Chapter 6 Fill-in-the
advertisement

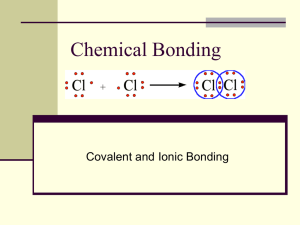
CHAPTER 6 NOTES Name:_____________________ Pd:_____ 6-1 Define chemical bond: Nature favors arrangement where potential energy is __________, so atoms will combine/bond to become more stable. Chemical bonding that results from the electrical attraction between large numbers of ___________ and ___________ is called ______________________. Covalent bonding results from ___________ of electron pairs. In purely covalent bonds the electrons are owned __________. Define electronegativity: The degree to which bonding between atoms of two elements is ionic (transfer of e-) or covalent (shared e-) can be estimated by calculating the difference between the elements’ _______________. Bonding between atoms with an electronegativity difference of _____ or less has an ionic character of ______________ is classified as _________________. Bonding between two atoms of the same element is completely ______________ because their electronegativities are the same. A ____________________ bond is an example of a bond with 0% ionic character and is a _____________ covalent bond, one in which the bonding electrons are shared equally by the bonded atoms, resulting in a balanced distribution of electrical charge. Bonds having 0-5% ionic character, corresponding to electronegativity differences of _______ are nonpolar covalent bonds. Bonds are polar if they have an _________ distribution of charge and the electronegatities are significantly different. Electronegativities of 0.3-1.7 are classified as polar. A ____________________ is a covalent bond in which the bonded atoms have an _____________ attraction for the shared electrons. Fill in the chart below from Fig. 1.2 Difference in electronegativities 0-0.3 Percent Ionic Character Type of Bond 5-50% Ionic Bond Look on Page 159 at Figure 3.11 and complete the chart below, using the chart you made above. Elements Electronegativity Difference (absolute value of difference) 2.5-2.1 = 0.4 Example: Sulfur and Hydrogen Sodium and Nitrogen Oxygen and Carbon Chlorine and Carbon Bromine and Iodine Chlorine and Barium Sulfur and Iron Chlorine and Bromine Circle the most electronegative element in each of the pairs above. 6-2 Define molecule: Define molecular compound: Define chemical formula: Type of Bond Polar Covalent Define molecular formula: Would you use a chemical formula or a molecular formula for a covalent bond? How many atoms are contained in a diatomic molecule? __________ There are seven diatomic molecules: Br, I, N, Cl, H, O, F (the Brinklehoffs) and they are always found in pairs in nature. Formation of a Covalent Bond: Nature favors bonding because it ___________ potential energy. When two hydrogen atoms approach each other, they are attracted and repel at the same time. Draw Figure 6-6 in the box below and answer the questions. 1. Why do the nuclei repel each other? 2. Why are the atoms attracted to one another? 3. At what point will the atoms stop moving closer together? Characteristics of the Covalent Bond The distance between two bonded atoms at their minimum potential energy or average distance between two bonded atoms is the ___________________. Energy is _____________ as atoms bond. In order to break the bond, that same amount of energy must be added back. That amount of energy required is referred to as __________________ and is reported in _________ (the unit). The Octet Rule, Lewis Structures, and Multiple Covalent Bonds Define the Octet Rule: Electron-dot notation can be used to represent molecules. Draw the Lewis structure images the book shows for hydrogen and fluorine as diatomic. H: F: Define lone pair: Hydrogen does not have any lone pairs. How many lone pairs does each fluorine have above? Both of the examples above have a single bond, which is _____________________________________________________________________________________. Define and draw an example of the following: DOUBLE BOND: TRIPLE BOND: