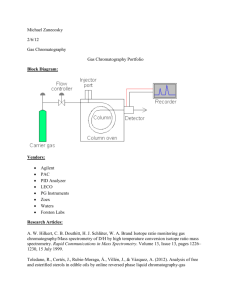
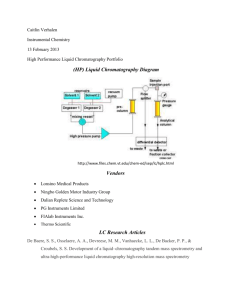
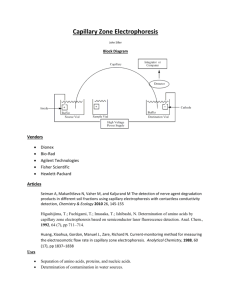
Addendum
advertisement
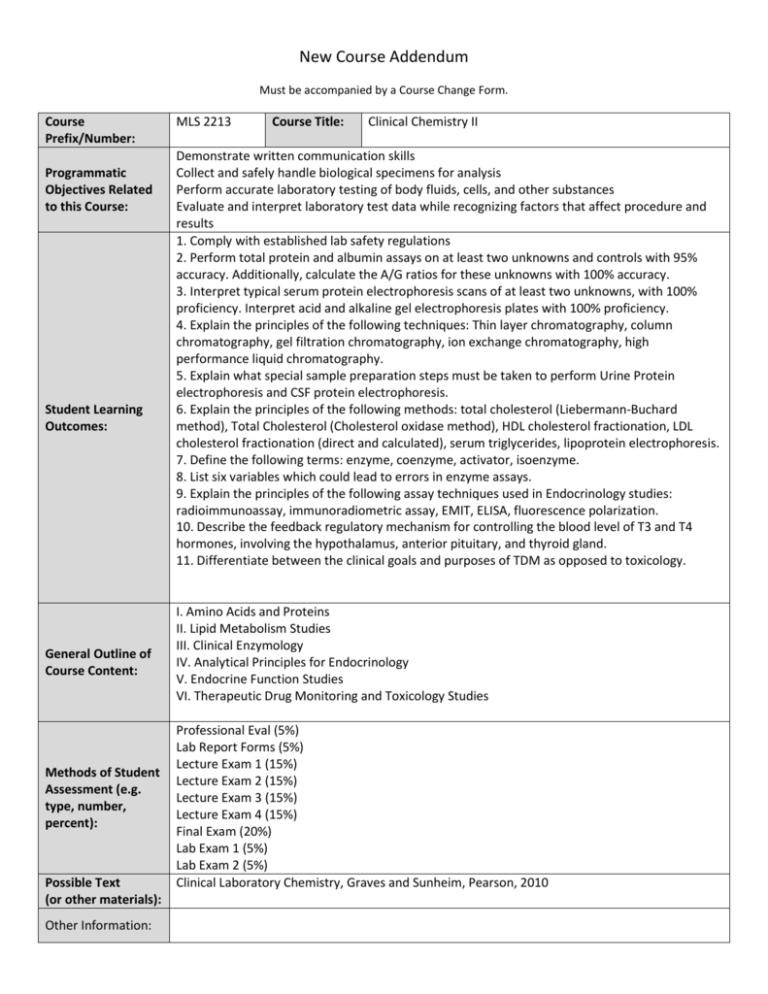
New Course Addendum Must be accompanied by a Course Change Form. Course Prefix/Number: Programmatic Objectives Related to this Course: Student Learning Outcomes: General Outline of Course Content: Methods of Student Assessment (e.g. type, number, percent): Possible Text (or other materials): Other Information: MLS 2213 Course Title: Clinical Chemistry II Demonstrate written communication skills Collect and safely handle biological specimens for analysis Perform accurate laboratory testing of body fluids, cells, and other substances Evaluate and interpret laboratory test data while recognizing factors that affect procedure and results 1. Comply with established lab safety regulations 2. Perform total protein and albumin assays on at least two unknowns and controls with 95% accuracy. Additionally, calculate the A/G ratios for these unknowns with 100% accuracy. 3. Interpret typical serum protein electrophoresis scans of at least two unknowns, with 100% proficiency. Interpret acid and alkaline gel electrophoresis plates with 100% proficiency. 4. Explain the principles of the following techniques: Thin layer chromatography, column chromatography, gel filtration chromatography, ion exchange chromatography, high performance liquid chromatography. 5. Explain what special sample preparation steps must be taken to perform Urine Protein electrophoresis and CSF protein electrophoresis. 6. Explain the principles of the following methods: total cholesterol (Liebermann-Buchard method), Total Cholesterol (Cholesterol oxidase method), HDL cholesterol fractionation, LDL cholesterol fractionation (direct and calculated), serum triglycerides, lipoprotein electrophoresis. 7. Define the following terms: enzyme, coenzyme, activator, isoenzyme. 8. List six variables which could lead to errors in enzyme assays. 9. Explain the principles of the following assay techniques used in Endocrinology studies: radioimmunoassay, immunoradiometric assay, EMIT, ELISA, fluorescence polarization. 10. Describe the feedback regulatory mechanism for controlling the blood level of T3 and T4 hormones, involving the hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and thyroid gland. 11. Differentiate between the clinical goals and purposes of TDM as opposed to toxicology. I. Amino Acids and Proteins II. Lipid Metabolism Studies III. Clinical Enzymology IV. Analytical Principles for Endocrinology V. Endocrine Function Studies VI. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Toxicology Studies Professional Eval (5%) Lab Report Forms (5%) Lecture Exam 1 (15%) Lecture Exam 2 (15%) Lecture Exam 3 (15%) Lecture Exam 4 (15%) Final Exam (20%) Lab Exam 1 (5%) Lab Exam 2 (5%) Clinical Laboratory Chemistry, Graves and Sunheim, Pearson, 2010 Areas in bold are required.