Notes: 1.1 Name: Atmosphere Date: ______ Hour: _____
advertisement

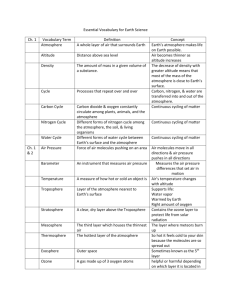
Notes: 1.1 Atmosphere Name: ___________________________ Date: __________ Hour: _____ Importance of the Atmosphere The Earth’s ________________ is a thin layer that forms a protective covering around the planet. If there was no atmosphere, days would be extremely _______ and nights would be extremely ________. It also protects from the Sun’s ______________ rays. Makeup of the Atmosphere The atmosphere is a mixture of ___________________________ that surrounds the planet. The atmosphere extends from the _________________ all the way to _______________. Earth’s early atmosphere contained mostly nitrogen and carbon dioxide Eventually, a layer that was rich in ozone was formed in the upper atmosphere, and protected Earth from the Sun’s harmful rays and allowed plants to flourish all over the Earth. These plants released tons of oxygen into the atmosphere and made the atmosphere like what it is today. Gasses in the Atmosphere Today’s atmosphere is a mixture of gases: _____________ – 78% _____________ – 21% _____________ – 0.93% _____________ – 0.03% Several trace elements The makeup of the atmosphere is always _____________. Car exhaust emits gasses into the atmosphere and _____________ like this can mix with other ___________and ____________. When they mix they form a brown haze called _________. Humans ________ fuel for energy and as the fuel is burned _______________ enters the _______________. If we increase the amount of energy used we will _____________ the amount of __________________ in the atmosphere. Solids and Liquids in the Earth’s Atmosphere The atmosphere contains small, solid particles such as ______________________. _________ gets picked up from the Earth’s surface from the wind. _________ gets picked up from ocean spray. _________ is released into the atmosphere by plants. The atmosphere also contains small, ______________________ other than water droplets in the clouds. The atmosphere constantly ___________ these solid and liquid particles from ___________________________. Layers of the Atmosphere There are ____________ of the Earth’s atmosphere. The lower atmospheric layers: _______________ _______________ The upper atmospheric layers: _______________ _______________ _______________ Lower Layers of the Atmosphere The _________________ is the lowest layer of the atmosphere Extends from the Earth’s surface to about ____ km into the atmosphere. Contains ____% of the water vapor in the atmosphere Contains ____% of all the gasses in the atmosphere The layer we ______ in The ______________ is the layer directly above the troposphere that Extends from ____ km to ____ km above the Earth’s surface. Contains the ___________ concentration of ozone gas Upper Layers of the Atmosphere The _____________ is the middle layer of the atmosphere. Extends from the stratosphere to about ____ km Contains part of the ______________ The _____________ is named for its high temperatures. Extends from the mesosphere to about _____ km Contains part of the ______________ The _____________ is the furthest layer of the atmosphere. Its where ______________ can be found Contains very ______ particles Atmospheric Pressure Atmospheric gasses extend ___________ of km above the Earth’s surface. As the Earth’s gravity pulls the gasses down on the Earth’s surface, the _________ of these gasses presses ________ on the air below. This causes the ___________ closest to the Earth’s surface to be ________ to each other. Which makes the air closest to the Earth’s surface to be more ________ than air further away. The ________ air closer to the Earth’s surface exerts more _______ than the less dense air near the top of the atmosphere. Force exerted on an area is known as __________. Air pressure is _________ near the Earth’s surface and __________ higher in the atmosphere. People find it harder to __________ in high mountains because ________ molecules of air exist there. Jets that fly above the troposphere must maintain ______________ cabins so that people can breathe. Temperature in Atmospheric Layers The Sun is the source of most of the _________ on Earth. Because some layers contain gasses that easily _________ the Sun’s energy while other layers do not, different layers have different _______________. Molecules of ozone in the ______________ absorb some of the Sun’s energy. Energy absorbed by ozone molecules __________ the temperature. There are more ozone molecule in the _________ portion of the stratosphere, the temperature __________ with _____________ altitude. Temperature in the _______________ and ______________ are high because there are few molecules, however each molecule has a great deal of energy. Ozone Layer The _______________ is a atmospheric layer that is about ____ km to ____ km above the Earth’s surface. The ozone layer consists of ozone molecules. Ozone = 3 ___________ molecules The ozone layer contains a _______ concentration of ozone and __________ you from the Sun’s harmful energy. Ozone absorbs most of the __________________ radiation that enters the atmosphere. _______________________ is one of the many types of energy that come to Earth from the sun. Too much exposure to ultraviolet radiation can damage your skin and cause ____________. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Air pollutants, like chlorofluorocarbons, are ______________ the atmosphere. ____________________________ (CFCs) are chemical compounds used in some refrigerators, air conditioners, and aerosol sprays, and in the production of some foam packaging. CFCs can enter the atmosphere if these appliances _________ or of they and other products containing CFCs are _________________ discarded. The Ozone Hole The _________________ of ozone molecules by CFCs seems to cause seasonal reduction in ozone over Antarctica called the ozone hole. Beginning in late August or early September the amount of ozone in the atmosphere over ________________ begins to ______________. By October, the ozone concentration reaches its ____________ values and then begins to increase again. By December, the ozone hole ______________. In the mid-1990s, many governments ____________ the production and use of CFCs. Since then, the concentration on CFCs in the atmosphere has started to _______________.