Science 9 ñ Chemistry 2
advertisement

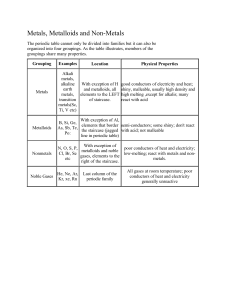
Science 9 – Chemistry 2 Sci 924 – Sci 926 Quick Review Law of Conservation of Mass review – In a chemical change, the total mass of the new substance is always the same as the total mass of the original substance. Law of Definite Composition – Compounds are pure substances that contain two or more elements mixed together in fixed or definite proportions. Therefore, we know that the mass of reactants must equal the mass of the products in every chemical reaction. Dalton’s Atomic Theory Dalton found that the particle theory could not explain why the properties of a compound are different then the properties of the element that make it up. The particle theory could not explain how particles of different substances could combine or decompose to form new ones. Then came Dalton’s theory: – All matter is made up of sm.particles clld atoms. – Atoms can’t be created or destroyed or split – All atoms of the same element are the same size and weight – Atoms of different elements differ in size and weight – Compounds are created when atoms of different elements link together in definite proportions Eg. Water and peroxide both contain H and O2 but in different proportion. Water is 11%H and 89% O2 whereas peroxide is 6% H and 94% O2 The Scientific Process Revised Hypothesis Theory Observations Experiments Hypothesis Laws, Theories, Models and Observations Law- describes and summarizes what always happens. Theory – a creative way to describe why something happens. Observation- Scientists observe how matter behaves and reacts during experiments. – Many observations and experiments are needed before a hypothesis can become an accepted theory. Model – helps to picture structures or processes that cannot be directly seen. Classifying Elements As elements were discovered, they were given names. The scientist who first discovered an element had the right to name it. Over time there were many elements with very long names So, a system of element symbols was developed. The symbol system is universal which means the same chemical symbols are used by scientists throughout the world As more and more elements were discovered, Scientists needed a way to classify the elements and organize their observations. Thus the invention of the periodic table by Dmitri Mendeleev. The periodic table invented my Mendeleev is still used today with a few modifications. Ways of Classifying Elements State at Room Temp. Appearance Conductivity Malleability and ductility Metals Eg. Mercury, Silver, Gold, Copper Solids Except for Mercury Shiny Good conductors of heat and electricity Malleable Ductile Non-Metals Eg. Oxygen, Sulpher Some gas Some solid One liquid Bromine Not very shiny Poor conductors of heat and electricity Brittle Non ductile Metalloids Eg. Silicone Solids Can be shiny or dull May conduct electricity Poor heat conductors Brittle Non ductile Groups of Elements Alkali Metals – Highly reactive (Boom!) – Has one unpaired electron – Gives up the unpaired electron Alkaline Metals (Earth metals) – Can react vigorously but not as reactive as the Alkali metals Noble Gases – Unreactive or inert gases – All the electrons here have “dates” Halogens – – – – Highly reactive Have unpaired electrons Takes an electron Corrosive There are other groups and families but were are only covering these. A couple things: – Sci 926 will be changing. Check to make sure my name is in the assignment before you complete it. There will be a quiz at the end of Sci 926 on the periodic table and symbols!