Evolution Practice Sheet
advertisement

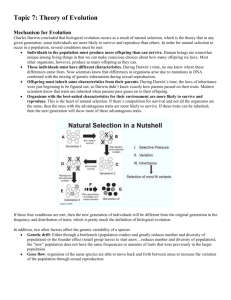
Name: _______________________________________ Date: ________________ Per: __________ #: ______ Evolution Practice Sheet Use your worksheets to complete the following: 1. _____________________An English geologist that claimed that Earth must be much older than 6,000 years old. 2. _____________________An English naturalist that had 3 things in common with Darwin: he developed a similar Theory of Evolution, tour South America, made similar observations as Darwin. 3. _____________________A French naturalist who was one of the 1st scientists to propose that traits acquired during one’s lifetime could be passed onto their offspring. 4. _____________________ A scientist that studied the effects of pollution on the peppered moth population. 5. _____________________ A scientist that began to develop his theory of natural selection aboard the HMS Beagle. Acquired Traits Inherited Traits Evolution Paleontologists Fossil Record Adaptation Vestigial Structures Natural Selection Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Overproduction Radiometric Dating Embryology Fossil Variation Successful Reproduction Competitors 6. _________________________ Traits passed on from one generation to the next. 7. _________________________ Traits organisms develop over a lifetime. 8. _________________________ Process that explains why species change over time. 9. _________________________ Type of cells that contain a nucleus. 10. _________________________ Scientists who study fossils to learn about the past. 11. _________________________ Preserved remains of organisms from the distant past. 12. _________________________ Traits differ between organisms. 13. _________________________ Organisms produce more offspring than are likely to survive. 14. _________________________ Organisms with the best traits will survive to pass them on to the next generation. 15. _________________________ The order in which fossils appear base on the layer of rock they are found in. 16. _________________________ Technique used to measure how much radioactive materials have broken down over time. 17. _________________________ Study of how organisms develop in their earliest stages of development 18. _________________________ Structures that have lost their purpose over time. An example is the tailbone in humans or the wings of ostriches. 19. _________________________ Process that states that traits that offer an advantage will be more likely to be passed along to offspring. 20. ________________________ One or more organisms that are struggling for a particular resource. 21. ________________________ A characteristic that improves an organisms ability to survive. 22. When were the two largest mass extinctions in time? How is it believed that each occurred? a. _____________________________________________________________________________________ b. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 23. Recall the fish in the pond classroom activity and Barballus Lab. Be prepared to explain a similar scenarios. 24. Explain in detail where the Industrial Revolution took place and how the peppered moth population differed before, during, and after the Industrial Revolution.___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 25. List the four major timeframes of geologic time and list two (or more) events that occurred during each. a. _____________________________________________________________________________________ b. _____________________________________________________________________________________ c. _____________________________________________________________________________________ d. _____________________________________________________________________________________ Use the diagram and paragraph below along with your knowledge of natural selection to answer the following questions. Average beak sizes of the seed-eating ground finch on one of the Galapagos Islands are shown in the diagram below. During wet years, all types of seeds are abundant. The ground finch prefers to eat small seeds that are easy to crush. However, during droughts (dry years), when small seeds are not as abundant, they eat the larger seeds on the island. 26. Why did the average beak size get larger in 1977, 1980, and 1982? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 27. How did variation exist in the ground finch population? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 28. What were the ground finches competing for? ______________ 29. Not all of the ground finches were able to survive the drought. What adaptation gave them a better chance to survive to pass on their genes to the next generation? How did this adaptation help them survive? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 30. How might an extended period of drought influence the ground finch population in the future? A. The birds with smaller beaks would be more numerous. B. The birds with larger beaks would be more numerous. C. Drought decreases seed availability, but has no influence on the ground finch. D. Drought increases seed availability, and all ground finches would be more numerous. 31. Explain your choice. ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ Name: ______ KEY_________ Date: ________________ Per: __________ #: ______ Evolution Practice Sheet Use your worksheets to complete the following: 1. CHARLES LYELL An English geologist that claimed that Earth must be much older than 6,000 years old. 2. ALFRED WALLACE An English naturalist that had 3 things in common with Darwin: he developed a similar Theory of Evolution, tour South America, made similar observations as Darwin. A French naturalist who was one of the 1st scientists to propose that traits 3. JEAN-BAPTISTE LAMARCK acquired during one’s lifetime could be passed onto their offspring. 4. BERNARD KETTLEWELL 5. CHARLES DARWIN A scientist that studied the effects of pollution on the peppered moth population. A scientist that began to develop his theory of natural selection aboard the HMS Beagle. Acquired Traits Inherited Traits Evolution Paleontologists Fossil Record Adaptation Vestigial Structures Natural Selection Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Overproduction Radiometric Dating Embryology Fossil Variation Successful Reproduction Competitors 6. INHERITED TRAITS Traits passed on from one generation to the next. 7. ACQUIRED TRAITS Traits organisms develop over a lifetime. 8. EVOLUTION Process that explains why species change over time. 9. EUKARYOTIC Type of cells that contain a nucleus. 10. PALEONTOLOGISTS Scientists who study fossils to learn about the past. 11. FOSSIL Preserved remains of organisms from the distant past. 12. VARIATION Traits differ between organisms. 13. OVERPRODUCTION Organisms produce more offspring than are likely to survive. 14. SUCCESSFUL REPRODUCTION Organisms with the best traits will survive to pass them on to the next generation. 15. FOSSIL RECORD The order in which fossils appear base on the layer of rock they are found in. 16. RADIOMETRIC DATING Technique used to measure how much radioactive materials have broken down over time. 17. EMBRYOLOGY Study of how organisms develop in their earliest stages of development 18. VESTIGIAL STRUCTURES Structures that have lost their purpose over time. An example is the tailbone in humans or the wings of ostriches. 19. NATURAL SELECTION Process that states that traits that offer an advantage will be more likely to be passed along to offspring. 20. COMPETITORS One or more organisms that are struggling for a particular resource. 21. ADAPTATION A characteristic that improves an organisms ability to survive. 22. When were the two largest mass extinctions in time? How is it believed that each occurred? a. AT THE END OF THE PALEOZOIC ERA – CAUSED BY THE FORMATION OF PANGAEA. REDUCING SHORELINE, REDUCED THE AMOUNT OF MARINE LIFE b. AT THE END OF THE MESOZOIC ERA – CAUSED BY EARTH COLLIDING WITH COMET OR ASTEROID. SUNLIGHT WAS REDUCED, KILLING PLANTS AND ANIMALS 23. Recall the fish in the pond classroom activity and Barballus Lab. Be prepared to explain a similar scenarios. 24. Explain in detail where the Industrial Revolution took place and how the peppered moth population differed before, during, and after the Industrial Revolution. THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION TOOK PLACE IN ENGLAND. BEFORE THE REVOLUTION, THERE WERE MORE LIGHT MOTHS THAN DARK BECAUSE THE LIGHT MOTH BLENDED IN WITH THE TREES BETTER AND THEREFORE WERE NOT EATEN AS MUCH. AFTER THE REVOLUTION, THE TREES WERE DARKER IN COLOR AND THE OPPOSITE OCCURRED… THE DARKER MOTHS WERE NOT EATEN AS MUCH SO THE PERCENTAGE OF DARKER MOTHS WENT UP AND LIGHER MOTHS WENT DOWN. 25. List the four major timeframes of geologic time and list two (or more) events that occurred during each. 1. Precambrian Began 4.6 billion years ago Prokaryotes appear Cyanobacteria appear The ozone layer develops. Cells with nuclei form. 2. Paleozoic 3. Mesozoic 4. Cenozoic Began 542 million years ago Began 251 million years ago Began 65.5 million years ago All major plant groups appear Insects appear. Age of Reptiles Dinosaurs dominate Earth. First birds appear. Humans appear. Age of Mammals Flowering plants appear Use the diagram and paragraph below along with your knowledge of natural selection to answer the following questions. Average beak sizes of the seed-eating ground finch on one of the Galapagos Islands are shown in the diagram below. During wet years, all types of seeds are abundant. The ground finch prefers to eat small seeds that are easy to crush. However, during droughts (dry years), when small seeds are not as abundant, they eat the larger seeds on the island. 26. Why did the average beak size get larger in 1977, 1980, and 1982? THERE WAS LESS RAINFALL IN THOSE YEARS AND THE SEEDS WERE THEREFORE LARGER. THE FINCHES NEED LARGER BEAKS TO EACH THE LARGER SEEDS. 27. How did variation exist in the ground finch population? THE SIZE OF THE BEAKS VARIED WITHIN THE POPULATION. SOME BEAKS WERE LARGE AND SOME WERE SMALL 28. What were the ground finches competing for? SEEDS 29. Not all of the ground finches were able to survive the drought. What adaptation gave them a better chance to survive to pass on their genes to the next generation? How did this adaptation help them survive? LARGER BEAK SIZE GAVE THEM A BETTER CHANCE TO SURVIVE BECAUSE THERE WERE ONLY LARGER SEEDS TO EAT. SMALL BEAKS COULD NOT EAT THE LARGER SEEDS. 30. How might an extended period of drought influence the ground finch population in the future? A. The birds with smaller beaks would be more numerous. B. C. D. The birds with larger beaks would be more numerous. Drought decreases seed availability, but has no influence on the ground finch. Drought increases seed availability, and all ground finches would be more numerous. 31. Explain your choice. THE BIRDS WITH THE LARGER BEAKS WOULD SURVIVE BETTER THAN THE ONES WITH THE SMALLER BEAKS AND THEREFORE PASS THEIR GENES ONTO THE NEXT GENERATION. THIS WOULD CONTINUE YEAR AFTER YEAR AND THE AVERAGE BEAK SIZE WOULD CONTINUE TO INCREASE.