7.E.1.4 Weather Prediction C.Notes What is a climate Climates on
advertisement

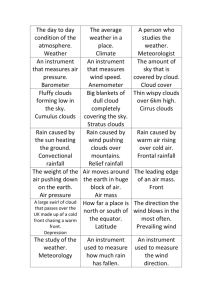
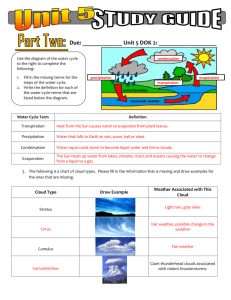
What is a climate 7.E.1.4 Weather Prediction C.Notes defined by average temperature, precipitation, humidity, air pressure, and wind, over time in a particular place Climates on Earth temperate (middle latitude) Summers can be hot but winters are not very cold Polar Consistently cold temperatures Every month of the year averages below 10 degrees Celsius tropical Close to equator = hot Receive most sunlight Can be dry or heavy rain Dry (arid) Usually get less than 25cm of rain per year Include deserts Not all dry zones are hot (Gobi Desert is cold) Continental Wider temperature range Much colder winters What is a weather forecast an attempt to make accurate predictions of future weather The accuracy of weather prediction is improving as technology advances Long range is more difficult than short-range weather predictions What does a weather map show precipitation, wind direction, temperature, cloud cover, high or low pressure, cold and warm fronts, stationary and occluded fronts What direction do weather systems generally move Technology Types of satellite maps west to east in US greatly influenced the ease and accuracy of making weather predictions computer Weather data at thousands of locations can be gathered instantaneously and applied to weather prediction to produce weather maps Satellite weather maps Visible satellite map o snapshot of the earth and is only available during the day as it uses light from the sun to detect the clouds o Low clouds are dark and high clouds are lighter Infrared satellite map o allows you to see cloud cover whether it is day or night o measure the temperature of cloud tops, which we can translate into cloud cover o Strong to severe thunderstorms will normally have very cold tops water vapor satellite map o indicate how much moisture is present in the upper atmosphere o useful for indicating where heavy rain is possible What is radar Weather data collection Main cloud types 7.E.1.4 Weather Prediction C.Notes electronic instrument, which determines the direction and distance of objects that reflect radio energy back to the radar site stands for Radio Detection and Ranging what meteorologists use to see rain or snow Doppler radar o what meteorologists use to see rain or snow o gives forecasters the capability of providing early detection of severe thunderstorms that may bring strong damaging winds, large hail, heavy rain, and possibly tornadoes wind speed wind direction air temperature measure of the energy of molecules the more energy the molecules in air have, the hotter it feels relative humidity compares the actual amount of water vapor in the air with the maximum amount of water vapor the air can hold at that temperature (its capacity) air pressure cirrus high level clouds and due to high altitude, the water is almost frozen to form ice crystals isolated Cirrus clouds do not indicate any instability in the weather and may not bring rain. if the clouds are dense they often indicate that a storm might be approaching stratus layered clouds that usually bring a drizzle and there is widespread rain and in some cases ocean air cumulus neutral weather clouds All the other clouds are combinations or variations of these types Cold front vs. warm front Cold front leading edge of a cooler air mass of air, replacing at ground level a warmer mass of air cooler, denser air wedges under the less-dense warmer air, lifting it upward motion causes lowered pressure along the cold front and can cause the formation of a narrow line of showers and thunderstorms when enough moisture is present weather map cold front is marked with the symbol of a blue line of triangles/spike pointing in the direction it is traveling can move up to twice as fast as warm front and can produce sharper changes in the weather usually associated with an area of high pressure warm front leading edge of a warm air mass that displaces colder air, bringing a temperature increase and heavy rain where the front makes contact with the 7.E.1.4 Weather Prediction C.Notes ground weather map represented by a red solid line with semicircles pointing towards the colder air and in the direction of the movement