limestone
from coral
deposition
reefs
compaction
cementation
Types of
sedimentary
rocks
Uses of
sedimentary
rocks
Chapter 10: Fossils
3. Radioactive 4. The geologic
dating
time scale
radioactive
geologic time
decay
scale
Science Explorer: Earth Science, Pearson/Prentice Hall, 2009
3. Using mineral resources
gemstone
ore
smelting
alloy
5. Metamorphic
rocks
metamorphic
rock (p.97)
Types of
metamorphic
rock
foliated rocks
non-foliated
rocks
Uses of
metamorphic
rocks
5. Early Earth
age of the
Earth
comet
continental
drift
life develops
6. The rock
cycle
rock cycle
Beginning
Continuing
The future
6. Eras of
Earth’s history
geologic
events
(pp. 338-341)
Unit #3: Rocks, Minerals, & Fossils
Strand: Earth & Space Science
Substrand: Earth Structure and Processes
Standard: 8.3.1.3. Rocks: Rocks and rock formations indicate evidence of the materials and conditions
that produced them.
Benchmarks: 1. Layers of Rocks & Fossils: Interpret successive layers of sedimentary rocks and their
fossils to infer relative ages of rock sequences, past geologic events, changes in environmental conditions,
and the appearance and extinction of life forms.
2. Rock & Mineral Characteristics: Classify and identify rocks and minerals using characteristics including,
but not limited to, density, hardness and streak for minerals; and texture and composition for rocks.
3. Formation of Rocks: Relate rock composition and texture to physical conditions at the time of formation
of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rock.
Unit Question: What makes up much of the world around me?
Area of Interaction: Environment
* Where do we live? * What resources do we have or need?
* What are our responsibilities?
Significant Concept: The Earth is made of many valuable yet limited resources, and we must consider
how these resources are made as well as how we use them in order to be responsible with them.
MYP Unit Assessment Criterion: B: Communication in science
Objective 1: Using sufficient scientific language
Objective 2: Using effective communication methods
Objective 3: Referencing resources used in research
MYP Unit Task Assessment: Rock or mineral research project (display & presentation)
Suggested method of recording vocabulary words, ideas, and concepts:
Word, idea, concept
Date and Title of Notes
Definition, explanation, description
Memory cue, picture, movement
Studying words, ideas, and concepts:
1. Identify the word, idea, concept, etc.
2. Create a definition, explanation, description, etc. in your own words.
3. Create a memory cue to help you remember. Use what you see, what you hear, a physical
movement, or touch as memory cues. Try using colors, as well.
4. Study new ideas for 10-15 minutes each night. Test yourself, test friends, create flash cards, write
down questions to ask the teacher the next day, etc. Write down the answers to your questions.
5. Continue practicing new and past words a little bit every day.
Science Explorer: Earth Science, Pearson/Prentice Hall, 2009










