Reviewing Stoichiometry Vocabulary
advertisement

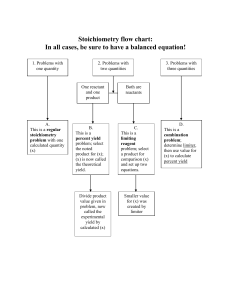
Name____________________________________ Date__________________________Pd________ Reviewing Stoichiometry Vocabulary Use the following terms to complete the statements. Some terms will be used more than once. actual yield excess reactant limiting reactant percent yield mole ratio stoichiometry theoretical yield 1. The reactant that limits the extent of the reaction is called the __________________. 2. The amount of product actually produced by a chemical reaction is called the _______________. 3. A(n) __________________ is a ratio between the number of moles of any two substances in a balanced chemical equation. 4. A(n) __________________ is a reactant that has a portion remaining after the reaction has stopped. 5. The ___________________ is the maximum amount of product that can be produced from a given amount of reactant. 6. The study of the quantitative relationships among the amounts of reactants used and the amounts of products formed by a chemical reaction is called ____________________. 7. The ratio of the actual yield to the theoretical yield expressed as a percent is called the ______________________ 8. The amount of product formed during a reaction depends on the __________________. 9. A chemical reaction rarely produces the ___________________ of the product. 10. Chemists sometimes use ______________________ to speed up a chemical reaction. Name____________________________________ Date__________________________Pd________ Understanding Main Ideas (Part A) Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Stoichiometry is based on the law of conservation of a. charge. b. mass. c. reactants. d. volume. 2. In a balanced chemical equation, the numbers of individual particles and the numbers of moles of particles are represented by the a. chemical symbols. c. molar masses. b. coefficients. d. subscripts. 3. Mole ratios for a reaction are obtained from the a. balanced chemical equation. b. molar masses. c. periodic table. d. total mass of products. 4. In the decomposition reaction of compound AB into substances A and B, what is the number of mole ratios? a. 1 b. 3 c. 6 d. 9 5. Calculating the mass of a reactant and product from the number of moles of another product or reactant in a chemical equation is an example of a a. mass-to-mass conversion. c. mole-to-mass conversion. b. mass-to-mole conversion. d. mole-to-mole conversion. 6. Limiting a reactant is often accomplished by a. producing excess product. b. overcoming conservation of mass. c. slowing down a chemical reaction. d. using an excess of another reactant. 7. In a reaction, substances A and B form substance C. If the actual mole ratio of substance B to substance A is less than the balanced equation mole ratio of substance B to substance A, substance B is the a. actual yield. b. excess reactant. c. limiting reactant. d. product. 8. Percent yield of a product is a measure of a reaction’s a. efficiency. b. heat production. c. rate. d. spontaneity. 9. The actual yield of a product is a. a negative value. b. independent of the reactants. c. the same as its theoretical yield. d. measured experimentally. 10. The most important industrial chemical in the world is a. carbon dioxide. b. oxygen. c. petroleum. d. sulfuric acid.